On this page
SnapLogic Hadoop Snaps support encryption zones transparently. If the HDFS cluster is configured with "Transparent at rest Encryption", the Snaps read/write into encryption zones.
HDFS implements transparent, end-to-end encryption. Once configured, data read from and written to special HDFS directories is encrypted and decrypted without any changes to the user application code. This encryption is end-to-end, means only the client can encrypt and decrypt the data. HDFS never stores or has access to unencrypted data or unencrypted data encryption keys. This satisfies two typical requirements for encryption: at-rest encryption (meaning data on persistent media, such as a disk) as well as in-transit encryption (such as when data is traveling over the network).
A new cluster service is required to manage encryption keys: the Hadoop Key Management Server (KMS). In the context of HDFS encryption, the KMS performs three basic responsibilities:
Providing access to the stored encryption zone keys.
Generating new encrypted data encryption keys for storage on the NameNode.
Decrypting the encrypted data encryption keys for use by HDFS clients.
Once a KMS has been set up and the NameNode and HDFS clients have been correctly configured, use the hadoop key and hdfs crypto command-line tools to create encryption keys and set up new encryption zones.
Follow the documents below to setup HDFS encryption:
Once HDFS encryption is configured, following are the instructions to create/delete encryption zones.
Create an encryption key:
$sudo -u <user_name> hadoop key create <key_name> |
Create a new empty directory and make it an encryption zone using the key created above:
$sudo -u hdfs hadoop fs -mkdir /encryption_zone $sudo -u hdfs hdfs crypto -createZone -keyName <key_name> -path /encryption_zone |
Delete encryption zones:
$sudo -u hdfs hadoop fs -rm -r -skipTrash /encryption_zone |
Once encrypted zones are created, follow the instructions below to enable it to work with SnapLogic Pipelines.
Hadoop allows you to configure proxy users to access HDFS on behalf of other users; this is called impersonation. When user impersonation is enabled on the Hadoop cluster, any jobs submitted using a proxy are executed with the impersonated user's existing privilege levels rather than those of a superuser.
When User Impersonation option is selected and Kerberos is not selected as the account type, the user who is executing the pipeline is used to impersonate for the HDFS Operations. For example, if the user logged into the SnapLogic platform is operator@snaplogic.com, the user name "operator" is used to proxy the super user. When a Kerberos account is configured and User impersonation is selected, the Client Principal configured in the Kerberos account impersonates the pipeline user.
This user is expected to be in the ACL as described below,
Set the right acls for impersonating the user to decrypt key (essentially read from encryption zone) in kms-acls.xml / KMS UI.
<property> <name>key.acl.<key_name>.DECRYPT_EEK</name> <value>user1,user2,userN group1,group2,groupN</value> <description> ACL for decryptEncryptedKey operations. </description> </property> |
Refer to the specific managed service for more information on how to do that in the UI/Configuration:
https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/r2.8.0/hadoop-kms/index.html#Decrypt_Encrypted_Key
https://www.cloudera.com/documentation/enterprise/5-8-x/topics/cdh_sg_kms_security.html#concept_fgf_42v_mp
https://docs.hortonworks.com/HDPDocuments/HDP2/HDP-2.6.1/bk_security/content/ranger-kms-admin-guide.html
-DHADOOP_CLIENT_CONF_DIR=<conf_dir> to the key jvm_options under Global properties.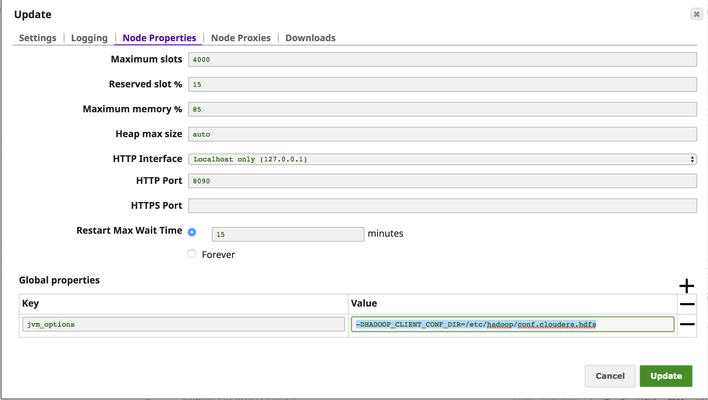
Add the following to the core-site.xml in cluster configuration or add it to core-site.xml located in the input directory pointed by HADOOP_CLIENT_CONF_DIR
<property> <name>hadoop.security.crypto.codec.classes.aes.ctr.nopadding</name> <value>org.apache.hadoop.crypto.OpensslAesCtrCryptoCodec, org.apache.hadoop.crypto.JceAesCtrCryptoCodec</value> </property> |