On this Page
Snap type: | Parse | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Description: | This Snap parses the incoming XML data into SnapLogic document objects. | ||||||||||
| Prerequisites: | [None] | ||||||||||
| Support: | Works in Ultra Task Pipelines. | ||||||||||
| Limitations | Mixed content such as below is not supported. XML data with mixed content may contain attributes, elements, and text.
| ||||||||||
| Account: | Accounts are not used with this Snap. | ||||||||||
| Views: |
| ||||||||||
Settings | |||||||||||
Label | Required. The name for the Snap. You can modify this to be more specific, especially if you have more than one of the same Snap in your pipeline. | ||||||||||
Inbound Schema | XSD schema definition file url for the incoming data. The currently supported url protocols are SLDB, HDFS, S3.
Example: sldb:///foo/bar/customer.xsd Default value: [None] | ||||||||||
| Validate XML | Required. If selected, the incoming data will be validated against the provided XSD schema definition.
Example: False Default value: False | ||||||||||
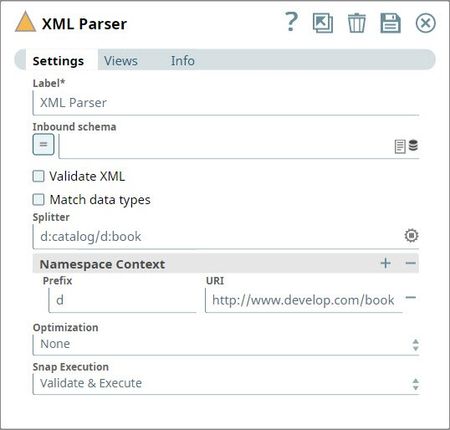
| Splitter | Splits the incoming XML document into multiple smaller documents using the XPath expression.
Example 1: Splitter Expression without prefix Default namespace can be accessed by giving a unique prefix in the splitter expression followed by a colon and the tag value. Provide its corresponding namespace value in the Prefix URI table.
The output view is:
Default value: [None] | ||||||||||
Namespace Context optional | Namespace context for the expression provided in the Splitter property. Namespaces are typically defined in the format of xmlns prefix:URI | ||||||||||
Prefix | Prefixes included in the expression provided in the Splitter property. | ||||||||||
URI | URIs associated with the prefixes. | ||||||||||
Match data types | Specifies the values in the input document as specified in the Inbound schema property.
| ||||||||||
| Optimization | Select the parameter that you want to optimize during Snap execution. Available options:
Default value: None | ||||||||||
Schema language supported : W3C XML Schema 1.0
Examples
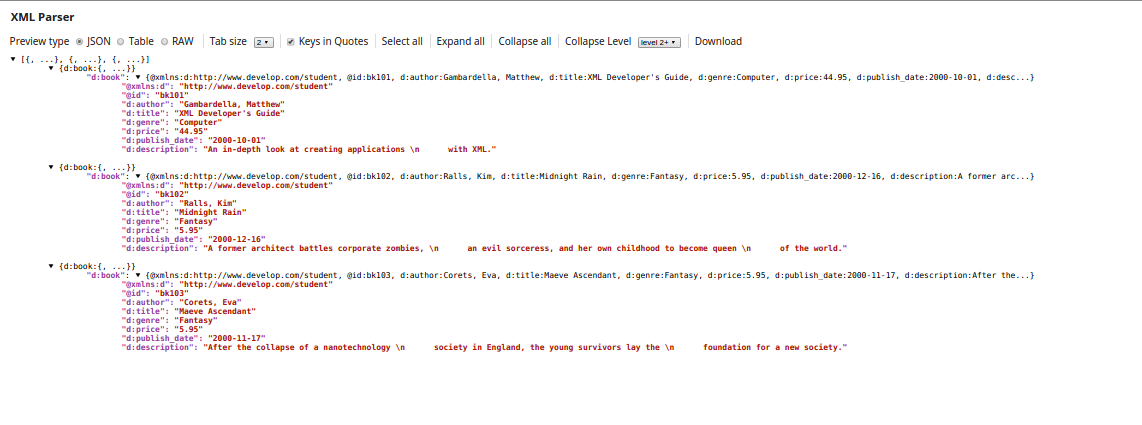
Splitting XML
In this example, XML that contains multiple purchase orders is split into individual orders.
The incoming XML looks something like this:
<po:PurchaseOrders xmlns:po="http://www.example.com">
<po:PurchaseOrder po:PurchaseOrderNumber="23578" po:OrderDate="2015-01-20">
<po:Address po:Type="Shipping">
<po:Name>Full Name</po:Name>
<po:Street>123 Maple Street</po:Street>
<po:City>City Name</po:City>
<po:State>CA</po:State>
<po:Zip>10101</po:Zip>
<po:Country>USA</po:Country>
</po:Address>
<po:Address po:Type="Billing">
<po:Name>Another Name</po:Name>
<po:Street>456 Oak Avenue</po:Street>
<po:City>Town Name</po:City>
<po:State>NJ</po:State>
<po:Zip>99999</po:Zip>
<po:Country>USA</po:Country>
</po:Address>
<po:DeliveryNotes>Please leave packages on side porch.</po:DeliveryNotes>po
<po:Items>
<po:Item po:PartNumber="123456">
<po:ProductName>Product</po:ProductName>
<po:Quantity>1</po:Quantity>
<po:USPrice>89.90</po:USPrice>
<po:Comment>Refurbished</po:Comment>
</po:Item>
</po:Items>
</po:PurchaseOrder>
<po:PurchaseOrder po:PurchaseOrderNumber="23579" po:OrderDate="2015-01-20">
...
</po:PurchaseOrder>
</po:PurchaseOrders>
|
Each PurchaseOrder contains the shipping address, billing address and the items purchased.
To split these into individual orders, the Splitter field should contain the hierarchy down to where you want the split to occur, including any specified prefix. In this case, the value is: po:PurchaseOrders/po:PurchaseOrder.
You will also need to specify the Namespace Context, which is defined in the sample as xmlns:po="http://www.example.com".
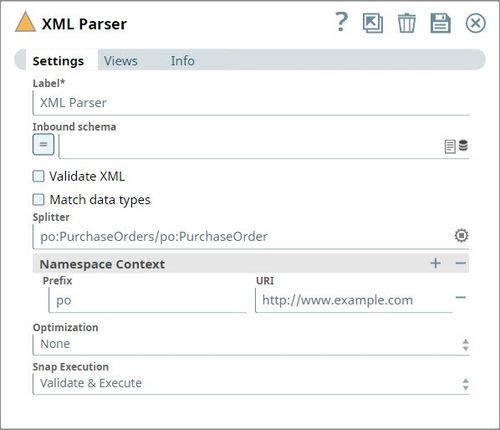
This will result in separating the orders into individual documents.
[{, ...}, {, ...}, {, ...}]
{po:PurchaseOrder:{, ...}}
{po:PurchaseOrder:{, ...}}
{po:PurchaseOrder:{, ...}}
|
.png?version=1&modificationDate=1491454352204&cacheVersion=1&api=v2&width=765)
.png?version=1&modificationDate=1491454350249&cacheVersion=1&api=v2)