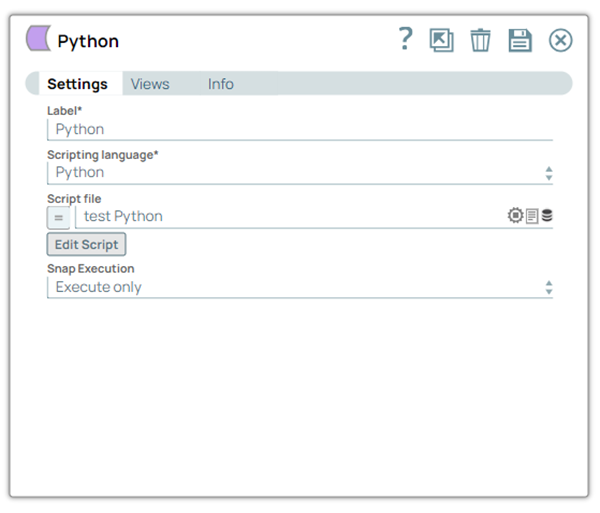
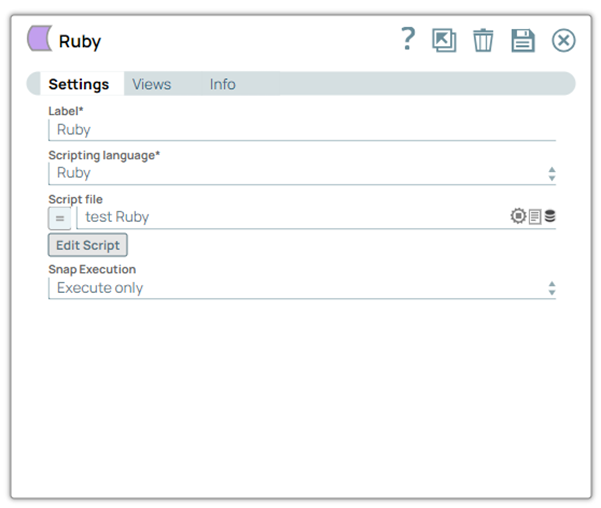
In this article

Overview
You can use the Script Snap to execute Javascript, Python, or Ruby scripts using the JVM ScriptEngine mechanism. Accounts are not required to work with this Snap.
You cannot create external process (like the popen function) on Cloudplex through the Script Snap or a Custom Snap. While external process creation on Groundplex is possible. You can request support@snaplogic.com to disable this if required. |
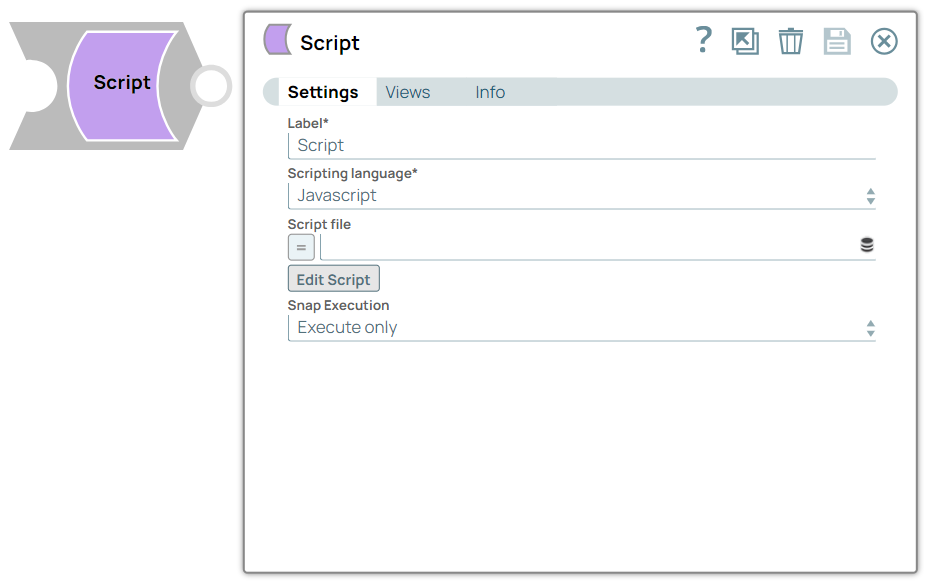
Snap Type
The Script Snap is a write-type Snap.
Support for Ultra Pipelines
Works in Ultra Pipelines if you pass the original document to the write() method for the output view. For example, in the JavaScript template, the body of the loop is per the following:
// Read the next document, wrap it in a map and write out the wrapper
var doc = this.input.next();
var wrapper = {
"original" : doc
}
this.output.write(doc, wrapper); |
noteNote the following two arguments in the output.write() method:
Both the arguments are required so that the lineage of the output document can be tied to the input document. This is important for an Ultra pipeline responding to web requests. The initial request becomes an input document to the first Snap in the SnapLogic pipeline, eventually resulting in an output document from the last Snap in the pipeline. The pipeline must maintain the lineage of each document so that each response can be correlated to the request that generated it.
Note the following two arguments in the output.write() method:
Both the arguments are required so that the lineage of the output document can be tied to the input document. This is important for an Ultra pipeline responding to web requests. The initial request becomes an input document to the first Snap in the SnapLogic pipeline, eventually resulting in an output document from the last Snap in the pipeline. The pipeline must maintain the lineage of each document so that each response can be correlated to the request that generated it.
Limitations and Known Issues
For JavaScript, objects written to the output view should be composed of serializable Java types. Some downstream Snaps, such as the Copy Snap, require this. To write out a map to the output view in a JavaScript, use a Java Map implementation, such as HashMap or LinkedHashMap, per the following:
importClass(java.util.LinkedHashMap);
...
var inDoc = this.input.next();
var outDoc = new LinkedHashMap();
outDoc.put("original", inDoc);
this.output.write(inDoc, outDoc); |
Breaking Changes
The following breaking changes apply to the pipelines using the Script Snap (or the deprecated Execute Script Snap) with the Python engine.
To implement Python in the Script Snap, we use Jython. We have upgraded the Jython engine from version 2.7-b3 (a beta version from 2014) to version 2.7.2 (March 2020). The following are the resultant issues and workarounds:
An open bug in 2.7 introduced a backward-incompatible change in the SnapLogic platform wherein the Jython engine automatically converts BigInteger values to primitive long values. This impacts all your scripts that perform numeric manipulation of integer values from documents (SnapLogic uses the BigInteger type to represent integers in documents). Your pipelines and Snaps with the Script Snap (or the deprecated Execute Script Snap) that use numeric manipulation scripts with integer or BigInteger data type may fail during execution. We recommend you prospectively replace integer or BigInteger values with long values.
Example:
sum = a.intValue() + b.intValue()
Here, a and b are of BigInteger type that now fail as Jython 2.7.2 automatically and transparently calls longValue() on any BigInteger value it encounters. So a and b would need to use the long and not BigInteger type.
The known fix is to rewrite the above calculation as sum = a + b by removing occurrences of .intValue() or .longValue() from your Python scripts.
Before the 4.22 release (August 2020), when using the Script Snap with the Scripting language option selected as Python, requesting a key that did not exist in a dictionary (for example, my_dict['missing_key']) would return None. Starting from the 4.22 release, the same request returns a KeyError exception. If you need to continue returning None, use the .get(key) method instead (for example, my_dict.get['missing_key']).
- zlib.compress():
The zlib library compresses the JSON files retrieved from the SnapLogic APIs and backs-up Pipelines and accounts to a database. The following Python code, when trying to compress displays an ascii … ordinal not in range(128) error.
Original code: in_doc["json"] = zlib.compress(in_doc["json"])
Fix: in_doc["json"] = zlib.compress(in_doc["json"].encode("utf-8"))
{dictionary}.values().toArray()[i]:
Before the 4.22 release (August 2020), to subscript a {dictionary}.values() method, you had to append the toArray() method to values(); else, you would see the Failure: ‘java.util.LinkedHashMap$LinkedValues’ object is unsubscriptable error. After the 4.22 release, toArray() returns Failure: ‘list’ object has no attribute ‘toArray’. However, the requirement for toArray() is no longer necessary for the subscript.
Original code: sLine = data.values().toArray()[0]
Fix: sLine = data.values()[0]
Snap Views
Type | Format | Number of Views | Examples of Upstream and Downstream Snaps | Description |
|---|
Input | Document | | | This Snap has at most one document input view. |
Output | Document | | | This Snap has at most one document output view. |
Error | Error handling is a generic way to handle errors without losing data or failing the Snap execution. You can handle the errors that the Snap might encounter when running the pipeline by choosing one of the following options from the When errors occur list under the Views tab: Stop pipeline Execution: Stops the current pipeline execution if the Snap encounters an error. Discard Error Data and Continue: Ignores the error, discards that record, and continues with the remaining records. Route Error Data to Error View: Routes the error data to an error view without stopping the Snap execution.
Learn more about Error handling in Pipelines. |
Snap Settings
Asterisk ( * ): Indicates a mandatory field. Suggestion icon ( ): Indicates a list that is dynamically populated based on the configuration. ): Indicates a list that is dynamically populated based on the configuration. Expression icon ( ): Indicates the value is an expression (if enabled) or a static value (if disabled). Learn more about Using Expressions in SnapLogic. ): Indicates the value is an expression (if enabled) or a static value (if disabled). Learn more about Using Expressions in SnapLogic. Add icon (  ): Indicates that you can add fields to the field set. ): Indicates that you can add fields to the field set. Remove icon (  ): Indicates that you can remove fields from the field set. ): Indicates that you can remove fields from the field set. Upload icon ( ): Indicates that you can upload files. ): Indicates that you can upload files.
|
Field Name | Field Type | Description |
|---|
Label* Default Value: Script
Example: Script | String | Specify a unique name for the Snap. You can modify this to be more specific, especially if you have more than one of the same Snap in your pipeline. |
|---|
Scripting Language* Default value: Javascript
Example: Ruby | Dropdown list | Choose a language for the script. The available options are: |
|---|
Script file Default value: None
Example: transform.py | String/Expression | Specify or select a script file that implements the ScriptHook interface. This field can be used if the script file is present in the SLDB. Click on the Upload  icon to upload the required script file from the SLDB. icon to upload the required script file from the SLDB. noteThis field accepts pipeline parameters as well as upstream parameters provided the script file is present in the SLDB.
This field accepts pipeline parameters as well as upstream parameters provided the script file is present in the SLDB.
|
|---|
Edit Script Default Value: A skeleton for the chosen scripting language. You can click the Generate Template link to regenerate the skeleton. | Button | Click the Edit Script button to edit a script within the Snap instead of through an external file. From this page, you can export the script to a file in a project, import a script, or generate a template for the selected Scripting Language. noteOnce you select the language of your choice, click the Edit Script button to open the script editor. By default, the editor is populated with a basic script you can modify. The basic script reads an input document, wraps it in a map, and writes the wrapper to the output view. If a script file is present in the SLDB, you can upload it to the Snap using the Script file property; this property also accepts pipeline parameters and upstream parameters.
Once you select the language of your choice, click the Edit Script button to open the script editor. By default, the editor is populated with a basic script you can modify. The basic script reads an input document, wraps it in a map, and writes the wrapper to the output view. If a script file is present in the SLDB, you can upload it to the Snap using the Script file property; this property also accepts pipeline parameters and upstream parameters.
|
|---|

Default Value: Execute only
Example: Validate & Execute | Dropdown list | 
|
|---|
ScriptHook Interface
noteThis example requires that an input view be defined for it to work.
This example requires that an input view be defined for it to work.
package com.snaplogic.scripting.language;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* ScriptHook is the interface that should be implemented as a callback mechanism for
* ExecuteScript snap to call into the script.
*/
public interface ScriptHook {
/**
* Scripts should implement this method to provide application logic.
*/
void execute();
/**
* Scripts should implement this method to cleanup any resources allocated in execute().
*/
void cleanup();
/**
* Input is interface that is used by the script to read input from the snap's input view.
*/
interface Input extends Iterator<Object> {
}
/**
* Output is interface that is used by the script to send output data to the snap output view.
*/
interface Output {
/**
* Write the data to the snap output.
*
* @param data
*/
void write(Object data);
/**
* Write the data that was generated for the given incoming data to the snap output.
* This method carries the lineage data forward.
*
* @param incomingData
* @param data
*/
void write(Object incomingData, Object data);
}
/**
* Error is interface that is used by the script to send error data to snap error view.
*/
interface Error extends Output {
}
} |
Importing Third-Party Libraries
While SnapLogic does not support importing third-party libraries directly using the Script Snap, you can add their package/JAR files in a directory in your Groundplex nodes and then import them using this Snap. For example, consider that you have added the JAR file, mongo-java-driver-3.12.7.jar, in the directory /opt/snaplogic/ext_jar/. For your Python scripts to be able to use this library, create a file named .jython in the home directory of the user running the JCC process. The .jython file should specify a value for the python.path, as follows:
python.path=/opt/snaplogic/ext_jar/mongo-java-driver-3.12.7.jar
noteYou can find the user’s home directory (user running the jcc) in the jcc filename “jcc_output.log" when you search with user.home. If you have multiple jar files, you can add all the paths in the same .jython file separated by colon, as shown below:
python.path=jar1_path:jar2_path:jar3_path
You can find the user’s home directory (user running the jcc) in the jcc filename “jcc_output.log" when you search with user.home. If you have multiple jar files, you can add all the paths in the same .jython file separated by colon, as shown below:
python.path=jar1_path:jar2_path:jar3_path
Here’s an example of Python script that imports and uses code from this library. Use the cleanup method to ensure that the mongoClient object is appropriately closed.
from com.snaplogic.scripting.language import ScriptHook
from com.mongodb.client import MongoClients
class TransformScript(ScriptHook):
def __init__(self, input, output, error, log):
self.input = input
self.output = output
self.error = error
self.log = log
def execute(self):
try:
self.mongoClient = MongoClients.create("mongodb://localhost:27017/?readPreference=primary&ssl=false")
for d in self.mongoClient.listDatabases():
self.output.write(d)
except Exception as e:
errDoc = {
'error' : str(e.args)
}
self.error.write(errDoc)
def cleanup(self):
self.mongoClient.close()
hook = TransformScript(input, output, error, log) |
The paths listed in python.path can be .jar files (Java libraries), directories containing Python libraries (compatible with Python 2.7), or .zip files packaging those Python libraries. Learn more about using the .jython file: Jython Registry. The python.path variable is Jython's version of CPython’s PYTHONPATH variable. Refer to the official Python documentation for more about the PYTHONPATH. If you are using multiple Groundplex nodes, you must add the package/JAR files in each node. You can import third party libraries only on Groundplex nodes.
|
Additional Information
The document data can be converted to and from the JSON data interchange language. By convention, the root of every document is conceptually a JSON object—a collection of name-value pairs, where each name is a string, and each value is an object, an array, a string, a number, a boolean, or a null. Every modern programming language has a corresponding type for this concept:
Script | Type |
|---|
Java | Map |
|---|
Python | Dictionary |
|---|
Ruby | Hash |
|---|
JavaScript | Object |
|---|
When writing a script for the Script Snap, each input document is an object that implements the Java Map interface and can be accessed as an instance of the scripting language’s native object class, such as a Python dictionary.
To write an output document, your script must create a new object. In Python or Ruby, you can create an instance of the required language’s native object type, a Python dictionary, or a Ruby hash. The values you add to these objects must be one of the JSON-compatible types, including objects, arrays, strings, numbers, and booleans. You can use the corresponding array or list type of the language for an array. Objects written to the output view should be of Java types. Some downstream Snaps require this, for example, the Join Snap. To write a Python map to the output view in a Python script, convert the map to a Java HashMap.
General Instructions for all Scripting Languages
The script author should declare a global variable named 'hook' (note that this variable name is case-sensitive). The Script engine makes the following four global variables available to the script as defined in the Script#ScriptHook Interface section:
The variable input is of type ScriptHook.Input
The variable output is of type ScriptHook.Output
The variable error is of type ScriptHook.Error
The variable log is of type org.slf4j.Logger
Type defined in the schema maps to the Java class per the following:
Data Type | Java class |
|---|
NUMBER | java.math.BigDecimal |
INTEGER | java.math.BigInteger |
STRING | java.lang.String |
DATETIME | org.joda.time. DateTime |
LOCALDATETIME | org.joda.time. LocalDateTime |
BOOLEAN | java.lang.Boolean |
DATE | org.joda.time.LocalDate |
TIME | org.joda.time.LocalTime |
BINARY | java.lang.Byte |
TABLE | java.util.List |
ANY | java.lang.Object |
COMPOSITE | java.util.Map |
Example Scripts
JavaScript
script = {
execute : function() {
var fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
var map = {"fruits" : fruits}
output.write(map)
}
}
var hook = new com.snaplogic.scripting.language.ScriptHook(script) |
Python
noteThis example requires an input view be defined in order for it to work.
This example requires an input view be defined in order for it to work.
from com.snaplogic.scripting.language import ScriptHook
from com.snaplogic.scripting.language.ScriptHook import *
class TransformScript(ScriptHook):
def __init__(self, input, output, error, log):
self.input = input
self.output = output
self.error = error
self.log = log
def execute(self):
self.log.info("Executing Transform script")
while self.input.hasNext():
data = self.input.next()
data["firstLast"] = "%s-%s" %(data["first"],data["last"])
data["firstLast2"] = data["first"] + data["last"]
data["numberMath"] = data["counter"] + 22
data["numberMath2"] = data["counter"] + 23
data["dateMonthPlusOne"] = data["birthday"].plusMonths(1)
data["numberMathType"] = type(data["counter"])
data["dateType"] = type(data["birthday"])
try:
data["mathTryCatch"] = data["counter2"] + 33
self.output.write(data)
except Exception as e:
data["errorMessage"] = e.message
self.error.write(data)
self.log.info("Finished executing the Transform script")
hook = TransformScript(input, output, error, log)
|
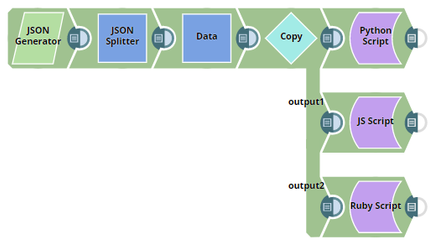
Script Snap Configuration Using Python, JS Script, and Ruby Script
The following pipeline demonstrates how the Script Snap executes in all three supported languages. This pipeline uses a simple JSON file with First Name, Last Name, and Birthday.
The following is a snapshot of the input for the Script Snap:
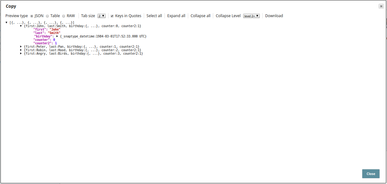
Python Script
Script Snap uses the Jython engine to execute the scripts written in Python.
from com.snaplogic.scripting.language import ScriptHook
from random import randint
from time import sleep
class TransformScript(ScriptHook):
def __init__(self, input, output, error, log):
self.input = input
self.output = output
self.error = error
self.log = log
def execute(self):
self.log.info("Executing Transform script")
i = 1
while self.input.hasNext():
data = self.input.next()
sleep(randint(1,10))
map = {"out": data}
self.output.write(map)
self.log.info("Finished executing the Transform script")
hook = TransformScript(input, output, error, log) |
Java Script
The Script Snap uses the Nashorn engine to execute the scripts written in JavaScript.
// Ensure compatibility with both JDK 7 and 8 JSR-223 Script Engines
try { load("nashorn:mozilla_compat.js"); } catch(e) { }
script = {
execute : function() {
while (input.hasNext()) {
var in_data = input.next()
var new_data = {}
var keyArray = in_data.keySet().toArray()
for (var index in keyArray) {
var key = keyArray[index]
new_data[key] = in_data.get(key)
}
new_data.firstLast = new_data.first + "-" + new_data.last
new_data.firstLast2 = new_data.first + in_data.get("last")
new_data.numberMath = (new_data.counter + 22) | 0
new_data.numberMath2 = new_data.counter + 23
new_data.dateMath = new_data.birthday.plusMonths(1).toString()
new_data.mathType = typeof(new_data.counter)
new_data.dateType = typeof(new_data.birthday)
output.write(new_data)
}
}
};
var hook = new com.snaplogic.scripting.language.ScriptHook(script) |
Ruby Script
Script Snap uses the JRuby engine to execute the scripts written in Ruby.
class MyScript
include com.snaplogic.scripting.language.ScriptHook
attr_reader :log, :input, :output, :error
def initialize(log, input, output, error)
@log = log
@input = input
@output = output
@error = error
@array = [java.lang.Integer.valueOf(1), java.lang.Integer.valueOf(2)]
end
def execute()
while input.hasNext() do
data = input.next()
data["firstLast2"] = data["first"] + data["last"]
data["numberMath"] = data["counter"] + 22
data["numberMath2"] = data["counter"] + 23
data["dateMonthPlusOne"] = data["birthday"].plusMonths(1)
begin
data["mathTryCatch"] = data["counter"] + 33
output.write(data)
rescue Exception=>e
data["errorMessage"] = e.message
error.write(data)
end
end
end
end
$hook = MyScript.new($log, $input, $output, $error) |
A sample preview output of the successful execution for all the three Snaps is shown below:
The exported pipeline is available in the Script#Downloads section below.
Script Snap Execution Using Pipeline Parameters
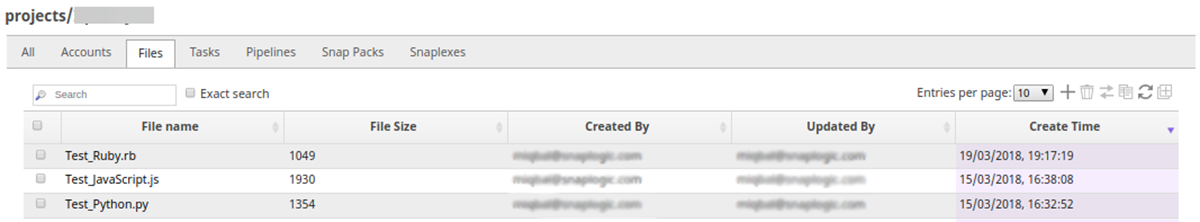
The following example demonstrates the execution of the Script Snap using the pipeline parameters; the script file in the SLDB is passed as a Pipeline parameter. The pipeline demonstrated above is modified to accept pipeline parameters by configuring the Script file property. For the scripts to be passed as a pipeline parameter, the script file should be present in the project folder in SnapLogic. Confirm that the script files are present in the Files section inside the Manager; if not, upload them by clicking on the '+' icon.
In this example, there are three files, one for each type of scripting language:
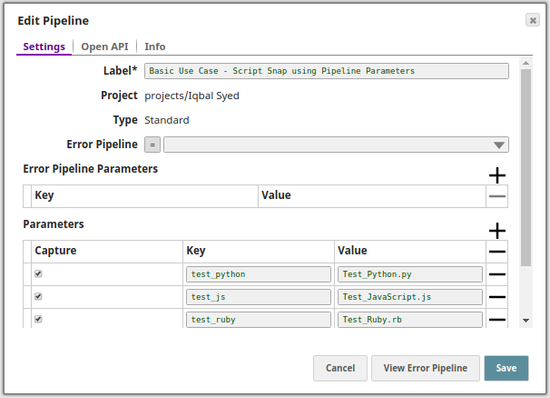
Below is a snapshot of the pipeline's properties and configured pipeline parameters.
The individual Script Snaps are configured as shown below:
As in the example above, this pipeline produces the same output on execution. The exported pipeline and sample script files used are available as a zip file in the Downloads section below.
Downloads

Related Content

 ): Indicates a list that is dynamically populated based on the configuration.
): Indicates a list that is dynamically populated based on the configuration. ): Indicates the value is an expression (if enabled) or a static value (if disabled). Learn more about Using Expressions in SnapLogic.
): Indicates the value is an expression (if enabled) or a static value (if disabled). Learn more about Using Expressions in SnapLogic. ): Indicates that you can add fields to the field set.
): Indicates that you can add fields to the field set. ): Indicates that you can remove fields from the field set.
): Indicates that you can remove fields from the field set. ): Indicates that you can upload files.
): Indicates that you can upload files.