In this article
| Table of Contents | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Overview
You can use this Snap to read a binary data stream from the input view and write it to a specified file destination. Possible file destinations include: SLDB, HTTP, S3, FTP, SFTP, FTPS, or HDFS. If File permissions for the file are provided, the Snap set those permissions to the file. This is a Write Snap type.
| Info |
|---|
This Snap has the ability to use an MD5 checksum that automatically checks for data integrity and corruption while uploading the file. |
Prerequisites
| Multiexcerpt include macro | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Support for Ultra Pipelines
Works in Ultra Pipelines.
Limitations
Files uploaded to SLFS have a 100-MB per file limit. This limit does not apply when writing to external storage.
Known Issues
- This Snap does not create an output file when using the input from SAS Generator Snap configured with only the DELETE SAS permission. This is not the case when the target file exists.
- This Snap does not fail and turns green after execution despite providing an expired SAS URI. As a workaround, select Validate after write to fail the Snap in case of invalid credentials.
Snap Input and Output
| Input/Output | Type of view | Number of views | Examples of Upstream/Downstream Snaps | Description | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Binary | Min: 1 Max: 1 | Any Snap with a binary output view can be connected upstream, such as CSV Formatter, JSON Formatter, XML Formatter, or File Reader. | Any binary data stream. | ||||
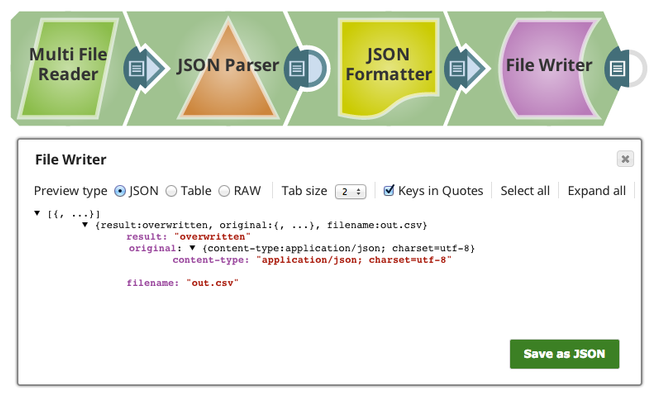
| Output | Document | Min: 0 Max: 1 | Downstream Snap is optional. Any Snap with a document input view can be connected downstream. | The output view for this Snap is optional. If an output view is open and the file write action is successful, the output view provides a document with information on the filename, result, and original data. An example is:
The value of the "result" field can be "overwritten", "created", "ignored", or "appended". The value "ignored" indicates that the Snap did not overwrite the existing file because the value of the File action property is "IGNORE".
|
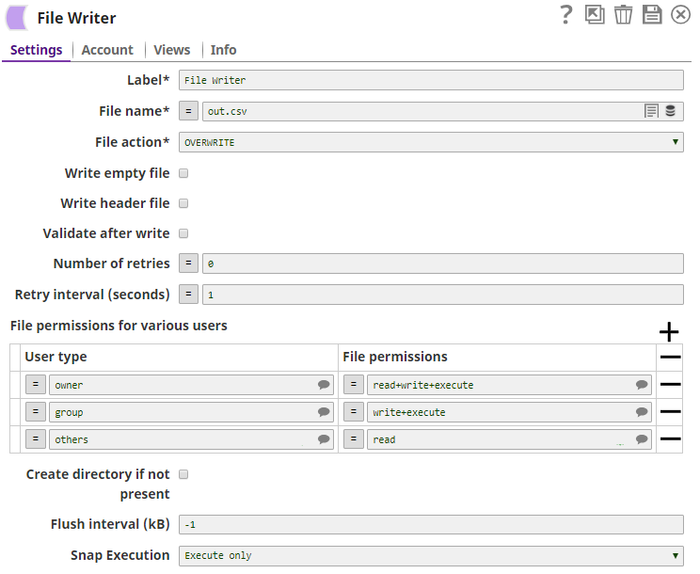
Snap Settings
| Field | Field Type | Description | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Label* | String |
Default Value: File Writer | |||||||||||||||||||||
File name* | String | Specify the URI of the destination file to which the the data (binary input from the upstream input view) is written. It may start with one of the following protocols:
Default Value: [None] Examples:
| |||||||||||||||||||||
File action* | Dropdown list | Specify the action to perform if the file already exists. The available options are:
Default Value: Overwrite | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Write empty file | Checkbox | Select this checkbox to write an empty file when the incoming binary document has empty data. If there is no incoming document at the input view of the Snap, no file is written regardless of the value of the property. Default Value: Not selected. | |||||||||||||||||||||
Write header file | String | The binary data stream in the input view may contain header information about the binary data in the form of a document with key-value-pair map data. Default Value: Not selected | |||||||||||||||||||||
Validate after write | Checkbox | Select this checkbox to enable the Snap to check if the file exists after the completion of the file write. This may delay a few more seconds for the validation. Default Value: Not selected | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of retries | Integer | Specify the maximum number of retry attempts when the Snap fails to write. If the value is larger than 0, the Snap first stores the input data in a temporary local file before writing to the target file.
Minimum value: 0 Default Value: 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Retry interval (seconds) | Integer | Specify the minimum number of seconds for which the Snap must wait before attempting recovery from a network failure. Minimum value: 1 Default Value: 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
File permissions for various users | Use this field set to provide any combination of permissions to the available users.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| User type | String/Expression | Choose one of the three standard user types. The available options are:
Each row can have only one user type and each user type should appear only once. Select one from the suggested list. Specify at most one row per user type. Default Value: N/A | |||||||||||||||||||||
| File permissions | String/Expression/Suggestion | Specify the privilege to provide to the user on the file. The available permissions are:
Default Value: N/A | |||||||||||||||||||||
Create directory if not present | Checkbox | Select this checkbox to enable the Snap to create a new directory if the specified directory path does not exist. This field is not supported for HTTP, HTTPS, SLDB and SMB file protocols. Default Value: Not selected | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Flush interval (kB) | Integer | Flush interval in kilobytes during the file upload. The Snap can flush a given size of data output stream written to the target file server. If the value is zero, the Snap flushes in maximum frequency after each byte block is written. Larger the value is, the less frequent flushes the Snap performs. Leave the property at default -1 for no flush during the upload. This property may help if the file upload experiences an intermittent failure. However, more frequent flushes will result in a slower file upload. Default Value: -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Advanced properties | Use this field set to add advanced properties, such as SAS URI. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Properties | String |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Values | String/Expression | Specify the value for the SAS URI.
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Snap Execution | Dropdown list |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Examples
- For SFTP files, if you attempt to write a file into a directory where you do not have a write access right, the write operation will fail with "access denied" error. When you get an SFTP account credential, it is also important to know where your home directory is, for example, sftp://ftp.snaplogic.com/home/mrtest for username "mrtest"
- HDFS Example
For HDFS file access, please use a SnapLogic on-premises Groundplex and make sure that its instance is within the Hadoop cluster and SSH authentication has already been established. You can access HDFS files in the same way as other file protocols in File Reader and File Writer Snaps. There is no need to use any account in the Snap.
| Note |
|---|
HDFS 2.4.0 is supported for the hdfs protocol. |
An example for HDFS is:
| Code Block |
|---|
hdfs://<hostname>:<port number>/<path to folder>/<filename> |
If Cloudera Hadoop Name node is installed in AWS EC2 and its hostname is "ec2-54-198-212-134.compute-1.amazonaws.com" and its port number is 8020, then you would enter:
| Code Block |
|---|
hdfs://ec2-54-198-212-134.compute-1.amazonaws.com:8020/user/john/input/sample.csv |
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Example pipeline file for an sldb file write as shown below: |
Troubleshooting
| Error | Reason | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
Could not evaluate expression: filepath Mismatched input ':' expecting {<EOF>, '||', '&&', '^', '==', '!=', '>', '<', '>=', '<=', '+', '-', '*', '/', '%', '?', '[', PropertyRef}. | The expression toggle (=) is selected on the File name field, so it is trying to evaluate the filepath as an expression. | Check the expression syntax. Click on the toggle to take the field out of expression mode. |
Failure: | The expression toggle (=) is selected on the File name field, so it is trying to evaluate the filename as an expression. | Check expression syntax and data types. Click on the toggle to take the field out of expression mode. |
Downloads
| Attachments | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
See Also
| Insert excerpt | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|