...
| Table of Contents | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Overview
SnapLogic support for the Groundplex (also known as an on-premise Snaplex) on a Docker container empowers customers to optimize IT infrastructure costs while benefiting from containerized technology.
...
If you are running with 11.0.10 onwards, endpoint connections to TLS 1.0 and 1.1 are disabled by default. We recommend that you update the endpoint to support TLS 1.2 or higher, for security.
Prerequisites
Familiarity with the SnapLogic Snaplex installation process.
Review the Groundplex requirements.
Depending on your OS, review Groundplex installation for Linux or Windows.
Installing Groundplex in a Dockerized Container
Retrieve the latest Docker image from Docker Hub using the following pull command:
Code Block docker pull registry.hub.docker.com/snaplogic/snaplex:main-<build number>>
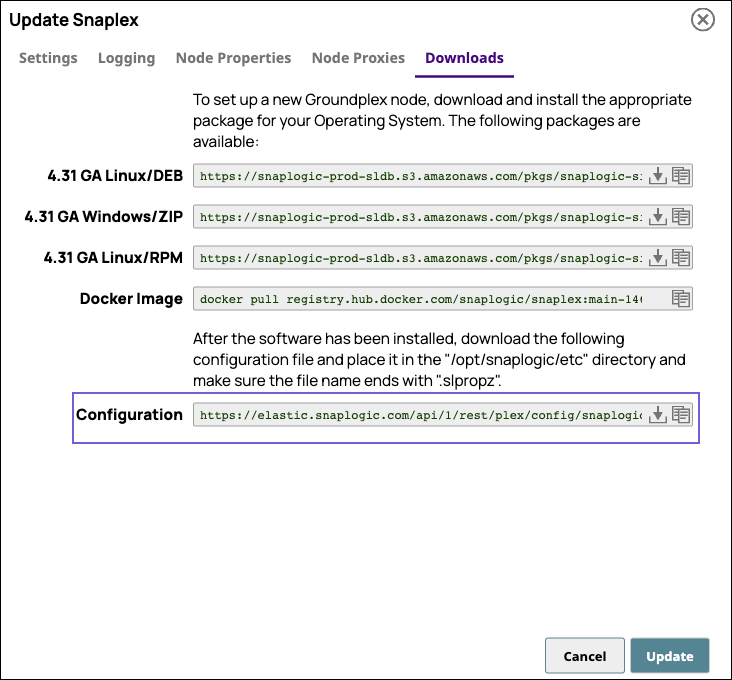
In SnapLogic Manager, navigate to your target Groundplex instance and click it to display the Update dialog.
In the Downloads tab, click
 in the Configuration option to download the
in the Configuration option to download the slpropzfile for your Groundplex node.
After downloading the configuration file, you are ready to launch your Groundplex as a Docker container.
Create a Docker Image for a Groundplex
You can now create a Docker image from Linux/RPM, available in the Downloads tab as a more secure alternative using the Docker file. The Docket file lists all the commands required to build the Docker image.
...
You can download the RPM from the Snaplex tab and the run.sh script can be copied from the published containers. The details of the image layer are shown in the repeating video.
...
Running a Snaplex Node from Docker
To run the Snaplex node from Docker:
...
| Note |
|---|
For this command to work, you need to complete the following tasks:
|
Example
...
| Info |
|---|
Depending on how you install Docker, you may need to use sudo. For more information on the Docker |
...