...
On this Page
| Table of Contents | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
Snap type:
Write
...
Description:
This Snap executes an SQL Server bulk load. The Snap uses the bcp utility program internally to perform the bulk load action. The input data is first written to a temporary data file, then the bcp utility program loads the data from the data file into the target table.
- Expected upstream Snaps: The columns of the target table need to be mapped upstream using a Mapper Snap. The Mapper Snap will provide the target schema, which reflects the schema of the target table.
- Expected downstream Snaps: None.
- Expected input: Document that needs to be loaded.
- Expected output: Document which represents the result of the bulk load operation.
Table Creation
If the table does not exist when the Snap tries to do the load, and the Create table property is set, the table will be created with the columns and data types required to hold the values in the first input document. If you would like the table to be created with the same schema as a source table, you can connect the second output view of a Select Snap to the second input view of this Snap. The extra view in the Select and Bulk Load Snaps are used to pass metadata about the table, effectively allowing you to replicate a table from one database to another.
The table metadata document that is read in by the second input view contains a dump of the JDBC DatabaseMetaData class. The document can be manipulated to affect the CREATE TABLE statement that is generated by this Snap. For example, to rename the name column to full_name, you can use a Mapper (Data) Snap that sets the path $.columns. Name.COLUMN_NAME to full_name. The document contains the following fields:
columns - Contains the result of the getColumns() method with each column as a separate field in the object. Changing the COLUMN_NAME value will change the name of the column in the created table. Note that if you change a column name, you do not need to change the name of the field in the row input documents. The Snap will automatically translate from the original name to the new name. For example, when changing from name to full_name, the name field in the input document will be put into the "full_name" column. You can also drop a column by setting the COLUMN_NAME value to null or the empty string. The other fields of interest in the column definition are:
TYPE_NAME - The type to use for the column. If this type is not known to the database, the DATA_TYPE field will be used as a fallback. If you want to explicitly set a type for a column, set the DATA_TYPE field.
_SL_PRECISION - Contains the result of the getPrecision() method. This field is used along with the _SL_SCALE field for setting the precision and scale of a DECIMAL or NUMERIC field.
_SL_SCALE - Contains the result of the getScale() method. This field is used along with the _SL_PRECISION field for setting the precision and scale of a DECIMAL or NUMERIC field.
primaryKeyColumns - Contains the result of the getPrimaryKeys() method with each column as a separate field in the object.
declaration - Contains the result of the getTables() method for this table. The values in this object are just informational at the moment. The target table name is taken from the Snap property.
importedKeys - Contains the foreign key information from the getImportedKeys() method. The generated CREATE TABLE statement will include FOREIGN KEY constraints based on the contents of this object. Note that you will need to change the PKTABLE_NAME value if you changed the name of the referenced table when replicating it.
indexInfo - Contains the result of the getIndexInfo() method for this table with each index as a separate field in the object. Any UNIQUE indexes in here will be included in the CREATE TABLE statement generated by this Snap.
| Note |
|---|
The Snap will not automatically fix some errors encountered during table creation since they may require user intervention to resolve correctly. For example, if the source table contains a column with a type that does not have a direct mapping in the target database, the Snap will fail to execute. You will then need to add a Mapper (Data) Snap to change the metadata document to explicitly set the values needed to produce a valid CREATE TABLE statement. SQL Server BCP program only accepts date time values in format YYYY-MM-dd HH:mm: ss, thus SQL Server Bulk Load Snap only accepts two types of data as the input of a DATETIME column: |
- A Joda DateTime object. For example, a Joda DateTime object can be created with expression Date.now() in Mapper Snap.
- A plain string in the format: YYYY-MM-dd HH: mm:ss. Example: 2016-10-22 11:11:11.
SQL Server Bulk Load Snap does not accept the results by the DateTime string from the expression Date.toLocaleDateTimeString().
...
The BCP utility must be installed on the Groundplex nodes on which you want to execute this Snap. To install the BCP utility on a Groundplex:
...
...
To verify BCP installation, enter bcp on the terminal or the command line console and press Enter.
| Paste code macro |
|---|
/u01/sqlncli> bcp |
The output should look similar to the following. These are the command-line options that can be used with the BCP utility. If you see this output, it means that the BCP utility is installed and ready for use.
| Paste code macro |
|---|
[-a packet_size]
[-b batch_size]
[-c]
[-C { ACP | OEM | RAW | code_page } ]
[-d database_name]
[-e err_file]
[-E]
[-f format_file]
[-F first_row]
[-G Azure Active Directory Authentication]
[-h"hint [,...n]"]
[-i input_file]
[-k]
[-K application_intent]
[-l login_timeout]
[-L last_row]
[-m max_errors]
[-n]
[-N]
[-o output_file]
[-P password]
[-q]
[-r row_term]
[-R]
[-S [server_name[\instance_name]]
[-t field_term]
[-T]
[-U login_id]
[-v]
[-V (80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 | 130 ) ]
[-w]
[-x] |
...
When using a Windows host as a SnapLogic node with the service installed (jcc.bat install_service), ensure that the service account used on the service credentials has access to the database for the bulk copy program utility (BCP) to work. Removing the database permissions result in the error, Unable to invoke BCP". However, you might still be able to execute the bcp -v command on the command line outside the Snaplogic node, despite the lack of service account database permissions.
...
Before the 4.33patches21119 release, empty strings and null values were treated as null when loaded into the SQL server. However, starting from the 433patches21119 release, data in the format of an empty string inserted into a string-based column is stored as an empty string in the SQL server. Similarly, inserting null data into a string-based column is stored as null in the SQL server.
To ensure consistent handling of both empty strings and null values, we recommend you to update the data to match how you would like it to be represented in the database before performing a bulk load operation.
...
Problem: Some characters appear as junk values after bulk load.
Reason: The Snaplex uses character sets defined in the OS on which they are installed. Due to this, any unrecognized character set is not supported by the Snaplex as well. As a result, such characters in the data set are represented as junk values in the database after a bulk load operation.
Resolution: This problem can be resolved by editing the bcp.bat file to accept custom characters. And using the absolute path to this bcp file in the BCP absolute path property. The bcp.bat file must contain the following:
| Paste code macro |
|---|
bcp.exe %* -C 1252 |
| Note |
|---|
This resolution is applicable only to Windows-based Snaplexes. |
...
Does not work in Ultra Pipelines.
...
This Snap uses account references created on the Accounts page of SnapLogic Manager to handle access to this endpoint. See Configuring SQL Server Accounts for information on setting up this type of account.
...
| Input | This Snap has one document input view by default. A second view can be added for metadata for the table as a document so that the target absent table can be created in the database with a similar schema as the source table. This schema is usually from the second output of a database Select Snap. If the schema is from a different database, there is no guarantee that all the data types would be properly handled. |
|---|---|
| Output | This Snap has at most one document output view. |
| Error | This Snap has at most one document error view and produces zero or more documents in the view. |
...
Settings
Label*
...
Schema Name
...
Specify the database schema name. In case it is not defined, then the suggestion for the Table Name will retrieve all tables names of all schemas. The property is suggestible and will retrieve available database schemas during suggest values.
| Note |
|---|
The values can be passed using the pipeline parameters but not the upstream parameter. |
Example: SYS
Default value: None
...
Table Name*
...
Specify the table on which to execute the bulk load operation.
| Note |
|---|
The values can be passed using the pipeline parameters but not the upstream parameter. |
Example: people
Default value: None
| Note |
|---|
| Currently, the BCP utility in the Linux environment has a limitation while processing the table names. When loading the data into a selected table and If the table name contains the characters '$%' or '!$', the combination works fine, however, BCP does not support if the table name contains the characters vice-a-versa as'%$' and '$!'. |
Examples:
Supported by BCP: "dbo"."sqldemo#^&$%"
Not supported by BCP: "dbo"."sqldemo#^&%$"
Create table if not present
...
Select this check box to enable the Snap to automatically create a table if a table does not exist.
| Note |
|---|
The data types for the columns in the new table depend on the data types coming from the upstream Snap. If a second input view exists, the Snap reads and uses the data types for the columns from this input view. |
Default value: Not selected
...
BCP absolute path
Specify the absolute path of the bcp utility program in JCC's file system. If empty, the Snap looks for it in JCC's environment variable PATH.
Example: C:\bcp.bat
Default value: [None]
| Note |
|---|
bcp.bat should include the ".exe" extension to ensure the executable is actually referenced. |
Handling Unrecognized Character sets in the Data set
Since the Snaplex uses the OS's default character set, it cannot recognize characters in other languages. Due to this, unrecognized characters in the data set are replaced with junk values when performing bulk load operations. To mitigate this, create a bcp.bat file and include the following line:
| Paste code macro |
|---|
bcp.exe %* -C 1252 |
Use the path to this bcp.bat file in the BCP absolute path.
| Note |
|---|
This is only applicable to Windows-based Snaplexes. |
Maximum error count*
Specify the maximum number of rows which can fail before the bulk load operation is stopped.
Default value: 10
...
The number of records batched per request. If the input has 10,000 records and the batch size is set to 100, the total number of requests batched would be 100.
Minimum value: 1
Default Value: [None]
Example: 1000
...
| Multiexcerpt include macro | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
| Multiexcerpt include macro | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
Example
...
In this article
| Table of Contents | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Overview
You can use this Snap to execute an SQL Server bulk load. This Snap uses the bcp utility program internally to perform the bulk load action. The input data is first written to a temporary data file, and then the bcp utility program loads the data from the data file into the target table.
...
Snap Type
The SQL Server - Bulk Load Snap is a Write-type Snap that inserts bulk data in one request.
Prerequisites
The BCP utility must be installed on the Groundplex nodes where you want to execute this Snap. To install the BCP utility on a Groundplex:
Download and install the BCP Utility in your Windows or Linux environment. For details on doing so, use the following links:
Verify that you can run the
bcpcommand. To verify BCP installation, enterbcpon the terminal or the command line console and press Enter.Paste code macro /u01/sqlncli> bcpThe output should look similar to the following. These are the command-line options that can be used with the BCP utility. If you see this output, it indicates that the BCP utility is installed and ready for use.
Paste code macro [-a packet_size] [-b batch_size] [-c] [-C { ACP | OEM | RAW | code_page } ] [-d database_name] [-e err_file] [-E] [-f format_file] [-F first_row] [-G Azure Active Directory Authentication] [-h"hint [,...n]"] [-i input_file] [-k] [-K application_intent] [-l login_timeout] [-L last_row] [-m max_errors] [-n] [-N] [-o output_file] [-P password] [-q] [-r row_term] [-R] [-S [server_name[\instance_name]] [-t field_term] [-T] [-U login_id] [-v] [-V (80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 | 130 ) ] [-w] [-x]Ensure the path to the
bcpcommand is correctly provided in the Snap.
When using a Windows host as a SnapLogic node with the service installed (jcc.bat install_service), ensure that the service account used on the service credentials can access the database for the bulk copy program utility (BCP) to work. Removing the database permissions result in the error, Unable to invoke BCP". However, you might still be able to execute the bcp -v command on the command line outside the Snaplogic node, despite the lack of service account database permissions.
Support for Ultra Pipelines
Does not work in Ultra Pipelines.
Behavior Change
Before the
4.33patches21119release, empty strings and null values were treated as null when loaded into the SQL server. However, starting from the433patches21119release, data in the format of an empty string inserted into a string-based column is stored as an empty string in the SQL server. Similarly, inserting null data into a string-based column is stored as null in the SQL server.
To ensure consistent handling of both empty strings and null values, we recommend you to update the data to match how you would like it to be represented in the database before performing a bulk load operation.
Known Issues
The SQL Server - Bulk Load Snap returns 0 rows copied for tables containing spatial-type columns.
Limitations
None.
Snap Views
Type | Format | Number of Views | Examples of Upstream and Downstream Snaps | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Input | Document |
|
| By default, this Snap has one document input view by default. A second view can be added for metadata for the table as a document so that the target absent table can be created in the database with a similar schema as the source table. This schema is usually from the second output of a database Select Snap. If the schema is from a different database, there is no guarantee that all the data types would be properly handled. The target table's columns need to be mapped upstream using a Mapper Snap. The Mapper Snap will provide the target schema, which reflects the target table's schema. Learn more: SQL Server - Bulk Load | Table Creation |
Output | Document |
|
| A document that represents the result of the bulk load operation. |
Error | Error handling is a generic way to handle errors without losing data or failing the Snap execution. You can handle the errors that the Snap might encounter when running the Pipeline by choosing one of the following options from the When errors occur list under the Views tab:
Learn more about Error handling in Pipelines. | |||
Snap Settings
| Info |
|---|
|
Field Name | Field Type | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Label* Default Value: Snowflake - Bulk Load | String | Specify a unique name for the Snap. | ||
Schema Name Default Value: N/A | String/Expression/Suggestion | Specify the database schema name. In case it is not defined, then the suggestion for the Table Name will retrieve all tables names of all schemas. The property is suggestible and will retrieve available database schemas during suggest values. You can pass the values using the pipeline parameters but not the upstream parameter. | ||
Table Name* Default Value: N/A | String/Expression/Suggestion | Specify the table on which to execute the bulk load operation.
Examples: Supported by BCP: "dbo"."sqldemo#^&$%" Not supported by BCP: "dbo"."sqldemo#^&%$" | ||
Create table if not present Default Value: Deselected | Checkbox | Select this checkbox to enable the Snap to automatically create a table if a table does not exist. The data types for the columns in the new table depend on the data types from the upstream Snap. If a second input view exists, the Snap reads and uses the data types for the columns from this input view. Learn more: SQL Server - Bulk Load | Table Creation | ||
BCP absolute path Default Value: N/A | String | Specify the absolute path of the bcp utility program in JCC's file system. If empty, the Snap looks for it in JCC's environment variable PATH. bcp.bat should include the ".exe" extension to ensure the executable is actually referenced. Handling Unrecognized Character sets in the Data set. As the Snaplex uses the OS's default character set, it cannot recognize characters in other languages. Due to this, unrecognized characters in the data set are replaced with junk values when performing bulk load operations. To mitigate this, create a bcp.bat file and include the following line:
Use the path to this bcp.bat file in the BCP absolute path. This is only applicable to Windows-based Snaplexes. | ||
Maximum error count* Default Value: 10 | Integer | Specify the maximum number of rows which can fail before the bulk load operation is stopped. | ||
Batch size Default Value: N/A | Integer/Expression | Specify the number of records batched per request. If the input has 10,000 records and the batch size is set to 100, the total number of requests batched would be 100. Minimum Value: 1 | ||
Snap Execution Default Value: Execute only | Dropdown list | Select one of the three modes in which the Snap executes. Available options are:
|
If the Auto commit option is enabled for an account and a downstream Snap relies on data processed by an upstream Database Bulk Load Snap, it may be necessary to introduce a delay to ensure the data is available. In such scenarios, you can use the Script Snap to add a delay between the processing steps. For instance, when performing sequential create, insert, and delete operations in a pipeline, using a Script Snap allows you to introduce a delay between the insert and delete functions. Without this delay, it is possible that the delete function could be triggered before the records are inserted into the table.
Table Creation
When attempting to load data, if the specified table does not exist and the Create table if not present checkbox is selected, the Snap creates the table along with the necessary columns and data types to accommodate the values in the first input document. If you want the table to have the same structure as a source table, you can connect the second output view of a Select Snap to the second input view of this Snap. The additional view in the Select and Bulk Load Snaps transmits metadata about the table, enabling the replication of a table from one database to another.
The metadata document, read by the second input view, contains a snapshot of the JDBC DatabaseMetaData class. By manipulating this document, you can modify the generated ‘CREATE TABLE' statement. For instance, if you wish to rename the 'name' column to 'full_name,’ you can utilize a Mapper (Data) Snap that sets the path '$.columns.Name.COLUMN_NAME' to 'full_name'. The document encompasses the following fields:
columns - Contains the result of the getColumns() method with each column as a separate field in the object. Changing the COLUMN_NAME value will change the column's name in the created table. Note that you do not need to change the field name in the row input documents if you change a column name. The Snap automatically translates from the original name to the new name. For example, when changing from
nametofull_name, the name field in the input document will be put into the"full_name"column. You can also drop a column by setting the COLUMN_NAME value to null or the empty string. The other fields of interest in the column definition are:TYPE_NAME - The type to use for the column. If this type is not known to the database, the DATA_TYPE field will be used as a fallback. If you want to explicitly set a type for a column, set the DATA_TYPE field.
_SL_PRECISION - Contains the result of the getPrecision() method. This field is used along with the _SL_SCALE field for setting the precision and scale of a DECIMAL or NUMERIC field.
_SL_SCALE - Contains the result of the getScale() method. This field is used along with the _SL_PRECISION field for setting the precision and scale of a DECIMAL or NUMERIC field.
primaryKeyColumns - Contains the result of the getPrimaryKeys() method with each column as a separate field in the object.
declaration - Contains the result of the getTables() method for this table. The values in this object are just informational at the moment. The target table name is taken from the Snap property.
importedKeys - Contains the foreign key information from the getImportedKeys() method. The generated CREATE TABLE statement will include FOREIGN KEY constraints based on the contents of this object. Note that you will need to change the PKTABLE_NAME value if you changed the name of the referenced table when replicating it.
indexInfo - Contains the result of the getIndexInfo() method for this table with each index as a separate field in the object. Any UNIQUE indexes in here will be included in the CREATE TABLE statement generated by this Snap.
| Info |
|---|
The Snap will not automatically fix some errors encountered during table creation since they may require user intervention to resolve correctly. For example, if the source table contains a column with a type without direct mapping in the target database, the Snap fails to execute. You will then need to add a Mapper (Data) Snap to change the metadata document to explicitly set the values needed to produce a valid CREATE TABLE statement. SQL Server BCP program only accepts date time values in format YYYY-MM-dd HH:mm: ss, thus SQL Server Bulk Load Snap only accepts two types of data as the input of a DATETIME column:
SQL Server Bulk Load Snap does not accept the results by the DateTime string from the expression Date.toLocaleDateTimeString(). |
Troubleshooting
Error | Reason | Resolution | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Some characters appear as junk values after bulk load. | The Snaplex uses character sets defined in the OS on which they are installed. Due to this, any unrecognized character set is not supported by the Snaplex as well. As a result, such characters in the data set are represented as junk values in the database after a bulk load operation. | This problem can be resolved by editing the bcp.bat file to accept custom characters. And using the absolute path to this bcp file in the BCP absolute path property. The bcp.bat file must contain the following:
|
Example
This example pipeline demonstrates how to load data from table bulk_test_source to table bulk_test_target with SQL Server Bulk Load Snap.
...
...
...
Step 1: Configure the SQL Server Select Snap
...
as follows to get records in the table bulk_test_source and
...
pass them to the SQL Server Bulk Load Snap
...
.
...
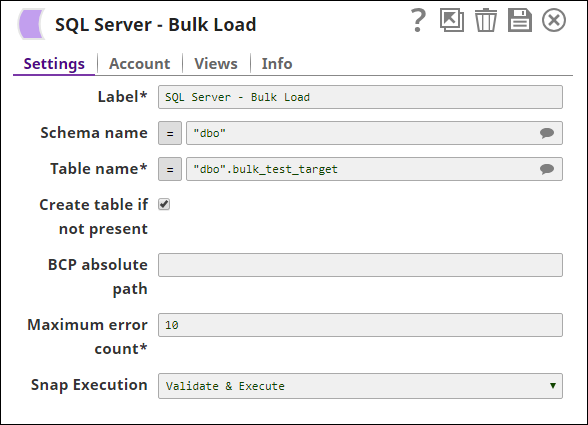
Step 2: Configure the SQL Server Bulk Load Snap
...
as follows to load inputs to the table bulk_test
...
...
_target. On successful validation, the SQL Server Bulk Load Snap
...
output displays the result of the tables copied.
Snap Pack History
| Expand | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
.png?version=1&modificationDate=1489654755277&cacheVersion=1&api=v2&width=540)
.png?version=1&modificationDate=1489654859797&cacheVersion=1&api=v2)