...
On this Page
| Table of Contents | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Overview
...
You can use this Snap to execute an SQL Insert statement. Document keys are used as the columns to insert into, and their values
...
are inserted into the column. Any missing column will
...
insert a null value
...
into
...
it.
...
| Multiexcerpt include macro | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Snap
...
Write
...
None
...
Type
The Oracle - Insert Snap is a Write-type Snap that inserts the specified data in the target table.
Prerequisites
A valid Oracle Thin Account or Oracle Thin Dynamic Account.
Support for Ultra Pipelines
Works in Ultra Task Pipelines if batching is disabled.
Known Issues
The Oracle - Insert Snap inserts incorrect time zone data for timestamp with time zone data type. For example, when an input value is 2021-08-10 17:30:43-07:00, the value written to the target table is 2021-08-10 17:30:43+07:00.
Workaround:
Use an expression Date.parse(2021-08-10 17:30:43-07:00) in Mapper Snap. The Mapper Snap converts it to a UTC timestamp string,
...
that is, 2021-08-11 00:30:43 00:00. The Snap will now insert the value successfully.
Works in Ultra Task Pipelines if batching is disabled.
...
This Snap uses account references created on the Accounts page of SnapLogic Manager to handle access to this endpoint. See Oracle Account for information on setting up this type of account.
...
Snap Views
Type | Format | Number of Views | Examples of Upstream and Downstream Snaps | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Input | Document
|
|
| Requires the Schema name and Table name to process a certain number of input documents into a prepared insert query. The second input view can be added for metadata for the table as a document so that the table is created in Oracle with a similar schema as the source table. If the table already exists, then the metadata is not used. |
Output |
...
This Snap has at most one document error view and produces zero or more documents in the view.
...
Document
|
|
| Snap outputs the number of documents successfully inserted into the target table in the output view document. | |
Error | Error handling is a generic way to handle errors without losing data or failing the Snap execution. You can handle the errors that the Snap might encounter when running the pipeline by choosing one of the following options from the When errors occur list under the Views tab:
Database Write Snaps output all records of a batch (as configured in your account settings) | |||
...
to the error view if the write fails during |
...
batch processing. |
Snap Settings
Field Name | Field Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
Label* Default value: Oracle - Insert | String | Specify the name for the Snap. You can modify this to be more specific, especially if you have more than one of the same Snap in your pipeline. | |
Schema name | |||
...
The database schema name. In case it is not defined, then the suggestion for the Table Name will retrieve all tables names of all schemas. The property is suggestible and will retrieve available database schemas during suggest values.
| Note |
|---|
The values can be passed using the pipeline parameters but not the upstream parameter. |
...
| String/Expression/Suggestion | Specify the database schema name. The suggestions in the Schema field are populated only when at least a single table exists in the schema. If no tables exist to use that schema, only SYS, SYSTEM, and XDB are populated. | |
Table name
| String/Expression/Suggestion | Specify the table that the rows will be inserted into. | |
...
| Note |
|---|
The values can be passed using the pipeline parameters but not the upstream parameter. |
Default value: None
Example: people
This list is populated based on the tables associated with the selected schema. | |||||||||
Create table if not present Default state: Deselected | Checkbox |
Learn more about table creation. | |||||||
Preserve case sensitivity | Checkbox | Select this checkbox to preserve the case sensitivity of the column names while performing the insert operation.
| |||||||
Number of retries Default value: 0 | |||||||||
...
Session parameters
3 | Integer/Expression | Specify the maximum number of attempts to be made to receive a response. The request is terminated if the attempts do not result in a response. | |
Retry interval (seconds) Default value: 1 | Integer/Expression | Specify the time interval between two successive retry requests. A retry happens only when the previous attempt resulted in an exception. | |
Session parameters | Use this field set to define the session parameters. This property lets you use | ||
...
the National Language Support (NLS) parameters. |
...
See the Oracle doc for detailed information about Setting NLS Parameters. The NLS parameters enable overriding the default value (e.g., a comma) that is set for the session in the initialization parameter file or set by the client with environment variables (e.g., a decimal point). You can add multiple parameters by using the plus (+) sign next to Session parameters. | ||
Session parameter name Default value: N/A | String/Expression | Name of the NLS parameter.
|
...
|
...
Session parameter value Default value: |
...
N/A | String/Expression | Value of the NLS parameter. This field |
...
supports only pipelines parameters |
...
Example: "CZECH REPUBLIC"
Default value: None.
...
Specify the maximum number of attempts to be made to receive a response. The request is terminated if the attempts do not result in a response.
Default value: 0
Example: 3
...
Specify the time interval between two successive retry requests. A retry happens only when the previous attempt resulted in an exception.
...
, and not upstream values. | |||||||
| |||||||
...
| Multiexcerpt include macro | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
Dropdown list | Specify the database schema name. Selecting a schema, filters the Table name list to show only those tables within the selected schema. The suggestions in the Schema field are populated only when at least a single table exists in the schema. If no tables exist to use that schema, only SYS, SYSTEM, and XDB are populated. The values can be passed using the pipeline parameters but not the upstream parameter. |
Auto commit
In a scenario where the Auto commit on the account is set to true, and the downstream Snap does depends on the data processed on an Upstream Database Bulk Load Snap, use the Script Snap to add delay for the data to be available.
For example, when performing a create, insert and a delete function sequentially on a pipeline, using a Script Snap helps in creating a delay between the insert and delete function or otherwise it may turn out that the delete function is triggered even before inserting the records on the table.
Oracle reports failures for the entire batch even if some rows successfully inserted/updated. Because the Snap must report what is reported by the database, the Snap sends all records to the error view and no record to the output view. If you want to see accurate results for each row you must set the batch size to 1 and execute the pipeline.
Table Creation
If the table does not exist when the Snap tries to do the insert, and the Create table if not present property is selected, the table will be created with the columns and data types required to hold the values in the first input document. If you would like the table to be created with the same schema as a source table, you can connect the second output view of a Select Snap to the second input view of this Snap. The extra view in the Select and Bulk Load Snaps are used to pass metadata about the table, effectively allowing you to replicate a table from one database to another.
The table metadata document that is read in by the second input view contains a dump of the JDBC DatabaseMetaData class. The document can be manipulated to affect the CREATE TABLE statement that is generated by this Snap. For example, to rename the name column to full_name, you can use a Mapper Snap that sets the path $.columns.name.COLUMN_NAME to full_name. The document contains the following fields:
columns - Contains the result of the getColumns() method with each column as a separate field in the object. Changing the COLUMN_NAME value will change the name of the column in the created table. Note that if you change a column name, you do not need to change the name of the field in the row input documents. The Snap will automatically translate from the original name to the new name. For example, when changing from name to full_name, the name field in the input document will be put into the "full_name" column. You can also drop a column by setting the COLUMN_NAME value to null or the empty string. The other fields of interest in the column definition are:
TYPE_NAME - The type to use for the column. If this type is not known to the database, the DATA_TYPE field will be used as a fallback. If you want to explicitly set a type for a column, set the DATA_TYPE field.
_SL_PRECISION - Contains the result of the getPrecision() method. This field is used along with the _SL_SCALE field for setting the precision and scale of a DECIMAL or NUMERIC field.
_SL_SCALE - Contains the result of the getScale() method. This field is used along with the _SL_PRECISION field for setting the precision and scale of a DECIMAL or NUMERIC field.
primaryKeyColumns - Contains the result of the getPrimaryKeys() method with each column as a separate field in the object.
declaration - Contains the result of the getTables() method for this table. The values in this object are just informational at the moment. The target table name is taken from the Snap property.
importedKeys - Contains the foreign key information from the getImportedKeys() method. The generatedCREATE TABLE statement will include FOREIGN KEY constraints based on the contents of this object. Note that you will need to change the PKTABLE_NAME value if you changed the name of the referenced table when replicating it.
indexInfo - Contains the result of the getIndexInfo() method for this table with each index as a separated field in the object. Any UNIQUE indexes in here will be included in the CREATE TABLE statement generated by this Snap.
Examples
We will provide two examples, the first one inserts input data into a table. The second one will show the error handling.
...
Examples
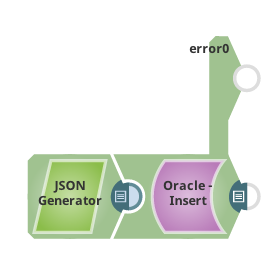
Insert input data into a table
The following example pipeline demonstrates how to insert a row of data into
...
TEST_EMPLOYEE
...
table.
...
Table dataset:
| Code Block |
|---|
CREATE TABLE "TECTONIC"."TEST_EMPLOYEE"
(
"Title" VARCHAR2(4000 BYTE),
"Employee_Name" VARCHAR2(4000 BYTE),
"Employee_ID" VARCHAR2(4000 BYTE)
); |
...
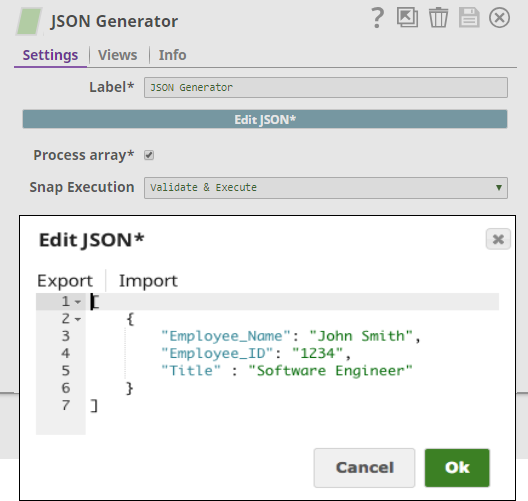
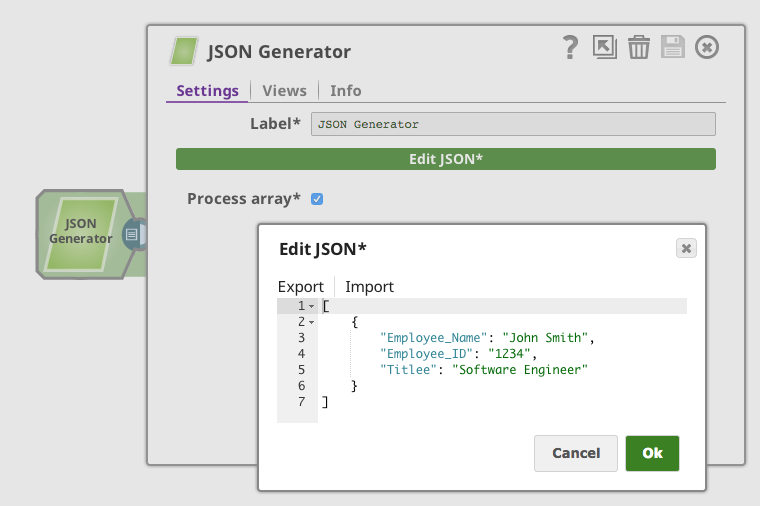
Step 1: Configure the JSON Generator Snap with the data
...
you want to insert
...
Then we simply connect the Oracle Insert Snap to it and set up the table name TEST_EMPLOYEE:
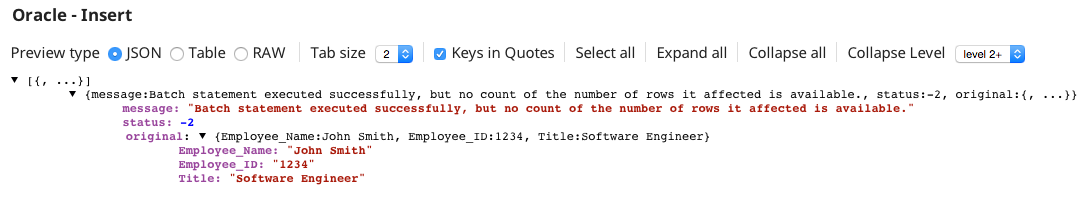
Here is an example output of the pipeline:
...
| title | 2. Error handling on the Snap |
|---|
In this example, we will show you the error handling.
...
into the target table.
...
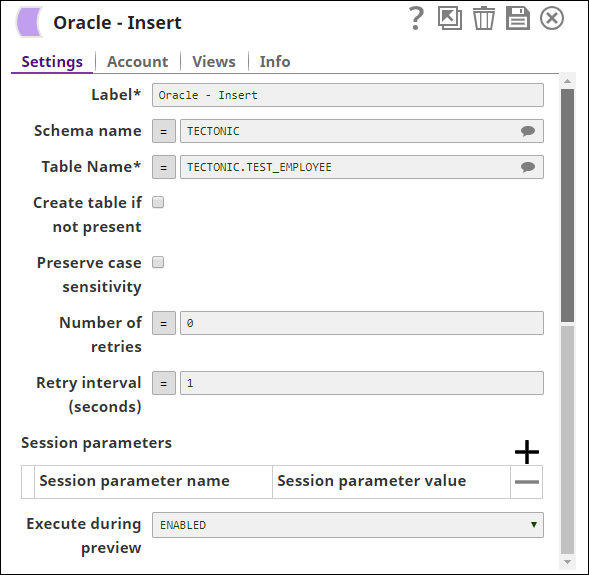
Step 2: Configure the Oracle - Insert Snap as shown below to insert this data into the TEST_EMPLOYEE table.
...
On validation, Snap inserts the employee details into the target TEST_EMPLOYEE table and displays the “success” message in the output.
...
Error Handling of the Snap
This example pipeline demonstrates error handling.
...
Use the same pipeline as the one used in Example
...
1. Insert a row with a non-existing column name "Titlee"
...
...
. In the Oracle - Insert Snap, choose Route Error Data to Error View under the Views tab.
On validation, the error message
...
is routed to
...
Snap's error view:
...
Snap Pack History
| Insert excerpt | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|