Read and write access to the Snowflake instance.
On this Page
You can use this Snap to execute multiple queries. If any query fails in execution, the changes are rolled back.
The Snowflake - Multi Execute Snap supports executing all Snowflake queries and does only write operations.
The Snowflake - Multi Execute Snap supports executing all Snowflake queries and does only write operations.
The Snowflake - Multi Execute is a Write type Snap.
Read and write access to the Snowflake instance.
You must have the following permissions in your Snowflake account to execute this Snap:
Usage (DB and Schema): Privilege to use database, role, and schema.
Create table: Privilege to create table on database. role and schema.
The following commands enable minimum privileges in the Snowflake Console:
grant usage on database <database_name> to role <role_name>; grant usage on schema <database_name>.<schema_name>; grant "CREATE TABLE" on database <database_name> to role <role_name>; grant "CREATE TABLE" on schema <database_name>.<schema_name>; |
Learn more about Snowflake privileges: Access Control Privileges.
The permissions to grant for using commands depends on the queries you provide in this Snap.
Does not Work in Ultra Pipelines.
The Snap may fail due to an error when the batch size specified in the account is 1 and the number of rows updated by an executed query exceeds 2.1 billion.
Because of performance issues, all Snowflake Snaps now ignore the Cancel queued queries when pipeline is stopped or if it fails option for Manage Queued Queries, even when selected. Snaps behave as though the default Continue to execute queued queries when the Pipeline is stopped or if it fails option were selected.

Select statement and transactional statements such as Begin, Commit, and Rollback are not supported.
Changes made to the database using Data Definition Language (DDL) queries are not rolled back if the Snap fails, this is since DDL statements are always auto-committed by default.
If there is one DDL query among other queries that the Snap is executing, then the rollback is only for the changes made by the queries executed after the DDL query. Ensure that the Disable session auto-commit property is selected when using DDL queries. See Snowflake Auto-commit for details. This is not applicable to Data Modification Language (DML) queries.
User-defined functions (UDFs) created in the Snowflake console can be executed using Snowflake - Multi Execute Snap. See Snowflake Multi Execute-Examples.
Type | Format | Number of Views | Examples of Upstream and Downstream Snaps | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Input | Document |
|
| While the Snap does not require an input document, it supports document input and generates document outputs. Snaps that accept or generate documents can be used upstream or downstream of the Snap. |
Output | Document
|
|
| The Snap will output one document for every record retrieved, hence any document processing Snap can be used downstream. |
Error | Error handling is a generic way to handle errors without losing data or failing the Snap execution. You can handle the errors that the Snap might encounter when running the Pipeline by choosing one of the following options from the When errors occur list under the Views tab:
Learn more about Error handling in Pipelines. | |||
|
Field Name | Field Type | Description | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Label* Default Value: Snowflake - Update | String | Specify a unique name for the Snap. You can modify this to be more appropriate, especially if you have more than one of the same Snap in your pipeline. | |||||||||||
SQL Statements* Default Value: N/A Example: INSERT into SnapLogic.book (id, book) VALUES ($id,$book) | String/Expression | Specify the Snowflake SQL statement to execute on the server. Provide the queries to be executed by the Snap. End each query with a semi-colon, except the last query. To add another query, click the + to add a row and there add the query. Using Where ClausesValid JSON paths that are defined in the WHERE clause for queries/statements are substituted with values from an incoming document. If the error view is enabled, documents are written to the error view if the document is missing a value to be substituted into the query/statement. Using Where ClausesValid JSON paths that are defined in the WHERE clause for queries/statements are substituted with values from an incoming document. If the error view is enabled, documents are written to the error view if the document is missing a value to be substituted into the query/statement. Without using expressions
Using expressions
| |||||||||||
Session auto-commit Default Value: Selected | Checkbox | Select this to enable the session's auto-commit. This is useful when using DDL queries since the changes made by such queries cannot be rolled back if the Snap/pipeline fails. If deselected, changes made by DML queries can be rolled back or changes made by DML queries after a DDL queries can be rolled back. | |||||||||||
Use Result Query Default Value: Deselected | Checkbox | Select this property to write the result of each of the query execution, in case of multiple queries, to Snap's output view after the successful execution. The output of the Snap will be enclosed within the key, Result Query and the value will be the actual output produced by the SQL query. The option would allow users to effectively track the query's execution by clearly indicating the successful executions and the number of records affected, if any, after the execution. | |||||||||||
Manage Queued Queries Default Value: Continue to execute queued queries when pipeline is stopped or if it fails | Drowpdown list | Select this property to decide whether the Snap should continue or cancel the execution of the queued Snowflake Execute SQL queries when you stop the pipeline. If you select Cancel queued queries when the Pipeline is stopped or if it fails, then the read queries under execution are canceled, whereas the write type of queries under execution is not canceled. Snowflake internally determines which queries are safe to be canceled and cancels those queries. If you select Cancel queued queries when the Pipeline is stopped or if it fails, then the read queries under execution are canceled, whereas the write type of queries under execution is not canceled. Snowflake internally determines which queries are safe to be canceled and cancels those queries. | |||||||||||
Default Value: Execute only | Drowpdown list |
The following example pipeline demonstrates how to process multiple Snowflake queries in a single transaction.

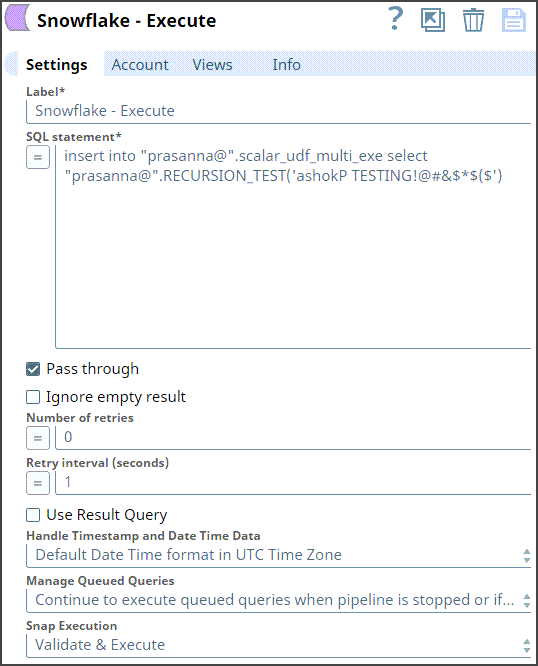
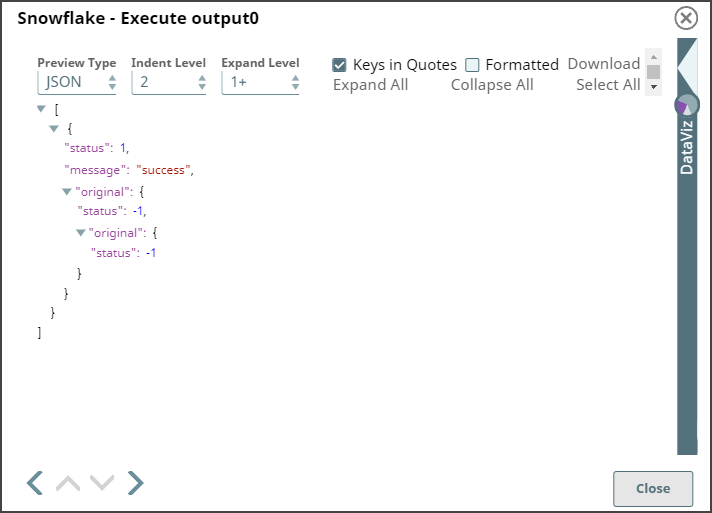
Step 1: Configure the Snowflake Execute Snap to define the user-defined function in the SQL statement. RECURSION_TEST is one of the Scalar JavaScript UDF in Snowflake. The Snap settings and the Output view are displayed as follows:
Step 2: Configure the Snowflake Multi Execute Snap as follows:
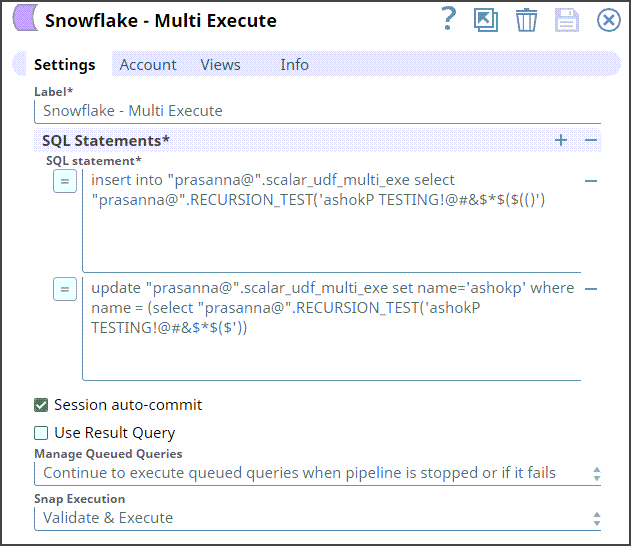
The Snap settings and the Output view are displayed as follows:
https://docs.snowflake.com/en/developer-guide/udf/sql/udf-sql-scalar-functions.html#scalar-sql-udfs
https://docs.snowflake.com/en/sql-reference/user-defined-functions.html