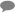In this article
Overview
Use this Snap to build SELECT SQL queries to fetch records from the specified table. Executed in its default state after providing database, schema, and table name, the Snap builds a standard SELECT * FROM query. However, you can use the inbuilt SQL query editor to build complex queries to perform complex operations spanning multiple tables such as JOIN, AGGREGATE, LIMIT, and DISTINCT. Additionally, this Snap can also connect to multiple upstream Snaps. This enables you to build a query to perform operations on multiple tables together or separately at the same time.
Prerequisites
A valid SnapLogic account to connect to the database in which you want to execute the query if you also want to preview the data.
SnapLogic accounts are also required if you want to use the Snap's suggest feature in fetching schema and table names. |
Limitation
Known Issue
- Suggestions displayed for the Schema Name field in this Snap is from all databases that the Snap account user can access, instead of the specific database selected in the Snap's account or Settings.
While you specify an SQL statement in the SQL Query Editor of the Snap as an expression, the dynamic validation for the expression displays inline errors when there is more than one incoming document and without the
'__sql__'key to the current Snap, when you select Get Preview Data checkbox in the previous Snap, and when Preview Document Count in your user settings is set to a value more than 1.To prevent this error and similar ones, do not select the Get Preview Data checkbox in the previous Snap, set the Preview Document Count in your user settings to 1, or append a condition
where 1 = 0to the SQL statement with the Get Preview Data checkbox selected.
Snap Input and Output
| Input/Output | Type of View | Number of Views | Examples of Upstream and Downstream Snaps | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Document |
|
| The database, schema, table names in which the query must be executed. You can also pass this information using an upstream ELT Snap. Additionally, you can also pass such information for several tables to the Snap using a separate input view for each table. |
| Output | Document |
|
| A SELECT SQL query for the table specified in the Snap. If you use the SQL editor, then an SQL query built based on your inputs in the editor. Optionally, the output also includes a preview of the query's output if the Get preview data checkbox is selected. |
Snap Settings
You can use the SQL Expressions and Functions supported for ELT to define your Snap or Account settings with the Expression symbol = enabled, where available. This list is common to all target CDWs supported. You can also use other expressions/functions that your target CDW supports. |
| Parameter Name | Data Type | Description | Default Value | Example | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Label | String | ELT Select | Fetch Sales Data | ||||||
| Get preview data | Checkbox |
| Not selected | Selected | |||||
| Database Name | String | The name of the database in which the target/source tables are located. Leave it blank to use the database name specified in the account settings.
If your target database is Databricks Lakehouse Platform (DLP), you can, alternatively, mention the file format type for your table path in this field. For example, DELTA, CSV, JSON, ORC, AVRO. See Table Path Management for DLP section below to understand the Snap's behavior towards table paths. | N/A | TESTDB DELTA ORC | |||||
| Schema Name (Not applicable to Databricks Lakehouse Platform) | String | The name of the database schema. In case it is not defined, then the suggestion for the table name retrieves all tables names of all schema in the specified database (except for DLP) when you click
| N/A | PUBLIC | |||||
| Table Name | String | The name of the table or view for which you want to build the SQL queries. If it is not defined, then the Snap retrieves all the table names and views associated with the specified schema when you click If your target database is Databricks Lakehouse Platform (DLP), you can, alternatively, include the path in this field. For example, `/mnt/elt/mytabletarget`. Learn more about the Snap’s behavior toward paths in the Table Path Management for DLP section.
| N/A | PUBLIC.EMPLOYEES `/mnt/elt/emp` | |||||
| Enable SQL query editor | Checkbox | Select this to enable the SQL query editor. You can use this editor to build all types of SQL queries that will execute on multiple tables. Enabling the SQL query editor activates the fieldset Input View to Virtual Table Map in the Snap.
| Not selected | Selected | |||||
| Input View to Virtual Table Map | Activates when you select the Enable SQL query editor checkbox. This is useful when you enable multiple input views in the ELT Select Snap. Use this field set to map each input view to a dummy table. You will reference the table name specified in each input view with this dummy/virtual table name.
Click + to add rows. Each input view must be specified in a separate row. This field set consists of the following fields:
| ||||||||
| Input View | String | Select the input view whose table reference is to be mapped. | N/A | input2 | |||||
| Virtual Table Name | String | Specify the dummy/virtual table name that will be assigned to the table reference in the selected input view. | N/A | tbl1 | |||||
| SQL Query Editor | Query editor | Enter the SQL queries that you want to build using this Snap. Even though the Snap's name is ELT Select, you can use this SQL query editor to build any SQL query.
| N/A | SELECT DISTINCT FROM MYTABLE | |||||
Table Path Management for DLP
| # | File Format Type | Table Path exists?# | All other requirements are valid? | Snap Operation Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DELTA | Yes | Yes | Success |
| 2 | DELTA | No | Yes | Failure. Snap displays error message. |
| 3 | DELTA | Yes | No | Failure. Snap displays error message. |
| 4 | AVRO/CSV/JSON/ORC/other | Yes | Yes | Success. |
# We recommend that you specify a table path that resolves to a valid data file. Create the required target file, if need be, before running your Pipeline.
Preventing SQL Injection
You can pass Pipeline parameters as values in an SQL query; however, if you do not phrase the query properly it can lead to the parameter's name being bound as a value in the database. This potentially incorrect information being inserted into the database is known as SQL injection. It is thus necessary to take precautions when including Pipeline parameters in your SQL query to prevent SQL injection. Based upon the intended use of the Pipeline parameter, use one or both the following methods to prevent accidental SQL injection:
Method-1: Simple Substitutions
You can reference the Pipeline parameter directly with a JSON-path without enabling expressions.
For example, consider a Pipeline parameter name which contains the value of a column. You want to write a SELECT query to fetch records from the table mytable where the column's name matches the value in the Pipeline parameter.
SELECT * FROM mytable WHERE colname = _name |
Method-2: Dynamic Substitutions
You must enable expressions when referencing table names using Pipeline parameters. Format the query, except the Pipeline parameter's reference, as a string.
For example, if you you want to write a SELECT query to fetch records from a table and you are passing the table's name in the Pipeline parameter table:
"SELECT * FROM" + _table |
In the example above, you must still use JSON-paths if you want to use another Pipeline parameter for substituting values in the SQL:
"SELECT * FROM " + _table + " WHERE colname = _name" |
The Snap evaluates the expression and also carries out path substitutions.
Here is how it works
The Snap pre-processes the query to extract any JSON-Paths and converts them to bound parameters. For example, consider the following query:
SELECT * FROM mytable WHERE name = _name |
The Snap converts this query into the following before turning it into a prepared statement for the database:
SELECT * FROM mytable WHERE name = ? |
The Snap evaluates the JSON-Path to get the value to bind the Pipeline parameter in the prepared statement.
When expressions are disabled, use \ as an escape character to treat underscore (_) as a string. For example:
|
Troubleshooting
| Error | Reason | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
Database cannot be blank. (when seeking the suggested list for Schema Name field) | Suggestions in the Schema Name and Target Table Name fields do not work when you have not specified a valid value for the Database Name field in this Snap. | Specify the target Database Name in this Snap to view and choose from a suggested list in the Schema Name and Target Table Name fields respectively. |
| Column names in Snowflake tables are case-sensitive. It stores all columns in uppercase unless they are surrounded by quotes during the time of creation in which case, the exact case is preserved. See, Identifier Requirements — Snowflake Documentation. | Ensure that you follow the same casing for the column table names across the Pipeline. | |
Database encountered an error during preview processing (Target CDW: BigQuery) | This can happen when the target database cannot recognize/interpret the table name. | Ensure that the table name is valid and the table with provided name exists. Using a wildcard in the SQL editor mode, ensure that the table name is enclosed between backticks (`). For example: `scd*`, `mode*`. |
Examples
Downloads
|
Edit the Excerpt Include macro below to link to the Snap Pack page for this Snap page. Ensure that the heading Snap Pack History is not within the Snap Pack's history Excerpt.
See Also
Provide links to the endpoint's official documentation, any relevant or related internal documentation, and any other links you have referred to on this page. Care should be taken when referencing external sites/documentation that it is an official site/documentation. Do not refer to forums such as stackoverflow.