In this Article
...
- The CPU Time displays how much the CPU is consumed.
- The Wait Time displays how much time the Snap took waiting for input/output or internal processes.
The Memory Allocated displays the number of bytes that are allocated by the Snap.
For example, a REST GET Snap that is configured to send a GET request to "Note This number does not reflect the amount of memory that was freed, and so it does not represent the peak memory usage of the Snap. Therefore, you should not necessarily rely on using this metric to estimate the required size of a Snaplex node. Rather, this number provides an insight into how much memory had to be allocated to process all of the documents.
For example, if the total allocated was 5MB and the Snap processed 32 documents, then Snap allocated roughly 164KB per document. When combined with the other statistics, this number can help you identify the potential causes of performance issues.
http://api.example.com/"has bars for "api.example.com:80". The bars represent the total number of bytes sent to and received by the remote host. If the Snap connects to multiple hosts, (because the target URLs come from the input docs), each host should have their own bar charts. Hosts are separated out in the display since the network behavior may be different across hosts, so displaying the overall total does not necessarily summarize usage.
Info title Caveats for Network Usage Statistics During validation, the preview data that is written to SnapLogic cloud servers may also appear in these statistics. During a regular execution, that transfer is not recorded.
- Only Linux nodes are supported right now (Windows is not supported).
Snaps that use an external program to transfer data, like some database bulk loaders, do not show any network usage.
...
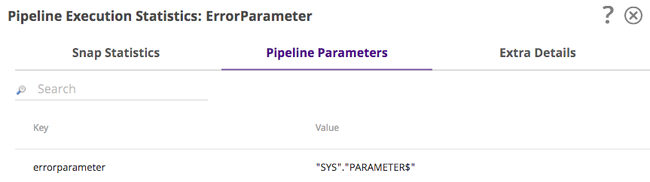
While this tab appears for all Pipelines, it only displays information for those Pipelines that are run either by a task or by another Snap (such as the Pipeline Execute Snap). Values are returned only for those parameters that have Capture selected in the Pipeline Properties dialog.
Extra Details
The Extra Details tabs provides basic information about the Pipeline and its execution, including details about Pipeline type and run policy.
...
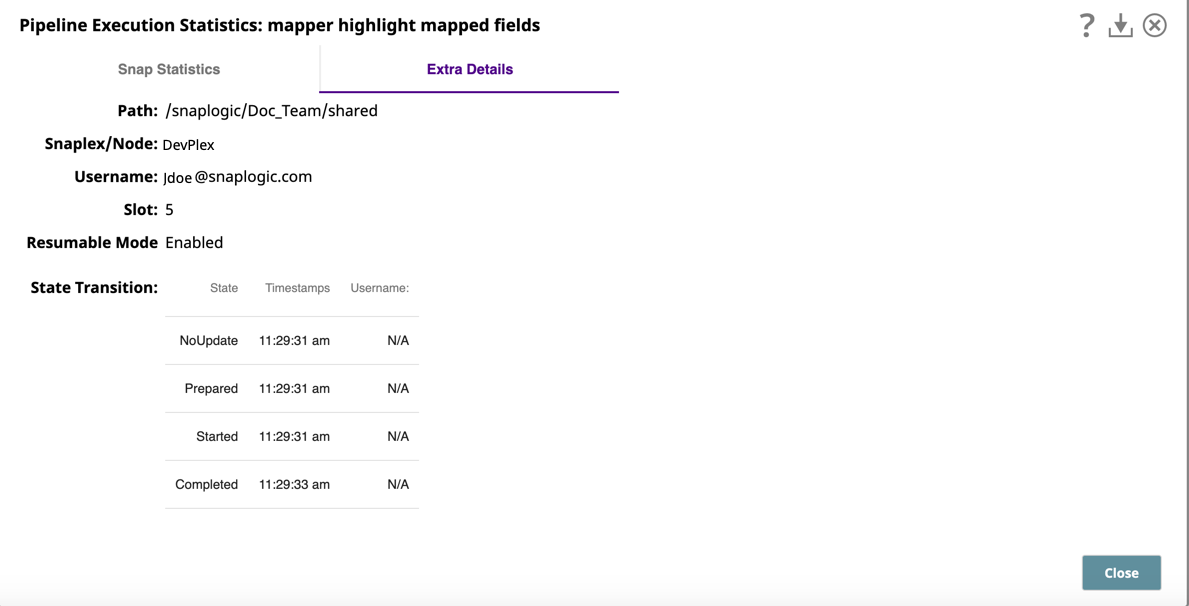
In the following image, the Extra Details tab displays information about a Resumable Pipeline.
The Extra Details tab provides additional information about the Pipeline run, including:
- Path to the pipeline.
- The Snaplex node used to run the Pipeline.
- The username of the person who ran the Pipeline.
- The Slot Count. See Maximum Slots on the Node Properties tab on the Update Snaplex dialog.
- Resumable Mode. Displays Enabled if the Pipeline is resumable. If not, the status is Disabled.
- The Task name. The name of the Task (if applicable).
- The Max-In-Flight value. The maximum number of documents that can be processed by an Ultra task instance at any one time.
- The Close reason for when an Ultra task goes into the Completed state.
- Reference no longer exists or is inaccessible
- Host Snaplex node restarted
- The Ultra task has been updated
- The task is no longer active
- Closing Ultra Pipeline instance to balance instances across the Snaplex
- Ultra Requests. These statistics are displayed during the processing of documents.
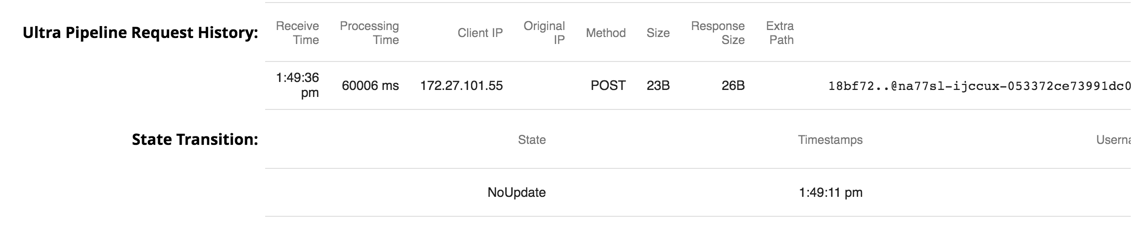
- Receive Time. The time that the request is received.
- Client IP. The IP address that the FeedMaster sees when the load balancer forwards a request.
- Original IP. The IP address of the external client that the load balancer, when configured to do so, forwards to the FeedMaster.
- Method. The underlying HTTP method of the request.
- Size. The size of the document payload in bytes.
- Extra Path. The path of the Ultra Pipeline task.
The Request History for Ultra tasks. These statistics display the last 100 documents processed in the Ultra Pipeline.
Info title Pipeline Monitoring API Available You can also collect the Ultra history statistics using the Pipeline Monitoring API.
Some statistics in common with those from the Ultra Request report are identical.Receive Time. The time that the request is received.
Processing Time. The total time for the Ultra Pipeline to process the documents associated with this request. For example, if the input document is copied, this time includes all the time needed to process each copy.
- Client IP. The IP address that the FeedMaster sees when the load balancer forwards a request.
- Original IP. The IP address of the external client that the load balancer, when configured to do so, forwards to the FeedMaster.
- Method. The underlying HTTP method of the request.
- Size. The size of the document payload in bytes.
- Response Size. The size of the document in bytes payload inside the response.
Extra Path. The path of the Ultra Pipeline task.
State Transition. These statistics display when multiple runs of an Ultra Pipeline occur.
State. Current state of the Ultra Pipeline.
Timestamp. The time that the most recent Ultra Pipeline execution occurred.
Username. The username of the person invoking the Ultra Pipeline.