In GrounIn this Article
| Table of Contents | ||
|---|---|---|
|
...
| Note | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
The Linux installer comes bundled with the JRE necessary for this SnaplexGroundplex. We recommend you use the patch version of Java 11 that is bundled with the installer for your Linux environment. To update your Snaplex Groundplex to the Java 11, see Upgrading Your Groundplex to Java 11. |
...
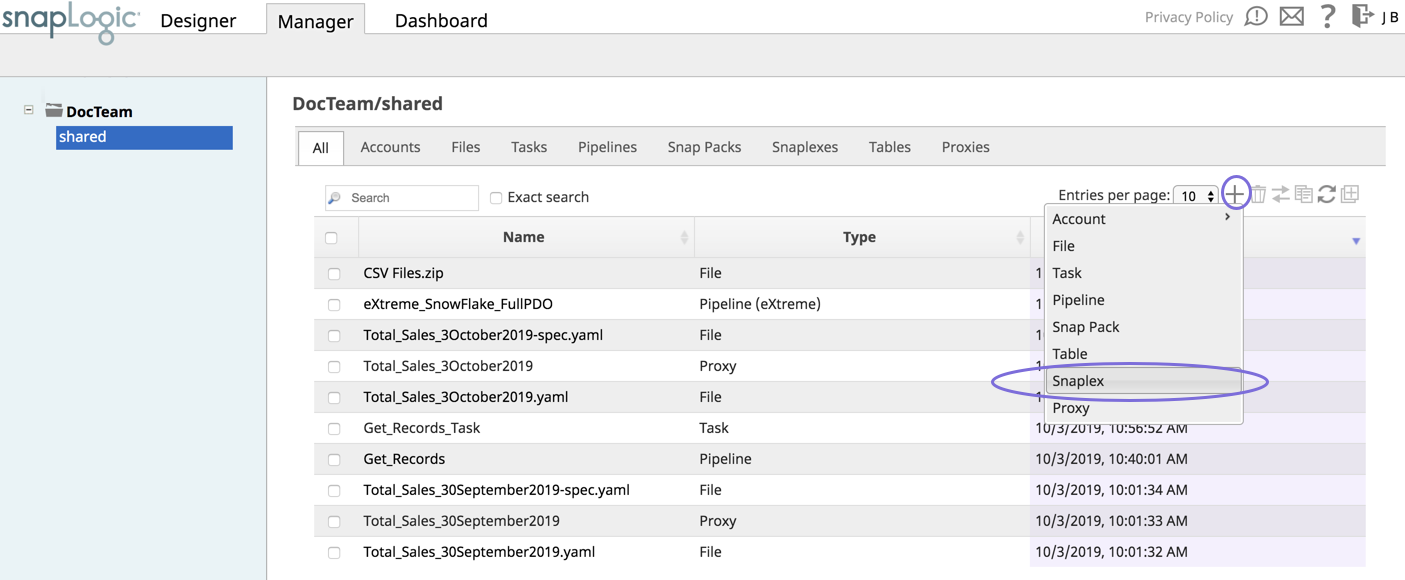
- Log into SnapLogic Manager as an Org admin.
- Navigate to the project where you want to create your Groundplex, then do one of the following:
- Click the Snaplex tab, then click to display the Snaplex popupdialog.
OR
- Click to display the Assets drop-down list, then select Snaplex; the Snaplex popup dialog appears.
- Click the Snaplex tab, then click to display the Snaplex popupdialog.
- Enter the required information on the Create Snaplex form. Once completed, the Downloads tab on the Snaplex popup appears. The Downloads tab has links to the installer and configuration files.
- Download the RPM/DEB and the configuration file onto a Linux machine:
For CentOS (or Redhat) 6.3 or newer, run the following command:
$ sudo rpm -i <filename>.rpmFor Ubuntu 14.04 or newer, run the following command:
$ sudo dpkg -i <filename>.deb
Where <filename> is the name of the current installer file.
After the software is installed, place the downloaded configuration file in the
/opt/snaplogic/etcdirectory and make sure the file name ends with.slpropz. Change the slpropz file so that snapuser owns it by running the following commands:Code Block $ sudo chown snapuser:snapuser /opt/snaplogic/etc/myplex.slpropz $ sudo chmod 600 /opt/snaplogic/etc/myplex.slpropz
- To start the Snaplex service for your Groundplex, run:
$ sudo /opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh start - To verify the Snaplex has the Groundplex has started, visit https://elastic.snaplogic.com/sl/dashboard.html#Health. The newly installed Snaplex Groundplex node should show up in the list of nodes for the Snaplexin the Snaplex tab on the Dashboard.
| Note | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Some Snaps, such as the SQL Bulk Load Snaps, require write and execute permissions to the |
...
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Ultra Pipelines require that you set up a FeedMaster along with the JCC (Java Component Container) nodes in your Groundplex. For details, see Deploying a FeedMaster Node. |
...
To generate and import a self-signed certificate on all the JCC nodes in the SnaplexGroundplex:
- Obtain the certificate (.pem) file by using SSH.
Import the file by using the following command in the JCC node:
Paste code macro /opt/snaplogic/pkgs/jre1.8.0_45/bin/keytool -import -file <path_to_pem_file_from_step_1> -alias <alias_name_optional> -keystore /opt/snaplogic/pkgs/jre1.8.0_45/lib/security/cacerts -vEnter keystore password: changeit
Note This example is an excerpt from 1.8.0_45; the directory path might vary based on the Java installation directory.
- Restart the JCC node process to confirm the import.
Run the following command to list certificates from the CAcerts file:
Paste code macro /opt/snaplogic/pkgs/jre1.8.0_45/bin/keytool -list --keystore /opt/snaplogic/pkgs/jre1.8.0_45/lib/security/cacerts -v+
...
You can use either the systemd or init.d utility to start and stop the SnaplexGroundplex. Procedures for both are included below. The procedures vary depending on which Linux distribution is installed on the Snaplex Groundplex host.
Starting and Stopping the Groundplex by Using the Linux Systems Call
Use this procedure for Red Hat-like Linux distributions such as Red Hat, Fedora CoreOS, CentOS, and SuSE.
...
- Log into the Groundplex host as a root or sudo user.
Create the startup service file:
Code Block touch /etc/systemd/system/snaplogic.service
Change the permissions on the file:
Code Block chmod 664 /etc/systemd/system/snaplogic.service
This change provides read and write permissions for the owner and group, and read permission for others.
Open the file with a text editor. For example, the using a vim editor:
Code Block vim /etc/systemd/system/snaplogic.service
Add the following text to the file:
Paste code macro [Unit] Description=SnapLogic JVM After=network.target [Service] Type=forking ExecStart=/opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh start ExecReload=/opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh restart ExecStop=/opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh stop [Install] WantedBy=default.target
- Save and exit the file.
Enable the service by running the following command:
Code Block systemctl enable snaplogic.service
The service will start automatically when the host reboots.
Start the service:
Code Block systemctl start snaplogic.service
To stop the Snaplex Groundplex as a service, run the following command:
Code Block systemctl disable snaplogic.service
...
| Note | ||
|---|---|---|
We recommend that you reboot the machine to verify if the Snaplex service is restarting automatically on machine reboot. Under some conditions, the symlink resolution might fail when the machine is starting up. In this case, you can change the Snaplex startup script to be a file instead of a symlink. Run the following commands a root user:
|
To delete the Snaplex as a service, remove the service from the chkconfig management:
...
- Log in to the Linux machine as root.
Change directories:
Code Block cd /etc/init.d/
Create a soft-link to the
jcc.shfile:Code Block ln -s /opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh snaplex
Install the service using
update-rc.d. For example:Code Block sudo update-rc.d snaplex defaults 98 02
Note title Troubleshooting if the machine reboot fails We recommend that you reboot the machine to verify whether the Snaplex service is restarting automatically on machine reboot. Under some conditions, the symlink resolution might fail when the machine is starting up. In this case, you can change the Snaplex startup script to be a file instead of a symlink. Run the following commands a root user:
Code Block rm /etc/init.d/snaplex cp /opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh /etc/init.d/snaplex echo "export SL_ROOT=/opt/snaplogic" >> /etc/sysconfig/jcc
On a Debian system, the
/etc/sysconfigdirectory would need to be created if not already present.To stop the Snaplex as a the Snaplex Service, remove the service from
update-rc.dmanagement:Code Block update-rc.d -f snaplex remove
...
- Stop the existing JCC node by running the following command:
$ sudo /opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh stop - Download the new Snaplex installer and install the Groundplex, running the RPM, DEB, or Docker installers as appropriate.
- For RPM systems, run the following command:
$rpm -U snaplogic-snaplex.rpm - For DEB systems, run the following command:
$dpkg -i snaplogic-snaplex.deb - For Docker, stop the existing container and start a new container using the latest image.
- For RPM systems, run the following command:
- Add the following entry to the
/etc/sysconfig/jccdirectory. You must create this directory and file if neither are present. :export SL_JAVA_HOME=/opt/snaplogic/pkgs/openjdk-11.0.5+10-jre/ - Start the JCC node by running the following command:
$ sudo /opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh start.
...
If you want to use the/myopt/myroot instead of the /opt/snaplogic as the installation folder and myuser instead of snapuser, do the following steps:
- Run the following commands after installing the RPM/DEB package:
$ sudo mv /opt/snaplogic /myopt/myroot$ sudo chown -R myuser /myopt/myroot
- Add the following properties in the
/etc/sysconfig/jccfile. If this file does not exist, create it.export SL_USER=myuserexport SL_ROOT=/myopt/myroot
- Restart the service with the following command:
$ sudo /myopt/myroot/bin/jcc.sh restart - To make a service using init.d, make the
/etc/init.d/snaplexfile a symlink to the/myopt/myroot/bin/jcc.shfile.
...
Some Linux installations have system ulimit settings that are set to low values. This low setting can cause errors when running higher Pipeline loads on the Groundplex JCC node, such as, java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: unable to create new native thread.
To fix this issue, you need to increase the system limits for the Snapuser user. You can add the following in the /etc/security/limits.conf folder to increase the file and process limits.
...