In this Page
| Table of Contents | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Install a Snaplex on Linux
This article describes the procedures for installing an on-premise Snaplex on Linux OS. For prerequisites, see Requirements for On-premises Snaplex.
| Note | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
Groundplex installation covers the following tasks:
- Setting up a Groundplex
- Deploying FeedMaster
- Importing a certificate to SnapLogic node.
To set up a Groundplex on Linux:
...
For CentOS (or Redhat) 6.3 or newer, do sudo rpm -i <filename>.rpm.
For Ubuntu 14.04 or newer, do sudo dpkg -i <filename>.deb.
where <filename> is the name of the current installer file.
After the software has been installed, place the downloaded configuration file in the "/opt/snaplogic/etc" directory and make sure the file name ends with .slpropz. Change the slpropz file to be owned by snapuser user, by running:
| Code Block |
|---|
sudo chown snapuser:snapuser /opt/snaplogic/etc/myplex.slpropz
sudo chmod 600 /opt/snaplogic/etc/myplex.slpropz |
...
To start the on-premises service, type: sudo /opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh start
...
To verify the Snaplex has started, visit https://elastic.snaplogic.com/sl/dashboard.html#Health. The newly install node should show up in the list of nodes for the Snaplex.
...
For Snaplex downloads prior to Fall 2016 (4.7):
Download the RPM/DEB provided by SnapLogic onto a Linux machine.
For CentOS (or Redhat) 6.3 or newer, do sudo rpm -i <filename>.rpm.
For Ubuntu 14.04 or newer, do sudo dpkg -i <filename>.deb.
where <filename> is the name of the current installer file.Copy the keys.properties file provided by SnapLogic onto /opt/snaplogic/etc/keys.properties
Edit /opt/snaplogic/etc/global.properties.
Update jcc.subscriber_id and jcc.environment to the values provided by SnapLogic.
You may also change the entry for the Java heap size (jcc.heap.max_size) to whatever the maximum JVM heap space on the machine should be set to. A reasonable heuristic is to set it to 1GB less than the amount of RAM available on the machine. If you don’t know, leave it as it is; in the future, you may want to check with the SnapLogic team for possible adjustment.To start the on-premises service, type: sudo /opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh start
To verify the Snaplex has started, visit https://elastic.snaplogic.com/sl/dashboard.html#Health. The newly install node should show up in the list of nodes for the Snaplex.
The RPM installation needs to be performed as the root user. The service startup needs to be done as the root user, the JCC process itself runs as the user snapuser. This allows enhanced security by allowing the keys stored in /etc/snaplogic to be protected from access by regular users. If enhanced encryption is not being used, it is possible to enable the service startup to be done directly as snapuser. To do that, perform steps 1 to 4 as above, then do:
- sudo /opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh genkey
- sudo chown -R snapuser:snapuser /etc/snaplogic
- sudo su - snapuser
- /opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh start
The service start and stop can then be done as snapuser without needing root access.
| Note |
|---|
By default, the Snaplex does not automatically restart in the event that the server is rebooted. Your system administrator would need to restart the Snaplex manually per the steps above. Alternatively, you can configure the Snaplex to run as a service to run automatically on startup or reboot. |
To set up a FeedMaster
You can designate a Groundplex as a FeedMaster by setting the Snaplex node types on the Node Properties panel in the Update Snaplex dialog. For complete instructions, see Deploying a FeedMaster Node.
| Info |
|---|
Prior to Fall 2016 (4.7)Setting up a FeedMaster should be the same as a JCC (installing the rpm, copying keys, etc). The only configuration change is to add the following to the global.properties file:
That will switch to the FeedMaster mode instead of JCC. The FeedMaster does not have the same outbound websocket requirement as the JCC, but it still needs to contact elastic.snaplogic.com. |
Import a Certificate to the SnapLogic JCC
While configuring accounts for various Snap Packs, you might encounter the following error message:
"Failed to validate account: Invalid credentials Cause: Could not send Message. (Reason: unable to find valid certification path to requested target; Resolution: Please provide valid credentials.)"
If this error occurs, update the cacert trust store in the SnapLogic JCCs to enable a successful SSL handshake to the endpoint.
Find the trust store at /opt/snaplogic/pkgs/java version/lib/security/cacerts, and confirm that every node in the Groundplex has the certificate imported. Perform the following task (for Linux) to generate and import a self-signed certificate on all the nodes in the Snaplex.
To import a certificate to the SnapLogic JCC:
...
Import the file by using the following command in the JCC node:
| Paste code macro |
|---|
/opt/snaplogic/pkgs/jre1.8.0_45/bin/keytool -import -file <path_to_pem_file_from_step_1> -alias <alias_name_optional> -keystore /opt/snaplogic/pkgs/jre1.8.0_45/lib/security/cacerts -vEnter keystore password: changeit |
| Note |
|---|
This example is an excerpt from 1.8.0_45; the directory path may vary based on the Java installation directory. |
...
Run the following command to list certificates from the cacerts file:
| Paste code macro |
|---|
/opt/snaplogic/pkgs/jre1.8.0_45/bin/keytool -list --keystore /opt/snaplogic/pkgs/jre1.8.0_45/lib/security/cacerts -v+ |
| Note |
|---|
The steps to import the certificate to the JCC can vary based on the certificate format and the OS. |
Automatically Start and Stop an On-premises Snaplex on Linux
You can use either the systemd or init.d utilty to start and stop the Snaplex. Procedures for both are included below. The procedures vary depending on which Linux distribution is installed on the Snaplex host.
Start/Stop the Snaplex by Using Systems
Red Hat-like distributions (Red Hat, Fedora Core, CentOS, and Suse)
To add the Snaplex as a Service:
...
Create the startup service file as follows:
| Code Block |
|---|
touch /etc/systemd/system/snaplogic.service |
Change the permissions on the file as follows:
| Code Block |
|---|
chmod 664 /etc/systemd/system/snaplogic.service |
...
Open the file wiht a text editor. For example, the vim editor:
| Code Block |
|---|
vim /etc/systemd/system/snaplogic.service |
Add the following text to the file:
| Paste code macro |
|---|
[Unit]
Description=SnapLogic JVM
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
ExecStart=/opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh start
ExecReload=/opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh restart
ExecStop=/opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh stop
[Install]
WantedBy=default.target |
...
Enable the service as follows – the service will start automatically when the host reboots.
| Code Block |
|---|
systemctl enable snaplogic.service |
Start the service as follows:
| Code Block |
|---|
systemctl start snaplogic.service |
To delete the Snaplex as a service:
Disable the service as follows:
| Code Block |
|---|
systemctl disable snaplogic.service |
Start/Stop the Snaplex by Using init.d
RedHat-like Distribution (Red Hat, Fedora Core, CentOS, Suse)
To add the Snaplex as a Service:
...
Change directories as follows:
| Code Block |
|---|
cd /etc/init.d/ |
Create a softlink to the jcc.sh file as follows:
| Code Block |
|---|
ln -s /opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh snaplex |
Add the softlink to chkconfig management as follows:
| Code Block |
|---|
chkconfig --add snaplex |
...
It is recommended to reboot the machine to verify whether the Snaplex service is restarting automatically on machine reboot. One issue which has been seen to cause the restart to fail is that the symlink resolution can fail when the machine is starting up. In that case, the Snaplex startup script can be changed to be a file instead of a symlink. To do that, run the following as root user:
| Code Block |
|---|
rm /etc/init.d/snaplex
cp /opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh /etc/init.d/snaplex
echo "export SL_ROOT=/opt/snaplogic" >> /etc/sysconfig/jcc |
To delete the Snaplex as a service:
Remove the service from chkconfig management as follows:
| Code Block |
|---|
chkconfig --del snaplex |
Debian-like Distribution (Debian, Ubuntu)
To add the Snaplex as a Service:
...
Change directories as follows:
| Code Block |
|---|
cd /etc/init.d/ |
Create a soft-link to the jcc.sh file as follows:
| Code Block |
|---|
ln -s /opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh snaplex |
Install the service using update-rc.d. For example:
| Code Block |
|---|
sudo update-rc.d snaplex defaults 98 02 |
| Note | ||
|---|---|---|
It is recommended to reboot the machine to verify whether the Snaplex service is restarting automatically on machine reboot. One issue which has been seen to cause the restart to fail is that the symlink resolution can fail when the machine is starting up. In that case, the Snaplex startup script can be changed to be a file instead of a symlink. To do that, run the following as root user:
On a Debian system, the /etc/sysconfig directory would need to be created if not already present. |
To delete the Snaplex as a Service:
Remove the service from update-rc.d management as follows:
| Code Block |
|---|
update-rc.d -f snaplex remove |
System Limits
Some Linux installations have system ulimit settings set to low values. This can cause errors when running higher pipeline load on the node. The error usually seen is "java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: unable to create new native thread". To fix this, system limits for the Snapuser user need to be increased. The below can be added in the /etc/security/limits.conf to increase the file and process limits.
| Note |
|---|
The JCC process needs to be restarted after the limits are updated. |
| Code Block |
|---|
snapuser soft nproc 8192
snapuser hard nproc 65536
snapuser soft nofile 8192
snapuser hard nofile 65536 |
Configuring Java 11 on Linux
To switch existing nodes to OpenJDK Java 11:
...
Changing the installation folder
If you want to use the/myopt/myroot instead of the /opt/snaplogicas the installation folder and myuser instead of snapuser, do the following steps:
- Run the following commands after installing the RPM/DEB package:
sudo mv /opt/snaplogic /myopt/myrootsudo chown -R myuser /myopt/myroot
- Add the following entities in the
/etc/sysconfig/jccfile. If this file does not exist, create it.export SL_USER=myuserexport SL_ROOT=/myopt/myroot
- Restart the service with the following command:
sudo /myopt/myroot/bin/jcc.sh restart - To make a service using init.d, make the
/etc/init.d/snaplexfile a symlink to the/myopt/myroot/bin/jcc.shfile.
Groundplex on Azure
When running a Linux Groundplex on Azure, the default TCP keep alive settings on Azure have been seen to cause connectivity issues between the Groundplex and the SnapLogic control plane. The workaround is to disable keep alive in the JCC configuration. Add the following in global.properties and restart the JCC using "/opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh restart"
| Code Block |
|---|
jcc.jvm_options = -Dhttp.keepAlive=False -Dcom.ning.http.client.AsyncHttpClientConfig.allowPoolingConnection=false -Dcom.ning.http.client.AsyncHttpClientConfig.allowSslConnectionPool=false |
...
In this article
| Table of Contents | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Install a Snaplex on Linux
This article describes the procedures for installing an on-premise Snaplex in a Linux environment. An on-premise Snaplex is also known as a Groundplex. This document uses the term Groundplex to distinguish this type of Snaplex (on-premise) from a Cloudplex, which SnapLogic manages. However, in command syntax and references to the UI, the generic term Snaplex is used.
Groundplex installation covers the following tasks:
For prerequisites, see Groundplex Deployment Planning.
| Note |
|---|
Linux-based Groundplex Installation Tips
|
Setting up a Groundplex
Log into SnapLogic Manager as an Org admin.
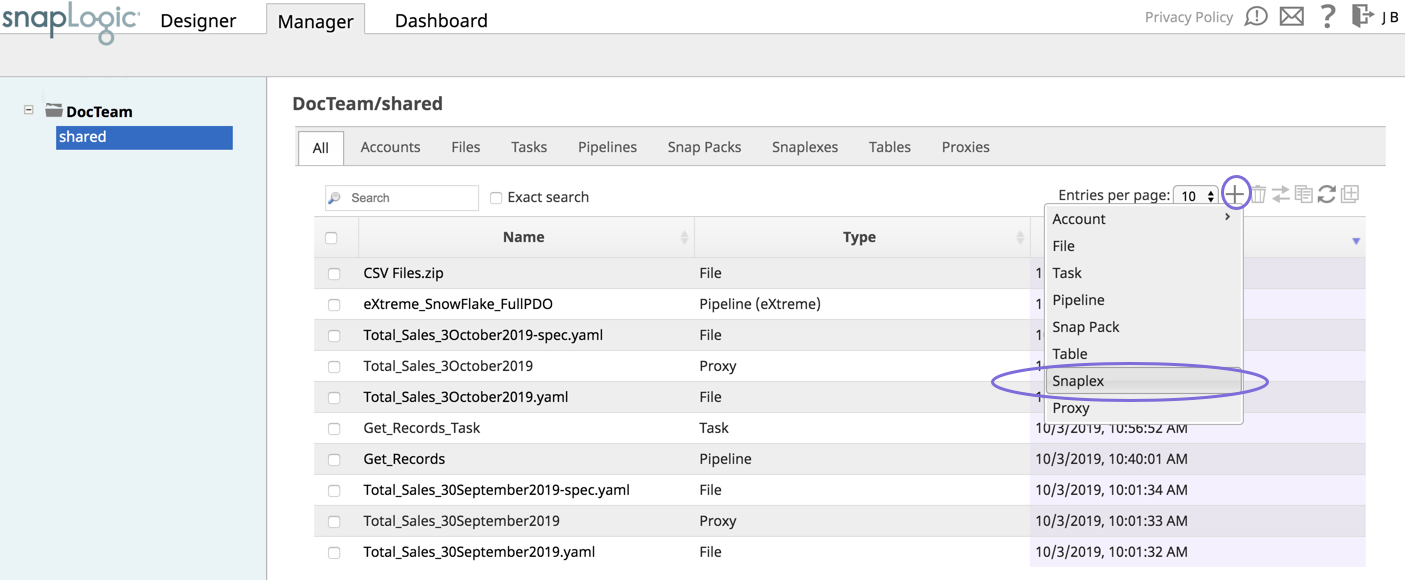
Navigate to the project where you want to create your Groundplex, and perform one of the following steps:
Click the Snaplex tab, then click
 to display the Snaplex dialog.
to display the Snaplex dialog.
OR
Click
 to display the Assets drop-down list, then select Snaplex; the Snaplex dialog appears.
to display the Assets drop-down list, then select Snaplex; the Snaplex dialog appears.
Enter the required information on the Create Snaplex form. Once completed, the Downloads tab on the Snaplex popup appears. The Downloads tab has links to the installer and configuration files.
Download the RPM or DEB-based installer and configuration files onto a Linux machine, where <filename> is the name of the current installer file and
fontconfigandzipare the required dependencies:For CentOS (or Redhat) 6.3 or newer, run the following commands:
$ sudo yum install fontconfig zip$ sudo rpm -i <filename>.rpmFor Ubuntu 14.04 or newer, run the following command:
$ sudo apt-get install fontconfig zip$ sudo dpkg -i <filename>.deb
After the software is installed, place the downloaded configuration file in the
/opt/snaplogic/etcdirectory and make sure the file name ends with.slpropz. Change the .slpropzfile so that snapuser owns it by running the following commands:Code Block $ sudo chown snapuser:snapuser /opt/snaplogic/etc/myplex.slpropz $ sudo chmod 600 /opt/snaplogic/etc/myplex.slpropzTo start the Snaplex service, run:
$ sudo /opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh startTo verify that the Snaplex has started, visit https://elastic.snaplogic.com/sl/dashboard.html#Health. The newly installed Snaplex node should appear in the list of nodes for the Snaplex.
| Note |
|---|
Disable noexec SettingSome Snaps, such as the SQL Bulk Load Snaps, require write and execute permissions to the |
| Info |
|---|
FeedMaster InstallationUltra Pipelines require that you set up a FeedMaster along with the JCC (Java Component Container) nodes in your Groundplex. For details, see Deploying a FeedMaster Node. |
Importing a Certificate to SnapLogic JCC nodes
Importing a certificate is not a requirement. However, we recommend that you import a certificate on your Groundplex nodes for any communication over TLS 1.2.
The following scenarios are two examples of where an SSL certificate is required:
Example 1 - New Groundplex installation with an SSL proxy. Groundplex nodes must communicate with an SSL proxy, so import the proxy self-signed certificate into the Truststore once at the time of installation.
Example 2 - Running a Pipeline where Snaps establish an SSL-encrypted JDBC connection to an endpoint where a Truststore requires the root CA’s certificate. You need to import the root CA’s certificate into the Java Truststore every time the Trustore does not include an endpoint’s CA certificate.
To generate and import a self-signed certificate on all the JCC nodes in the Snaplex:
Obtain the certificate (.pem) file by using SSH.
Import the file by using the following command in the JCC node:
Code Block /opt/snaplogic/pkgs/jre1.8.0_45/bin/keytool -import -file <path_to_pem_file_from_step_1> -alias <alias_name_optional> -keystore /opt/snaplogic/pkgs/jre1.8.0_45/lib/security/cacerts -vEnter keystore password: changeitNote This example is an excerpt from 1.8.0_45; the directory path might vary based on the Java installation directory.
Restart the JCC node process to confirm the import.
Run the following command to list certificates from the CAcerts file:
Code Block /opt/snaplogic/pkgs/jre1.8.0_45/bin/keytool -list --keystore /opt/snaplogic/pkgs/jre1.8.0_45/lib/security/cacerts -v+
| Note |
|---|
The steps to import the certificate to the JCC node can vary based on the certificate format and the OS. |
| Info |
|---|
Invalid Self-signed certificateWhile configuring accounts for various Snap Packs, you might encounter the following error message:
If this error occurs, update the CAcert trust store in the SnapLogic JCC nodes to enable a successful TLS (SSL) handshake to the target endpoint. Find the trust store at |
Automatically Start and Stop a Groundplex on Linux
You can use either the systemd or init.d utility to start and stop the Snaplex. Procedures for both are included below. The procedures vary depending on which Linux distribution is installed on the Snaplex host.
Starting and Stopping the Groundplex by Using the Linux Systems Call
Use this procedure for Red Hat-like Linux distributions such as Red Hat, Fedora CoreOS, CentOS, and SuSE.
To add the Snaplex as a Service:
Log in to the host as a root or sudo user.
Create the startup service file:
Code Block touch /etc/systemd/system/snaplogic.serviceChange the permissions on the file:
Code Block chmod 664 /etc/systemd/system/snaplogic.serviceThis change provides read and write permissions for the owner and group, and read permission for others.
Open the file with a text editor. For example, using a vim editor:
Code Block vim /etc/systemd/system/snaplogic.serviceAdd the following text to the file:
Paste code macro [Unit] Description=SnapLogic JVM After=network.target [Service] Type=forking ExecStart=/opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh start ExecReload=/opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh restart ExecStop=/opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh stop [Install] WantedBy=default.targetSave and exit the file.
Enable the service by running the following command:
Code Block systemctl enable snaplogic.serviceThe service will start automatically when the host reboots.
Start the service:
Code Block systemctl start snaplogic.serviceTo stop the Snaplex as a service, run the following command:
Code Block systemctl disable snaplogic.service
Starting and Stopping the Groundplex by Using the init.d Utility
Use this procedure for Red Hat-like Linux distributions such as Red Hat, Fedora CoreOS, CentOS, and SuSE.
To add the Snaplex as a service:
Login to the Linux machine as root.
Change directories:
Code Block cd /etc/init.d/Create a softlink to the
jcc.shfile:Code Block ln -s /opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh snaplexAdd the softlink to
chkconfigmanagement:Code Block chkconfig --add snaplex
| Note | ||
|---|---|---|
We recommend that you reboot the machine to verify if the Snaplex service is restarting automatically on machine reboot. Under some conditions, the symlink resolution might fail when the machine is starting up. In this case, you can change the Snaplex startup script to be a file instead of a symlink. Run the following commands a root user:
|
To delete the Snaplex as a service, remove the service from the chkconfig management:
| Code Block |
|---|
chkconfig --del snaplex |
Debian-like Distribution (Debian and Ubuntu)
To add the Snaplex as a Service:
Log in to the Linux machine as root.
Change directories:
Code Block cd /etc/init.d/Create a soft-link to the
jcc.shfile:Code Block ln -s /opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh snaplexInstall the service using
update-rc.d. For example:Code Block sudo update-rc.d snaplex defaults 98 02Note title Troubleshooting if the machine reboot fails We recommend that you reboot the machine to verify whether the Snaplex service is restarting automatically on machine reboot. Under some conditions, the symlink resolution might fail when the machine is starting up. In this case, you can change the Snaplex startup script to be a file instead of a symlink. Run the following commands a root user:
Code Block rm /etc/init.d/snaplex cp /opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh /etc/init.d/snaplex echo "export SL_ROOT=/opt/snaplogic" >> /etc/sysconfig/jccOn a Debian system, the
/etc/sysconfigdirectory would need to be created if not already present.To stop the Snaplex as a Service, remove the service from
update-rc.dmanagement:Code Block update-rc.d -f snaplex remove
Manage disk volumes for Groundplex nodes
To address issues that cause disk full errors and to ensure smoother operations of the systems that affect the stability of the Groundplex, you need to have separate mounts on Groundplex nodes. Follow the steps suggested below to create two separate disk volumes on the JCC nodes.
| Note |
|---|
The commands and the steps specified are validated on *nix (RHEL based systems). |
The JCC nodes are equipped with two separate disk volumes to ensure that the operating system and pipeline execution workspace remain segregated.
The JCC is installed in
/(root)volume, and the workspace is separated in the bind mounts.The second disk volume is mounted on
/workspace,and bind mount directories are created.Code Block sudo su mkdir /workspace
Create subdirectories in
/workspaceand/opt/snaplogic/rundirectories using the commands specified below:
| Code Block |
|---|
mount /dev/nvme2n1 /dev/workspace #(replace nvme2n1 with the device name)
mkdir -p /workspace/{fs,broker,tmp}
mkdir -p /opt/snaplogic/run/{fs, broker}
chown -R snapuser:snapuser /workspace && chmod -R 0755 /workspace |
Create the bind mounts using the commands specified below:
| Code Block |
|---|
mount --bind /workspace/fs /opt/snaplogic/run/fs
mount --bind /workspace/broker /opt/snaplogic/run/broker
mount --bind /workspace/tmp /tmp |
Workspace | Bind Mount | Ownership | Permissions |
|---|---|---|---|
/workspace/fs | /opt/snaplogic/run/fs | snapuser:snapuser | 0775 |
/workspace/broker | /opt/snaplogic/run/broker | snapuser:snapuser | 0775 |
/workspace/tmp | /tmp | snapuser:snapuser | 0775 |
...
| Info |
|---|
To ensure that the changes remain in effect after system reboots, it is necessary to create entries in |
For Example:
| Code Block |
|---|
/dev/nvme1n1 /workspace xfs noatime 0 0
/workspace/fs /opt/snaplogic/run/fs none bind 0 0
/workspace/broker /opt/snaplogic/run/broker none bind 0 0
/workspace/tmp /tmp none bind 0 0 |
Configure Java 11 on Linux
The JRE is bundled with the Snaplex installer. While a Snaplex auto upgrade updates the SnapLogic binaries in the installed Snaplex, the JRE version is not automatically updated. You must manage the JRE versions of your Snaplex.
| Info |
|---|
We recommend installing the latest JRE 11 version available at https://adoptium.net/temurin/releases/?version=11. |
To update your JCC nodes to OpenJDK Java 11:
Stop the existing JCC node by running the following command:
$ sudo /opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh stopDownload the new Snaplex installer and install the Groundplex, running the RPM, DEB, or Docker installers as appropriate.
For RPM systems, run the following command:
$ rpm -U snaplogic-snaplex.rpmFor DEB systems, run the following command:
$ dpkg -i snaplogic-snaplex.debFor Docker, stop the existing container and start a new container using the latest image.
Add the following entry to the
/etc/sysconfig/jccdirectory. You must create this directory and file if neither are present.export SL_JAVA_HOME=/opt/snaplogic/pkgs/jdk-11.0.12+7-jre/Start the JCC node by running the following command:
$ sudo /opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh start.
Older Versions of JRE and TLS
JRE versions prior to 11.0.8 have issues connecting to TLS 1.3 endpoints. We recommend using a newer JRE version.
| Note |
|---|
If you are running with 11.0.10 onwards, endpoint connections to TLS 1.0 and 1.1 are disabled by default. We recommend that you update the endpoint to support TLS 1.2 or later, for security. |
Renabling Support for Older Versions
If updating the TLS endpoint is not possible, then the Snaplex JRE can be updated to re-enable support for older TLS versions by doing these steps:
Open the jre/conf/security/java.security file in the JRE installation /opt/snaplogic/pkgs folder.
Change the jdk.tls.disabledAlgorithms configuration property by removing TLSv1, TLSv1.1.
Restart the Snaplex to re-enable support for TLS 1.0 and 1.1.
Changing the Installation Folder
If you want to use the/myopt/myroot instead of the /opt/snaplogic as the installation folder and myuser instead of snapuser, perform the following steps:
Run the following commands after installing the RPM/DEB package:
$ sudo mv /opt/snaplogic /myopt/myroot$ sudo chown -R myuser /myopt/myroot
Add the following properties in the
/etc/sysconfig/jccfile. If this file does not exist, create it.export SL_USER=myuserexport SL_ROOT=/myopt/myroot
Restart the service with the following command:
$ sudo /myopt/myroot/bin/jcc.sh restartTo make a service using init.d, make the
/etc/init.d/snaplexfile a symlink to the/myopt/myroot/bin/jcc.shfile.
Uninstalling the SnapLogic RPM from your environment
To uninstall the SnapLogic Linux-based package from your environment:
Remove all content from the /etc/snaplogic and /opt/snaplogic folders by running the following commands:
$ rpm -qa | grep snaplogic$ sudo rpm -e snaplogic-sidekick-4.main_9292-1.x86_64$ sudo rm -rf /opt/snaplogic$ sudo rm -rf /etc/snaplogic
Verify that the packages were deleted from the /etc/snaplogic and /opt/snaplogic folders.
| Note |
|---|
Enhanced Encryption KeysWhen using Enhanced Account Encryption, the private key for the Org is stored in the /etc/snaplogic directory. We recommend that you also maintain a copy of the private key elsewhere. If the private keys are not available, then Accounts created in SnapLogic cannot be used. |
System Limits
Some Linux installations have system ulimit settings that are set to lower values. This low setting can cause errors when running higher pipeline loads on the Groundplex JCC node, such as, java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: unable to create new native thread.
To fix this issue, you need to increase the system limits for the Snapuser user. You can add the following in the /etc/security/limits.conf folder to increase the file and process limits.
| Note |
|---|
The JCC process needs to be restarted after the limits are updated. |
| Code Block |
|---|
snapuser soft nproc 8192
snapuser hard nproc 65536
snapuser soft nofile 8192
snapuser hard nofile 65536 |
| Info |
|---|
Setting limits for Docker ContainersFor Docker deployments, you may not be able to set these limits because of permissions issues with the |
...
Related content
Video: Installing a Groundplex through a Debian-based Linux Distribution