On this Page
| Table of Contents | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Overview
This Snap reads a document at the input, formats it as CSV based on the specified parameters, and writes CSV data to the output.
Input and Output
- Expected input: Any document that contains data structured as key-value attributes.
- Expected output: CSV data formatted using specifications provided in the Snap's settings.
- Expected upstream Snaps: Any Snap that offers documents. For example, CSV Generator or Mapper.
- Expected downstream Snaps: Any Snap that accepts binary data. For example, File Writer or CSV Parser.
Prerequisites
None.
Configuring Accounts
Accounts are not used with this Snap.
Configuring Views
Input | This Snap has exactly one document input view. |
|---|---|
| Output | This Snap has exactly one binary output view. |
| Error | This Snap has at most one document error view. |
Troubleshooting
- None.
Support for Ultra Pipelines
Does not work in Ultra Pipelines.
Limitations and Known Issues
- The Snap ignores escape characters when used along with any quote characters. When this happens, the resultant data cannot be parsed correctly using CSV Parser Snap which can cause an error. See Apache CSV Format Issue for details.
- The Snap prepares the column header for the output view (and hence the CSV file) using the keys defined in the first record. This may result in ignoring any additional key passed in the subsequent records. We recommend that you pass values for a comprehensive set of all keys used in the input view, for the first record.
Snap Settings
| Label |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binary header properties | Use these fields to add binary-header properties to the output data. These properties contain information related to the data and tell the system how the data must be interpreted. Click + to add a binary header. Binary headers in a document can be accessed and used in the expression-enabled properties of downstream Snaps. For example, you can use binary headers to specify custom statuses associated with the output data. Example:
Similarly, a 'content-location' property added to the binary header in this Snap can be referenced in the File name property of a File Writer Snap with the expression: $['content-location']. Example:
Default value: N/A | ||||||||||||
| Expression | The value to be associated with a specific binary header property. Example: text/csv Default value: N/A | ||||||||||||
| Target Path | The target JSON path where the value in the expression is written. Example: $['content-location'] to write the property 'content-location'. Default value: N/A | ||||||||||||
| Quote character | Required. The character that you want to use as the escape character in the CSV document. For example, if you use double quotes (") as the escape character, then commas in the actual data will need to be escaped using double-quotes on both sides. This property can be an expression. However, if the value associated with the expression contains more than one character, only the first character is used as the quote character. Example: “ Default value: “ Format: Character | ||||||||||||
| Quote mode | This property specifies how the quote character should be used in formatting the CSV data. Available choices are:
If the Quote character property is empty, the selection of this property is ignored and the Snap uses NONE for the Quote mode. Default value: ALL | ||||||||||||
| Delimiter | Required. The character that must be used as a delimiter in formatting the CSV data. Tabs are common delimiters. To use a tab as your delimiter, enter \t. This property accepts any delimiter that resolves to a single character. For example, \t resolves to a tab and \n resolves to a new line. You can also use an escaped Unicode string, such as \U0007. This property can be an expression, and can contain values from Pipeline parameters. Example: \t, \u0001 Default value: , Format: Character or Unicode | ||||||||||||
| Use header | Enables you to indicate whether the column names in the Header fields property should be used to format the CSV data. If this property is unchecked, the key set of the first document data will be used as a CSV header. Default value: Not selected | ||||||||||||
| Header fields | Enables you to specify the header values that you want to use in the output CSV data. Example: $name Default value: N/A | ||||||||||||
| Write CSV header | Enables you to indicate whether the header strings listed in the Header fields properties should be written to the output CSV data. Default value: Selected. | ||||||||||||
| Header size error policy | Enables you to handle any header size errors. The Snap determines the CSV header from the key set of the first input document if the Use header property is not selected; if the Write CSV header property is selected, then the Snap writes the CSV header to the output view binary stream. The header size error condition occurs when any subsequent input document has additional column names which are not present in the header. To handle header size errors, you can select any of the following options:
Default value: Default | ||||||||||||
| Ignore empty stream | Enables you to indicate whether you want the Snap to ignore empty streams received at the input view during Pipeline execution. If this option is selected, the Snap does not produce any output stream; else, the Snap writes an empty array to the output stream. Default value: Not selected. | ||||||||||||
| Character set | The character set in which the input CSV data is encoded. The supported selections are:
Default value: UFT-8 | ||||||||||||
| Write BOM | Enables you to indicate the behavior of the Snap when it starts to write the CSV output data. If this option is selected, the Snap writes the BOM (Byte Order Mark) for the character set selected in the Character-set encoding property; else, the Snap skips writing BOM. Default value: Not selected | ||||||||||||
| Newline | Specifies the newline characters that will be used as a line break. The available options are: LF, CR+LF and CR. Example: CR+LF (if the CSV file will be used in Microsoft Windows) Default value: LF | ||||||||||||
| Escape character | The escape character is used when formatting rows. Only single characters are supported. As of 4.3.2, this property can be an expression, which is evaluated with the values from the pipeline parameters. Leave this property empty if no escape character is used in the input CSV data. Default value: \ | ||||||||||||
|
|
Examples
Line Feeds for Windows while Formatting Documents
Text files created on Windows have different line endings than files created on Linux. Windows uses the carriage return and line feed ("\r\n") as a line ending, while Linux uses just a line feed ("\n").
In this example, we create a Pipeline that reads CSV data and then formats it for Windows-style line feeds using the CSV Formatter Snap.
Download this Pipeline.
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
We use the CSV Generator Snap to supply CSV documents:
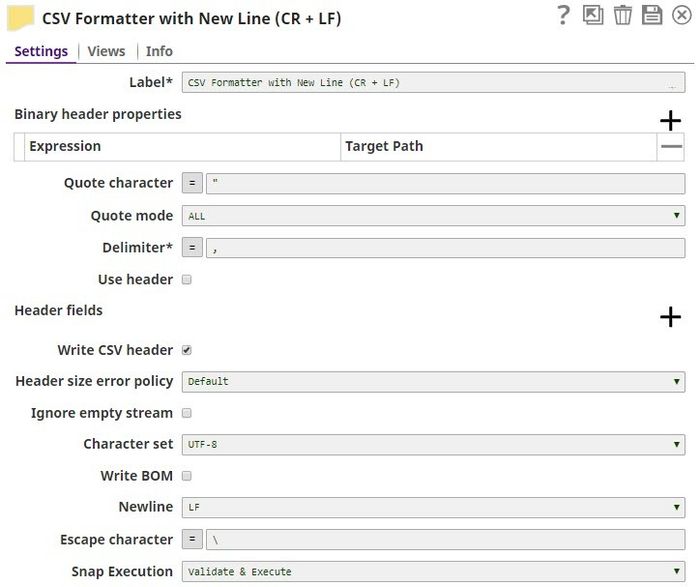
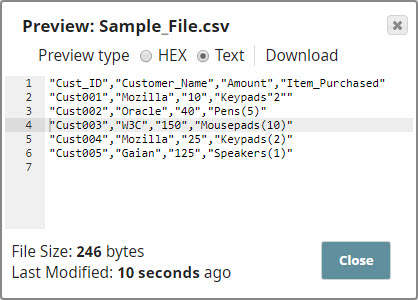
The raw output from the CSV Formatter Snap is as follows: Notice how the double-quotes used in the first line of the input CSV data is escaped in the output document. The CSV Formatter Snap formats the input data and produces an output in the line feeds for Windows style. We selected the Newline Property with CR+LF to give the line feeds in Windows format. We also leave the Quote character field unchanged as '"'. This tells the Snap that all special characters have to be placed in quotes in the CSV output.
We use the File Writer Snap to create a file using the output. Successful execution of the Pipeline displays the following output: Download this Pipeline. |
Creating Filenames Using the CSV Formatter Snap
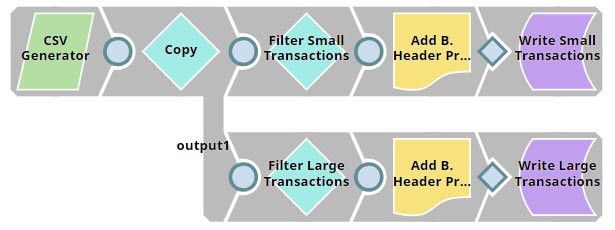
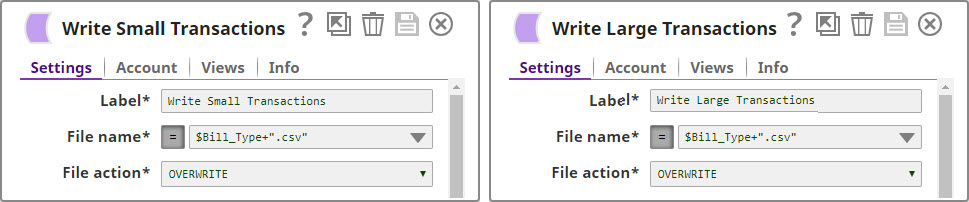
In this example, we pick up CSV documents that contain details related to simple purchases and, depending on the value of the purchases, we route them into two documents, picking up their names using the output of the CSV Formatter Snap.
Download this Pipeline.
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
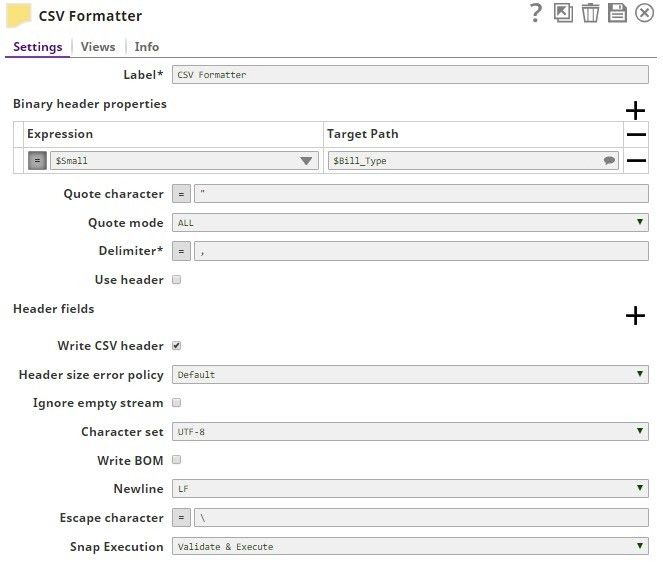
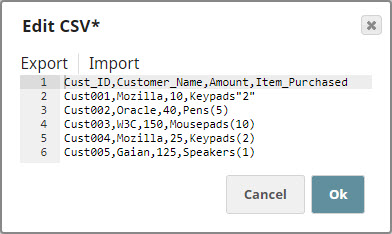
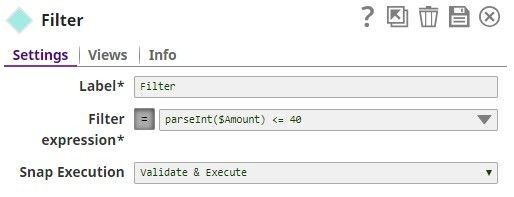
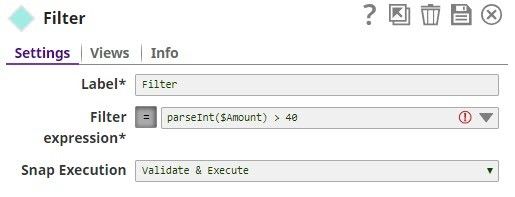
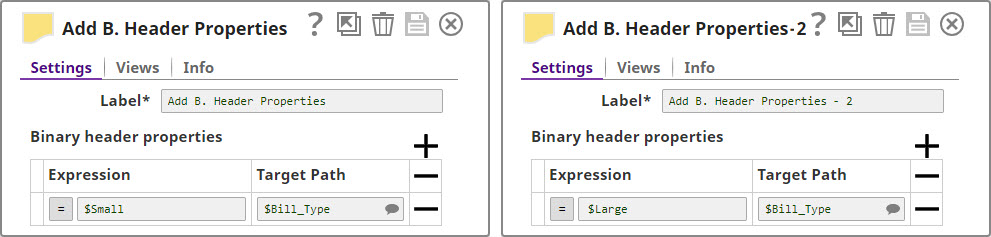
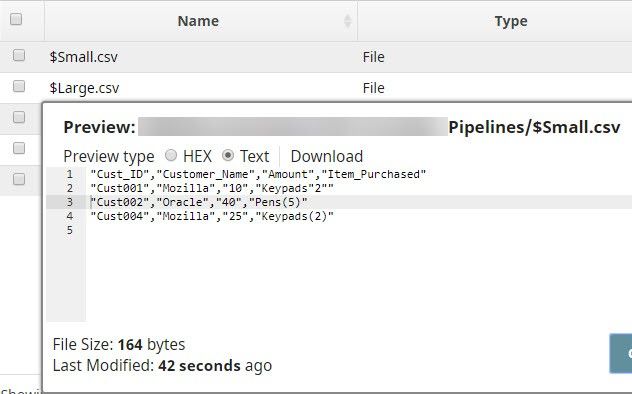
For the purposes of this example, we are picking up CSV data from a CSV Generator Snap. You can also supply this data using a combination of File Reader and CSV Parser Snaps. The CSV Generator Snap contains transaction details, as shown below: We copy the output of the CSV Generator Snap and connect each copy to a Filter Snap, where we filter out transactions based on whether they are worth more or less than $40: We now add a 'Bill_Type' binary header property to each set of filtered outputs, so each document is tagged appropriately: We now have two records, one containing all transactions that are worth less than or equal to $40, and another containing all transactions over $40. We now write each of these files to the SLDB using the File Writer Snap, configuring it to include this classification of transactions in the filename. We do this by using the expression $Bill_Type+".csv" in the File name property. You can now see that two new files were created in the project: $Small.csv and $Large.csv: Download this Pipeline. |
Passing Execution Status Codes through Binary Header Properties of the CSV Formatter Snap
In this example, we shall send CSV data from ServiceNow into SnapLogic using a Triggered Task. We shall then see how you can use the CSV Formatter Snap in the triggered Pipeline to manipulate the execution status (error) codes generated during Pipeline execution.
Download this Pipeline.
| Expand | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
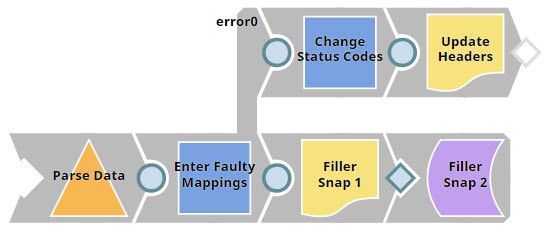
For the example to work, the Pipeline triggered by the Task should lead to an error. We shall route the error output to an error view. We shall then use the error view to manipulate the Status header of the error document. Once this is done, the parent Task sends the updated error output back to ServiceNow, and we should see the updated status code in the ServiceNow Administration interface. We need to perform the following tasks:
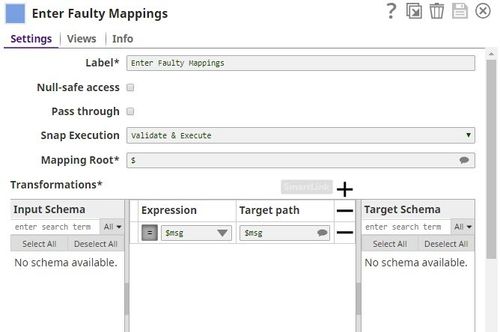
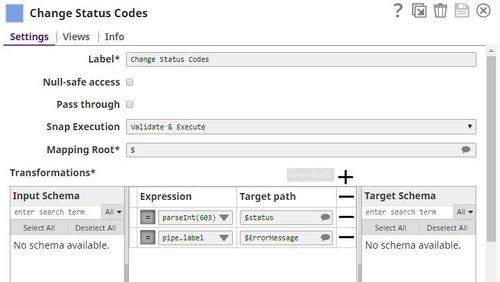
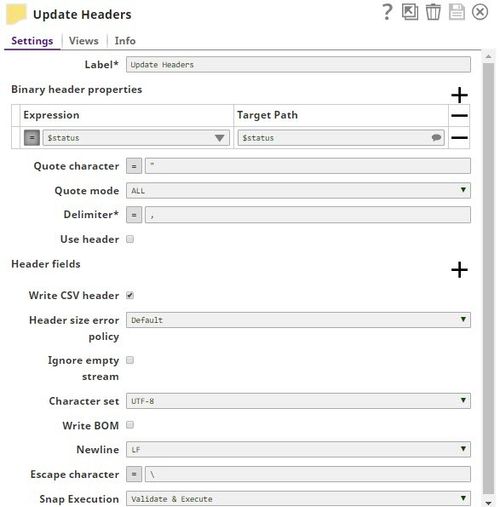
Let us look at each of these tasks in some detail: Creating a Pipeline to accept CSV and manipulate error document dataThis Pipeline is structured as shown in the screenshot above. Let us now look at its constituents:
Creating a Triggered Task that sends CSV data into the TriggeredTask_CSVFormatter_Example PipelineTo create a Triggered Task:
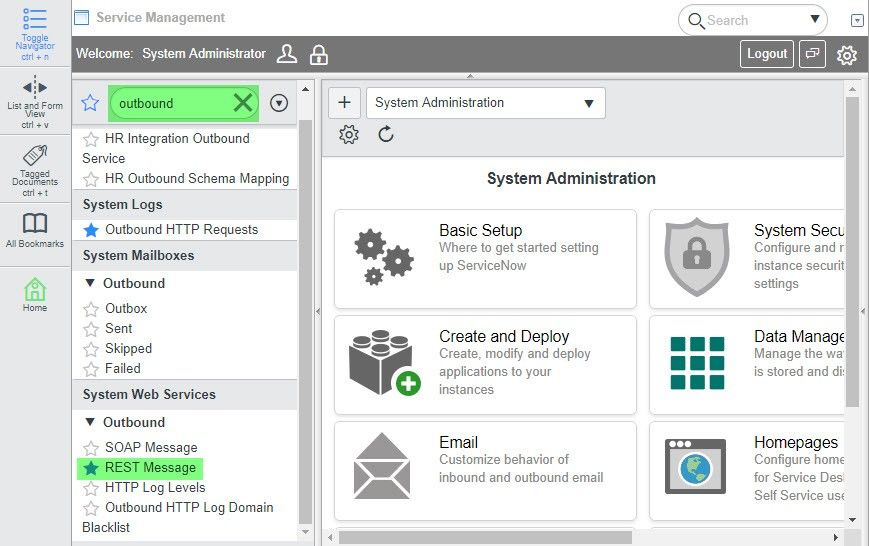
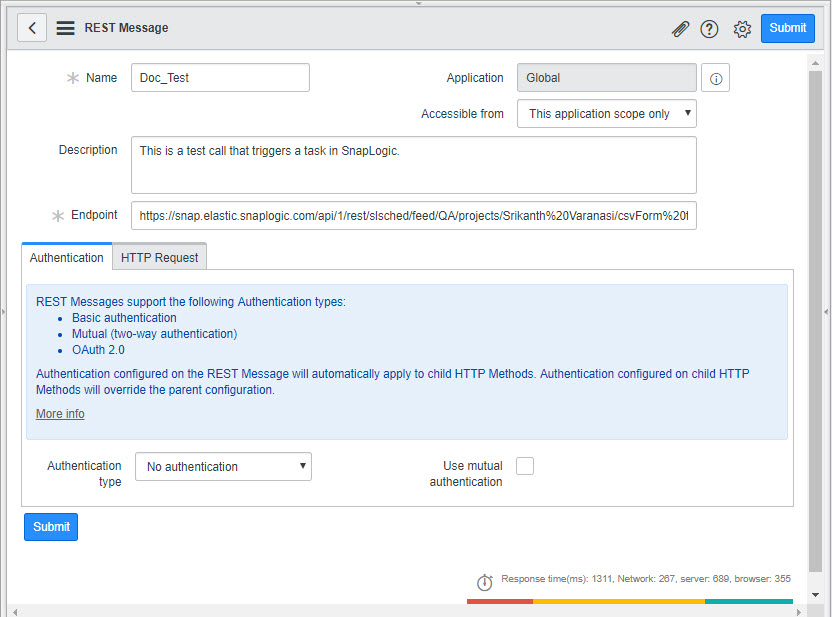
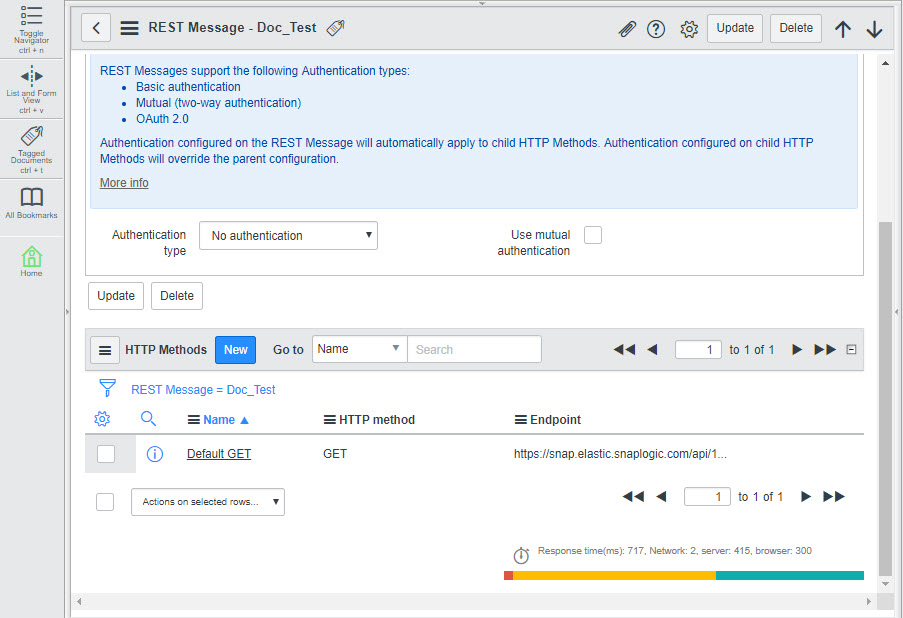
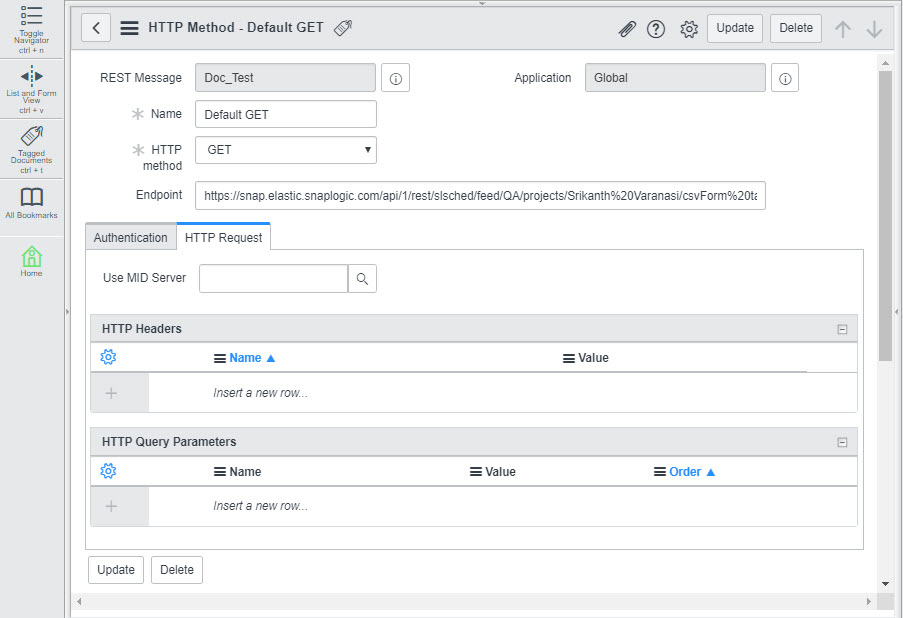
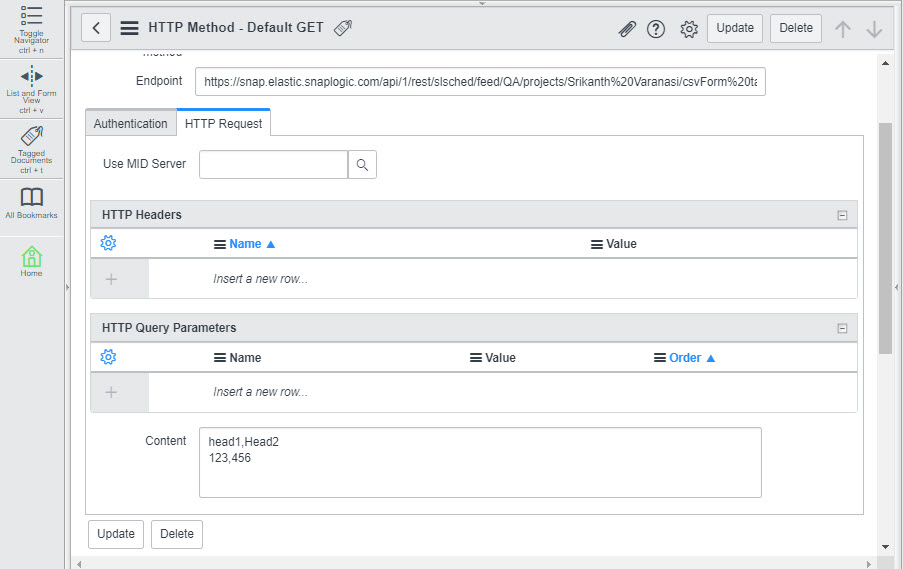
Your Task is now configured. You now need to configure your ServiceNow account to send CSV data to this Task. Configuring ServiceNow to send and receive CSV data from the Triggered Task
To configure ServiceNow to send and receive CSV data from the Triggered Task created in Step 2:
You can similarly use the CSV Formatter Snap to update binary header values associated with any input document. Download this Pipeline. |
Downloads
| Multiexcerpt include macro | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Attachments | ||
|---|---|---|
|
| Insert excerpt | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|