In this article
Overview
A PIVOT operation converts unique values in a specified column into their own individual columns. You can then specify a pivot column and perform aggregate calculations such as sum, count, and average on the values in the column. You can use this Snap to add the PIVOT operation to an incoming SQL query for Snowflake, Redshift, Azure Synapse, Databricks Lakehouse Platform (DLP), and BigQuery databases. Azure Synapse and Databricks Lakehouse Platform (DLP) do not support Pivot/Unpivot operations natively, but this Snap supports them internally through a series of rewrite mechanisms.
A typical use of this Snap is categorizing table data, and calculating the performance of sales professionals.
Prerequisites
None.
Limitation
Known Issues
Snap Input and Output
| Input/Output | Type of View | Number of Views | Examples of Upstream and Downstream Snaps | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Document |
|
| The SQL query in which you want to add the PIVOT function. Typically, it would be a SELECT query reading the source table. |
| Output | Document |
|
| The incoming SQL query with the PIVOT function. |
Snap Settings
You can use the SQL Expressions and Functions supported for ELT to define your Snap or Account settings with the Expression symbol = enabled, where available. This list is common to all target CDWs supported. You can also use other expressions/functions that your target CDW supports. |
| Parameter Name | Data Type | Description | Default Value | Example | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Label | String | ELT Pivot | Pivot Student Data | ||
| Get preview data | Check box | Not selected | Selected | ||
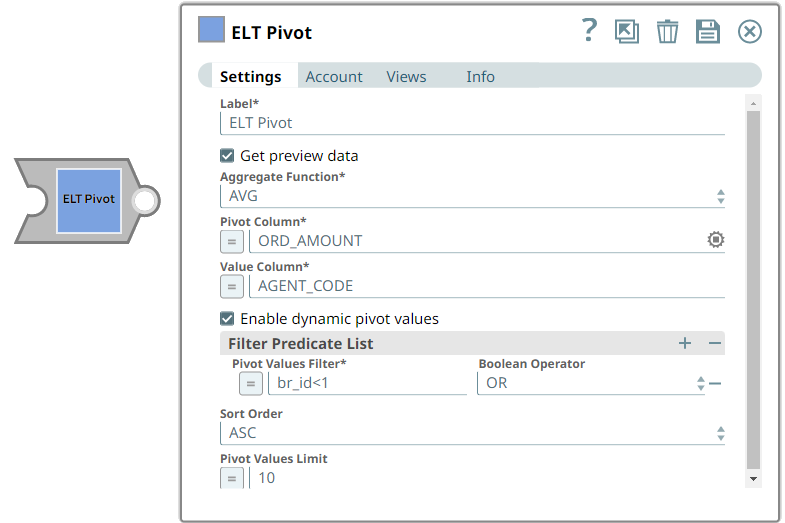
| Aggregate Function | String | Select the aggregate function to apply to the pivot column. Available options are:
| AVG | SUM | |
| Pivot Column | String | Required. Specify the column in the source table upon which to apply the aggregate functions. | N/A | ORDER_AMOUNT | |
| Value Column | String | Required. Specify the column to calculate the aggregate on the pivot columns. | N/A | AGENT_CODE | |
| Pivot Value List | Required. This field set enables you to specify the values in the Value Column for which you want to see the aggregated values. Specify each value in a separate row. Click + to add a new row. This field set consists of the following field:
| ||||
| Pivot Value | String | Required. Enter the list of unique values in the Value Column to include in the output. The column contains null values if the specified value here does not have any records in the input table. | N/A | A002 A004 | |
Troubleshooting
| SQL Error: An object or column name is missing or empty for SELECT INTO statements. | Incorrect syntax near the keyword 'AS'. | Verify each column has a name. For other statements, look for empty alias names. Aliases defined as "" or [] are not allowed. Change the alias to a valid name. Note: the same empty value like '' works fine on SF and DLP. |
Examples
Analyzing Sales Agent's Performance
We want to analyze the sales made by two agents in a company. We can construct a query that reads the source table, filters the sales records of these two agents using a WHERE clause, and then add aggregate functions grouped by the agent's identifier. However, this approach only provides us with the aggregated score without further details.
In a sales environment, we typically need additional details such as dates of sale, products sold, and a number of orders. This Pipeline shows how we can use the ELT Pivot Snap to accomplish this task.
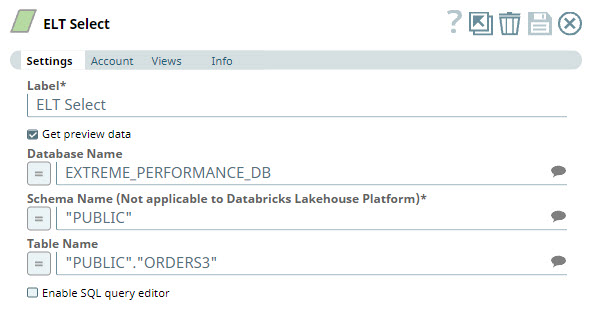
First, we build a SELECT query to read the target table. To do so, we use the ELT Select Snap. Sales data is maintained in the table ORDERS3. We configure the ELT Select Snap to read this table. Additionally, we also configure the Snap to show a preview of the SELECT query's execution:
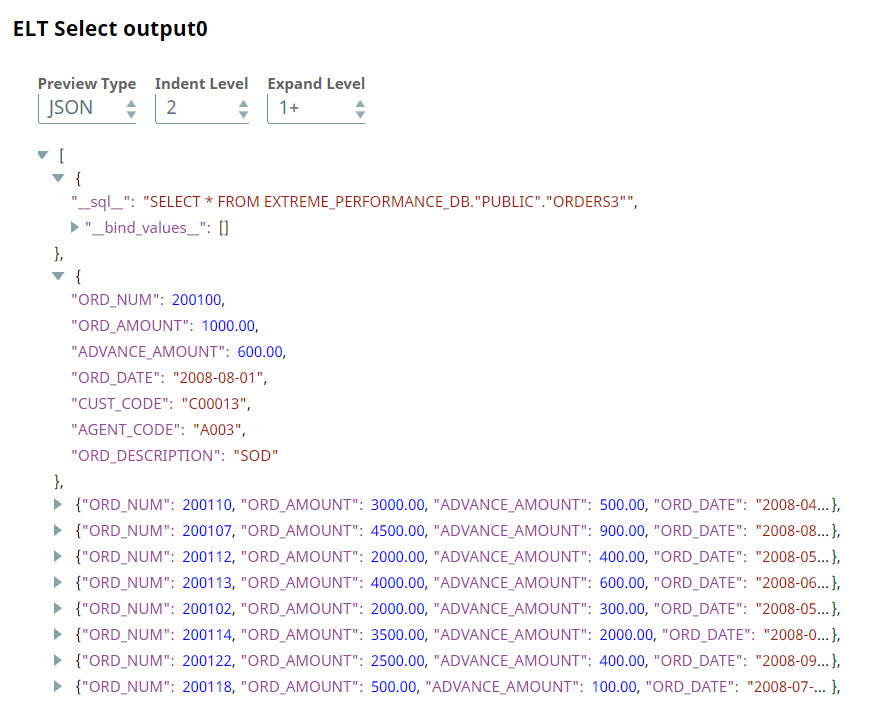
A preview of the output from the ELT Select Snap is shown below:
We want to calculate the total sales made by the agents, A002, and A010, on each day. Therefore, we use the ELT Pivot Snap and configure it as shown below:
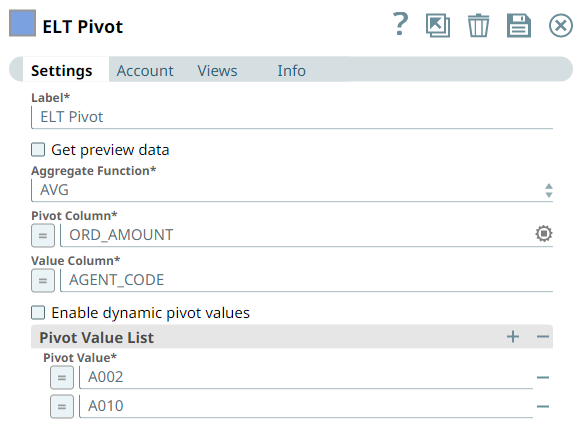
This Snap builds the following query based on this configuration:

A tabular representation of this output is as shown below:
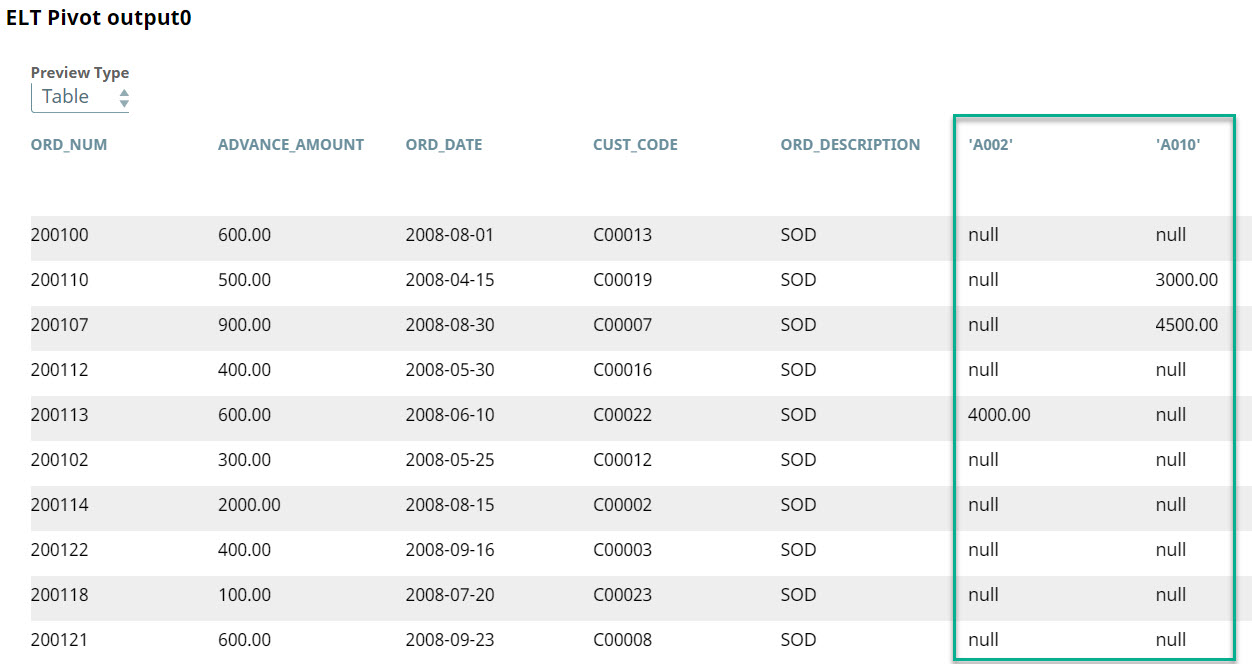
The days on which the agents did not make any sales are automatically assigned a null value. We can use an ELT Insert-Select Snap to write the query's output into another table. Additionally, we can use a combination of the ELT Copy and ELT Filter Snaps to write each of the agent's performances into separate tables.
Downloads
|
See Also
Provide links to the endpoint's official documentation, any relevant or related internal documentation, and any other links you have referred to on this page. Care should be taken when referencing external sites/documentation that it is an official site/documentation. Do not refer to forums such as stackoverflow.
- ELT Snap Pack
- Best Practices for Using the ELT Snap Pack
- SnapLogic Product Glossary
- Getting Started with SnapLogic