In this article
| Table of Contents | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Snap Type: | Write | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Description: | This Snap executes a SQL delete with the given properties. ETL Transformations & Data FlowThis Snap enables the following ETL operations/flows: Snap will delete all the records from the input table when there is no WHERE clause in the Delete condition provided or it will delete only the specific records matching with the WHERE clause provided in the properties. Input & Output
| |||||||||||||
| Prerequisites: | None. | |||||||||||||
| Limitations and Known Issues: | Works in Ultra Task Pipelines.Tasks.
| |||||||||||||
| Configurations: | Account and Access This Snap uses account references created on the Accounts page of SnapLogic Manager to handle access to this endpoint. See Redshift Account for information on setting up this type of account. Views
| |||||||||||||
| Troubleshooting: | None at this moment | |||||||||||||
Settings | ||||||||||||||
Label | Required. The name for the Snap. You can modify this to be more specific, especially if you have more than one of the same Snap in your pipeline. | |||||||||||||
Schema name | The database schema name. Selecting a schema filters the Table name list to show only those tables within the selected schema. The property is suggestible and will retrieve available database schemas during suggest values.
| |||||||||||||
Table name | Required. Table name to execute the delete on,
| |||||||||||||
Delete Condition (Truncates Table if emptycondition (deletes all records from table if left blank) | This is an expression property to specify the SQL WHERE clause of the delete statement. The delete condition may also be passed via an upstream Snap or through the pipeline parameters.
Examples: name | ME_DB_Snaps_Query_Examples | page | Oracle - Update
Default value: [None] | ||||||||||
| Number of retries | Specifies the maximum number of attempts to be made to receive a response. The request is terminated if the attempts do not result in a response. Example: 3 Default value: 0
| |||||||||||||
| Retry interval (seconds) | Specifies the time interval between two successive retry requests. A retry happens only when the previous attempt resulted in an exception. Example: 10 Default value: 1 | |||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||
Troubleshooting
| Multiexcerpt include macro | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Examples
Basic Use Case
The following pipeline describes how the Snap functions as a standalone Snap in a pipeline:
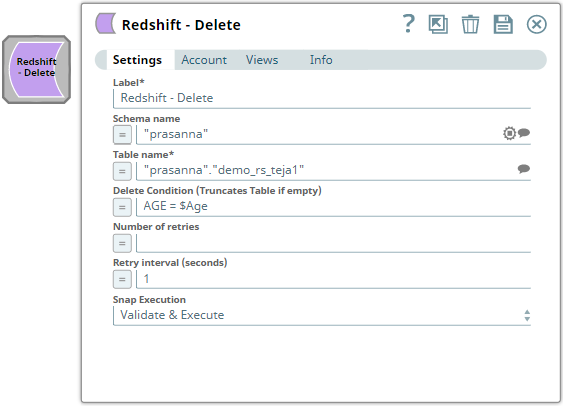
In the pipeline below, Configure the Redshift Delete Snap deletes to delete all the records in the demo_rs_teja1 table belonging to in the prasanna schema. All the records are deleted since there is no WHERE clause specified in the Delete condition.
In the image below
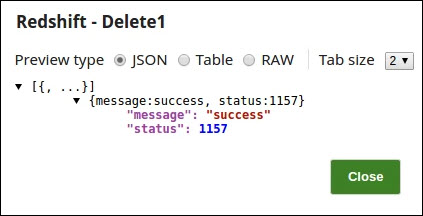
On validation a "success" message can be seen denoting the successful execution of the Snap.
Typical Snap Configurations
The key configuration of the Snap lies in how you pass the SQL statements to delete Redshift records. SQL statements can be passed:
- Without Expression
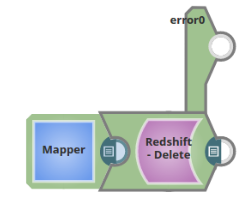
The pipeline below shows a configuration where a Mapper Snap is used to pass Key-Value pair to the Redshift Delete Snap.
The image below shows the configuration of the Mapper Snap, here the $id parameter is assigned the value 1.
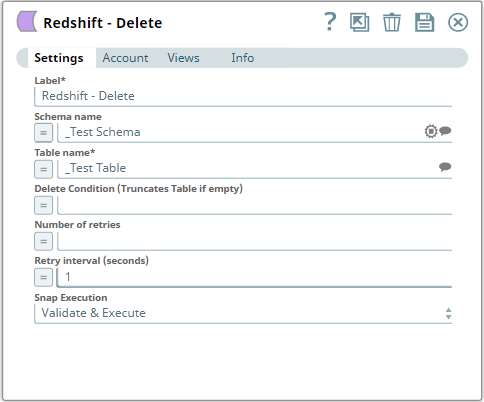
The image below shows the configuration of the Redshift Delete Snap. Note the Delete condition id>$id. When executed all the records in the table kzhou2 within the prasanna schema where the id is more than 1 will be deleted.
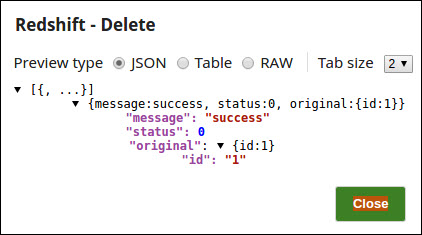
The successful execution of the pipeline displays the below output preview:
- With Expression
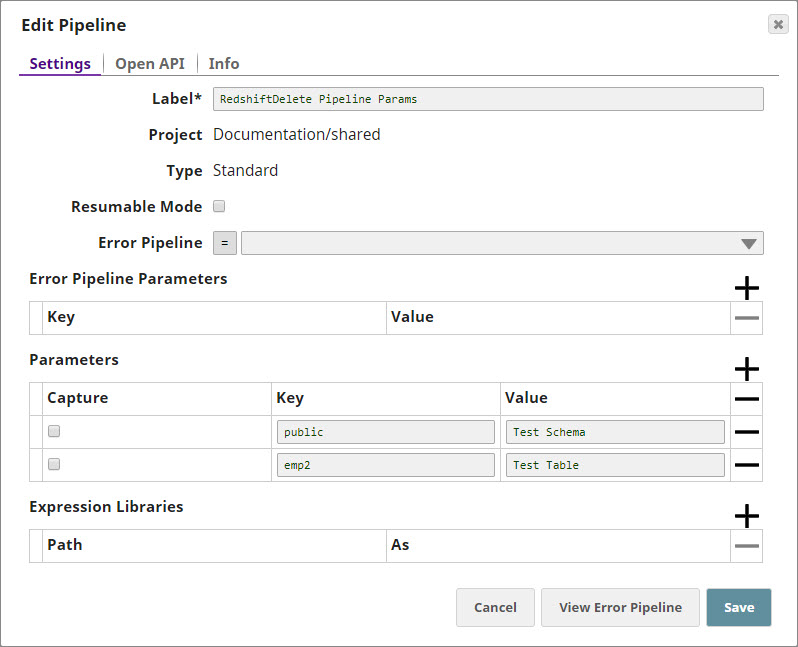
- Pipeline Parameter: Pipeline parameters set to pass the required Schema name and Table name to the Redshift Delete Snap.
Upon execution, the table belonging to the schema, both passed as pipeline parameters Test Schema and Test Table, will be deleted by the Redshift Delete Snap.
Advanced Use Case
The following describes a pipeline, with a broader business logic involving multiple ETL transformations, that shows how typically in an enterprise environment, Redshift Delete functionality is used. Pipeline download link below (Downloads Section).
The below pipeline extracts the records from the MySQL database and transfers them to the Redshift database. The Mapper Snap then maps the input and the Target schemas from the Redshift tables for the records to be deleted. The Redshift Select Snap displays the remaining records.
Extract: The MySQL Select Snap retrieves the records from a table on the MySQL database.
Transform: The Mapper Snap maps the input schema to the target schema for the records to be deleted.
Load: The Redshift Bulk Load Snap loads the records into a table on the Redshift database.
Extract: The Redshift Select Snap retrieves the remaining records.
Downloads
| Multiexcerpt include macro | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Attachments | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
See Also
https://community.snaplogic.com/t/error-on-redshift-delete/10075
| Insert excerpt | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|