In this article
| Table of Contents | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Overview
This Snap takes an expression, evaluates it, and writes You can use this Snap to evaluate an expression and write the result to the provided specified target path. If an expression fails to evaluate, use the Views tab to specify error handling. For more information on expressions, see Understanding Expressions in SnapLogic.
This Snap supports both binary and document data streams. The default input and output is document, but you can select Binary from the Views tab in the Snap's settings.
...
|
Any future changes made to either "$MyArray" or "$OtherArray" are in the both arrays. In that case, make a copy of the array as shown below: |
|
The same is true for objects, except you can make a copy using the ".extend()" method as shown below: |
|
Passing Binary Data
You would convert binary data to document data by preceding the Mapper Snap with the Binary-to-Document Snap. Likewise, to convert the document output of the Mapper Snap to binary data, you would add the Document-to-Binary Snap after the Mapper Snap.
Currently, you can do this transformation within the Mapper Snap itself. You set the Mapper Snap to take binary data as its input and output by using the $content expression.
| Info |
|---|
Binary Input and Output If you are only working with a binary stream as both input and output, you must set both source and target fields with $content, then manipulate the binary data using the Expression Builder. If you do not specify this mapping, then the binary stream from the binary input document is passed through unchanged. |
Prerequisites
None.
...
Snap Type
Mapper Snap is a TRANSFORM-type Snap that transforms data and writes or passes it to the downstream Snap.
Prerequisites
None.
Support for Ultra Pipelines
Works in Ultra Pipelines.
...
Expressions used in this Snap, downstream of any Snowflake Snap, that evaluate to very large values such as EXP(900) are displayed in the input/output previews as Infinity . However, you can see the exact values in the validation previews; hence, ignore this error.
...
Type | Format | Number of Views | Examples of Upstream and Downstream Snaps | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Input | Document |
| Binary-to-Document | This Snap can have a most one document or binary input view. If you do not specify an input view, the Snap generates a downstream flow of one row. | ||
Output | Document |
| Any Document Snap | This Snap has exactly one document or binary output view. | ||
Error | Error handling is a generic way to handle errors without losing data or failing the Snap execution. You can handle the errors that the Snap might encounter while running the Pipeline by choosing one of the following options from the When errors occur list under the Views tab. The available options are:
Learn more about Error handling in Pipelines. This Snap has at most one document error view and produces zero or more documents in the view. If the Snap fails during the operation, an error document is sent to the error view containing the fields error, reason, original, resolution, and stacktrace:
| |||||
Snap Settings
...
Field Name
...
Field Type
...
Description
Label*
Default Value: Mapper
Example: Mapper
...
String
...
The name for the Snap. You can modify this to be more specific, especially if you have more than one of the same Snap in your Pipeline.
Null-safe access
Default Value: Mapper
Example
...
Checkbox
...
Enabled: Lets you set the target value to null in case the source path does not exist. For example $person.phonenumbers.pop() ->$ lastphonenumber may result in an error if person.phonenumbers does not exist on the source data. Enabling Null-safe access allows the Snap to write null to lastphonenumber instead of causing an error.
Disabled: Fails if the source path does not exist, ignores the record entirely, or writes the record to the error view depending on the setting of the error view property.
Pass through
Default Value: Mapper
Example
...
Checkbox
Required. This setting determines if data should be passed through or not. If not selected, then only the data transformation results that are defined in the mapping section will appear in the output document and the input data will be discarded. If selected, then all of the original input data will be passed into the output document together with the data transformation results.
| Note |
|---|
This setting is impacted by Mapping Root. If Mapping Root is set to $ and Pass through is not selected, anything not mapped in the table will not pass through. However, if Mapping Root is set to $customer and Pass through is not selected, it will only apply to the items within the Mapping Root level. That means that anything above the Mapping Root level will pass though and items at the Mapping level that are not mapped in the table will not pass through. |
Default: Not selected.
When to always select Pass through
Always select Pass through if you plan to leave the Target path field blank in the Mapper Snap; otherwise, the Snap throws an error informing you that the field that you want to delete doesn't exist. This is expected behavior.
Say you have an input file that contains a number of attributes; but you need only two of these downstream. So, you connect a Mapper to the Snap supplying the input file, select the two attributes you need by listing them in the Expression fields, leave the Target path field blank, and select Pass through. When you execute the pipeline, the Mapper Snap evaluates the input documents/binary data and picks up the two attributes that you want, and passes the entire document/binary data through to the Target schema. From the list of available attributes in the Target Schema, the Mapper Snap picks up the two attributes you listed in the Expression fields, and passes them as output. However, if you hadn't selected the Pass through check box, the Target Schema would be empty, and the Mapper would display a No schema available error.
Mapping Root
Default Value: Mapper
Example
...
String/Suggestion
...
Snap Settings
Field Name | Field Type | Description | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Label* Default Value: Mapper | String | The name for the Snap. You can modify this to be more specific, especially if you have more than one of the same Snap in your Pipeline. | ||||||
Null-safe access Default Value: Deselected | Checkbox | Select this checkbox to set the target value to null in case the source path does not exist. For example, | ||||||
Pass through Default Value:Deselected | Checkbox | This setting determines if data should be passed through or not. If you select this checkbox, then all the original input data is passed into the output document together with the data transformation results. If you deselect this checkbox, then only the data transformation results that are defined in the mapping section appear in the output document and the input data is discarded.
When to always select Pass throughAlways select Pass through if you plan to leave the Target path field blank; else, the Snap displays an error that the field that you want to delete does not exist. This is the expected behavior. For example, you have an input file that contains a number of attributes; but you need only two of these downstream. So, you connect a Mapper to the downstream Snap supplying the input file, select the two attributes you need by listing them in the Expression fields, leave the Target path field blank, and select Pass through. When you execute the Pipeline, this Snap evaluates the input documents/binary data and picks up the two attributes that you want, and passes the entire document/binary data through to the Target schema. From the list of available attributes in the Target Schema, the Mapper Snap picks up the two attributes you listed in the Expression fields, and passes them as output. However, if you had not selected the Pass through checkbox, the Target Schema would be empty, and the Mapper would display a | ||||||
Transformations* | Use this fieldset to configure the settings for data transformations. | |||||||
Mapping Root Default Value: $ | String/Suggestion | Specify the sub-section of the input data to be mapped. For more information, see Learn More: Understanding the Mapping Root. Default: $ | String/Expression | Required. Expression and target to write the result of the expression. Expressions that are evaluated will remove the source targets at the end of the run. For example: | ||||
| Expression | Target Path | |||||||
Input Schema | Dropdown list | Select the input data (that comes from the upstream Snap) that you want to transform. | ||||||
Mapping table | Use this field set to specify the source path, expression, and target path columns used to map schema structure. This field set contains the following fields:
| |||||||
Expression Default Value: N/A
| $full | String/Expression | Specify the expression to write to the target path. Expressions that are evaluated will remove the source targets at the end of the run.
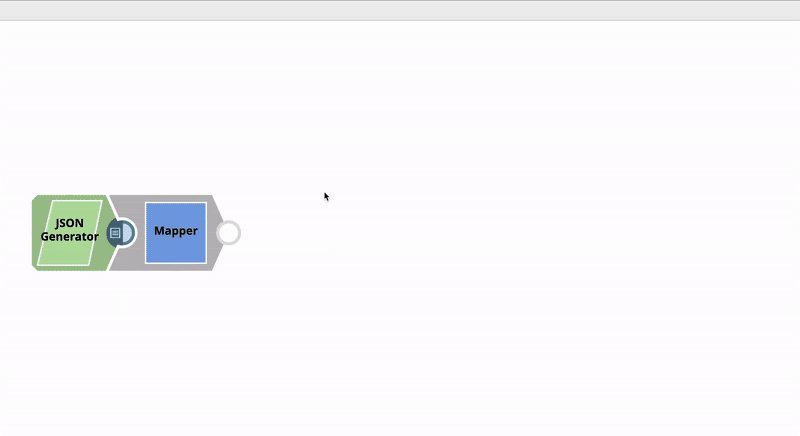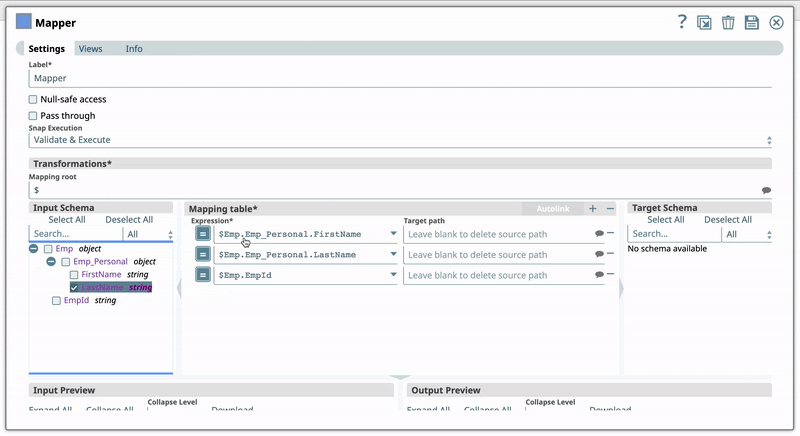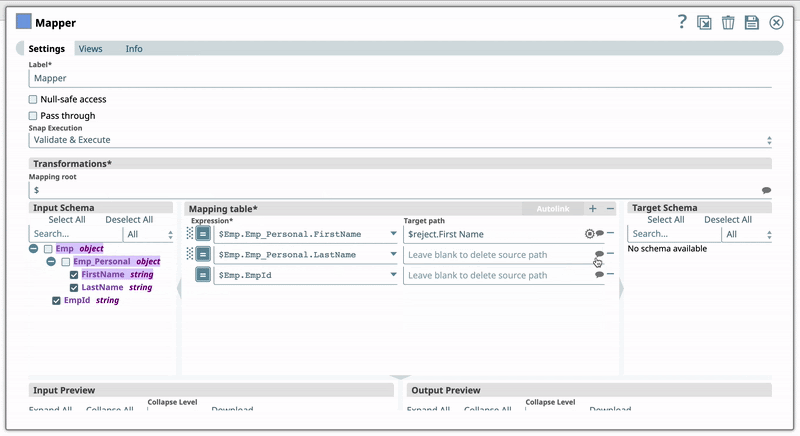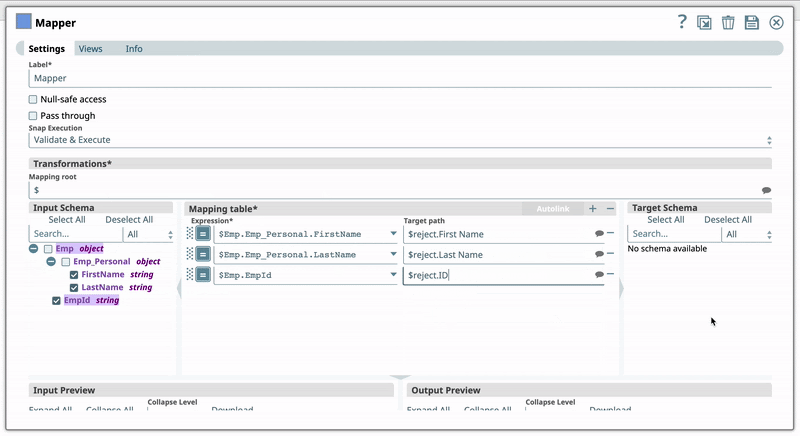
See Lear More: Understanding Expressions in SnapLogic for more information on the expression language and Using Expressions for usage guidelines. Target Path RecommendationIris simplifies configuring the Target path property in the Mapper Snap by recommending suggestions for the Expression and Target path property mapping. To make these suggestions, Iris analyzes Expression and Target path mappings in other Pipelines in your Org and suggests the exact matches for the Expressions in your current Pipeline. The suggestions are displayed upon clicking against the Target path. For example, you have the Expression $Emp.Emp_Personal.FirstName in one of your Pipelines. And you have set the Target path for this expression as $FirstName. Now, if you use the expression $Emp.Emp_Personal.FirstName in a new Pipeline, then Iris suggests $FirstName as one of the recommended Target paths. This helps you standardize the naming standards within your org. The following video illustrates how Iris recommends Target path in a Mapper Snap: Anchor | | NumericInputs | NumericInputs | ||
| Expression | Target path | |||||||
| $num + 100 | $numnew | |||||||
| Expression | Target path | |||||||
| parseFloat($num1) + 100 | $numnew |
| Dropdown list |
| ||||
| name | Snap_Execution_Introduced | page | Anaplan ReadManaging Numeric Inputs in Mapper Expressions||||||
Target path Default Value: N/A | String/Suggestion | Specify the target path at which the expression should be written. Target Path Recommendation
For example, you have the Expression $Emp.Emp_Personal.FirstName in one of your Pipelines. And you have set the Target path for this expression as $FirstName. Now, if you use the expression $Emp.Emp_Personal.FirstName in a new Pipeline, then Iris suggests $FirstName as one of the recommended Target paths. This helps you standardize the naming standards within your org. The following video illustrates how Iris recommends Target path in a Mapper Snap: | ||||||
Snap Execution | Dropdown list | Select one of the three modes in which the Snap executes. Available options are:
| ||||||
Mapping Table
The mapping table makes it easier to do the following:
Determine which fields in a schema are mapped or unmapped.
Create and manage a large mapping table through drag-and-drop.
Search for specific fields.
For more information, see Learn More: Using the Mapping Table.
Example
...
In this example, you read an Excel file from the SLDB and remove columns that you do not need from the file. You then write the updated data back into the SLDB as a JSON file.
...
...
Add a File Reader Snap to the Canvas and configure it to read the Excel file from which you want to remove specific columns. | |
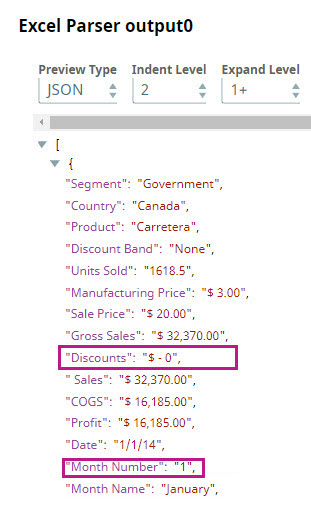
Parse the file using the Excel Parser Snap. You can preview the parsed data by clicking the icon. | |
...
From the preview file, you can see the columns that you want to remove. In this instance, you decide to remove the Discounts and Month Number columns. To do so, you add a Mapper Snap to the Pipeline. |
...
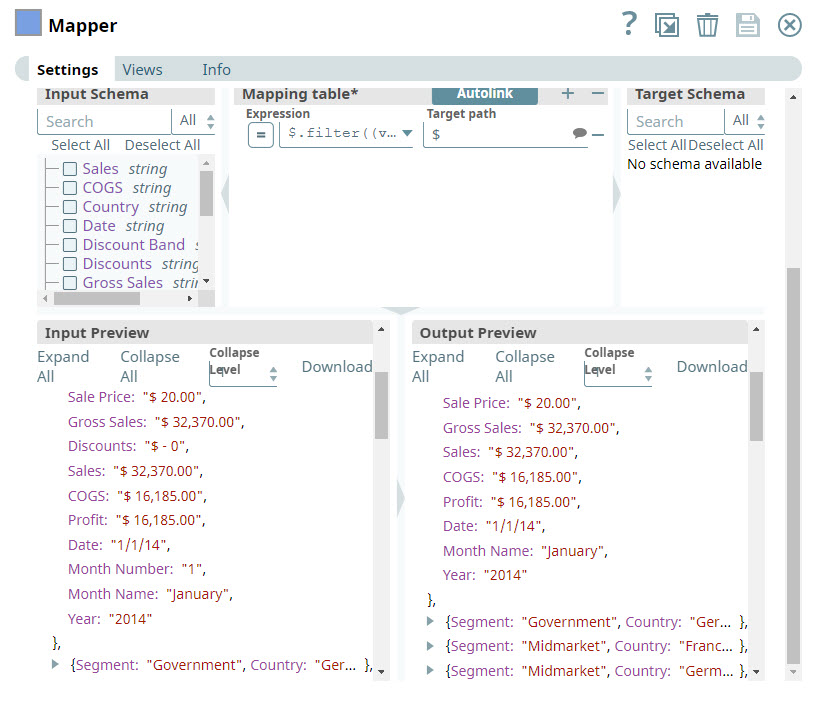
In the Expression field, you enter the criteria that you want to use to remove the Discounts and Month Name columns. |
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
You enter $ in the Target field to indicate that you want to leave the other column names unchanged.
...
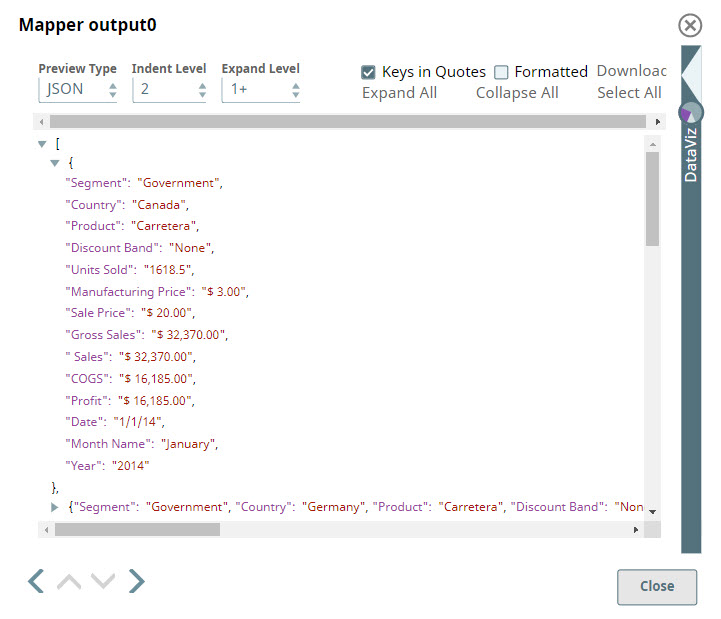
You validate the Snap, and can see that the Discounts and Month Name columns are skipped.
...
You now need to write the updated data back into the SLDB as a JSON file. To do so, you add a JSON Formatter Snap to the Pipeline to convert the documents coming in from the Mapper Snap into binary data. You then add a File Writer Snap and configure it to write the input streaming data to the SLDB.
You can now view the saved file in the destination project in SnapLogic Manager.
Example Data Output
Successful Mapping
If your source data looks like:
...
And your mapping looks like:
Expression:
$first_name.concat(" ", $last_name)Target path: $full
$full_name
Your outgoing data will look like:
| Code Block |
|---|
{
"full_name": "John Smith",
"phone_num": "123-456-7890"
} |
Unsuccessful Mapping
If your source data looks like:
...
And your mapping looks like:
Expression: $middle
$middle_name.concat(" ", $last_name)Target path: $full
$full_namename
An error will be thrown.
Example
...
Escaping Special Characters in Source Data
This example demonstrates how you can use the Mapper Snap to customize source data containing special characters so that it is correctly read and interpreted by downstream Snaps.
...
Download the Pipeline.In the sample Pipeline,
Add custom JSON data |
...
in the JSON Generator Snap, wherein the values of |
...
The output preview of the JSON Generator Snap displays the special character correctly: | |
...
Before sending this data to downstream Snaps, you may need to prefix the special characters with an escape character so that downstream Snaps correctly interpret these. You You can do this using the Expression field in the Mapper Snap. Based on the accepted escape characters in the endpoint, you can select from the following expressions:
If the Escape Character is | Use Expression | Sample Output | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
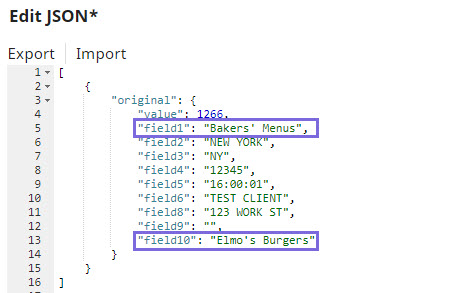
Single quote (') | JSON: $original.mapValues((value,key)=> value.toString().replaceAll("'","''")) OR $original.mapValues((value,key)=> value.toString().replaceAll("'","\''")) CSV: $[' Business-Name'].replace ("'","''") | |||
Ampersand (&) | JSON: $original.mapValues((value,key)=> value.toString().replaceAll("'","\&'")) OR $original.mapValues((value,key)=> value.toString().replaceAll("'","&'")) CSV: $[' Business-Name'].replace ("'","&'") | |||
Backslash (\) | JSON: $original.mapValues((value,key)=> value.toString().replaceAll("'","\\'"))
CSV: $[' Business-Name'].replace ("'","\\'") |
In this way, you can customize the data to be passed on to downstream Snaps using the Expression field in the Mapper Snap.
...
The SnapLogic Data Mapper
...
| Widget Connector | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
SnapLogic Best Practices: Data Transformations and Mappings
| Widget Connector | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
| Attachments | ||
|---|---|---|
|
...
Related Links
Community Links:
| Insert excerpt | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|