...
...
...
...
...
...
...
...
...
...
...
In this
...
article
| Table of Contents | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
Snap type:
Read
...
Description:
This Snap fetches messages from a RabbitMQ destination and acknowledges them.
...
Overview
You can use this Snap to fetch messages from a RabbitMQ destination.
...
Snap Type
RabbitMQ Consumer Snap is a READ-type Snap.
Prerequisites
Access to the RabbitMQ Server.
Privileges to perform various actions on the Queues such as receive and send messages.
Support for Ultra Pipelines
Works in Ultra Pipelines.
Limitations and Known Issues
None.
Snap Views
Type | Format | Number of Views | Examples of Upstream and Downstream Snaps | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Input | Document |
| Upstream Snap is optional. |
...
You can connect any Snap with a document output view |
...
, such as Mapper or Copy Snaps upstream of this Snap. | The Snap does not require input data. Input documents may be used to evaluate any JavaScript expression in the File property. |
...
Output | Binary |
|
| Message consumed from RabbitMQ server as binary document. |
...
- Access to the RabbitMQ Server.
- Privileges to perform various actions on the Queues such as receive and send messages.
...
This Snap uses account references created on the Accounts page of SnapLogic Manager to handle access to this endpoint. See Configuring RabbitMQ Accounts for information on setting up this type of account.
...
| Input | This Snap has at most one optional document input view. |
|---|---|
| Output | This Snap has exactly one binary output view. |
| Error | This Snap has at most one document error view and produces zero or more documents in the view. |
...
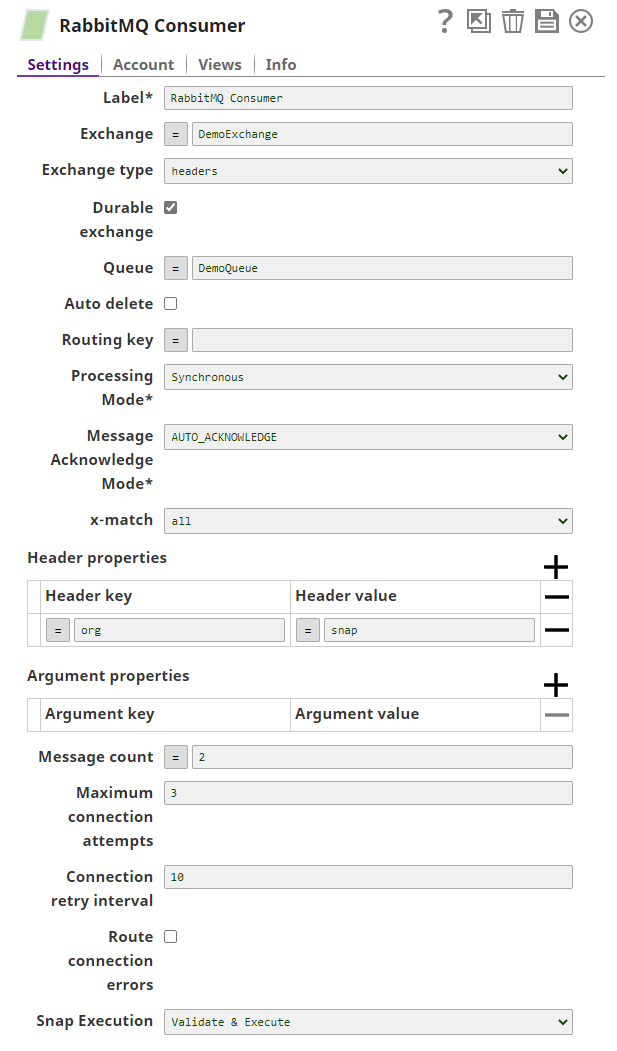
Settings
Label
...
Exchange
...
Error | Error handling is a generic way to handle errors without losing data or failing the Snap execution. You can handle the errors that the Snap might encounter while running the Pipeline by choosing one of the following options from the When errors occur list under the Views tab:
Learn more about Error handling in Pipelines. | |||
Snap Settings
| Info |
|---|
|
Field Name | Field Type | Field Dependency | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Label* Default Value: RabbitMQ Consumer | String | None | Specify a unique name for the Snap. | |
Exchange Default Value: N/A | String/Expression | None | Specify a name of the RabbitMQ exchange bound to the queue. If | |
...
you do not specify a value for exchange, the default exchange provided by RabbitMQ is considered.
| ||||
Exchange type Default Value: direct | Dropdown list | None | The type of RabbitMQ exchange used to push messages. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
...
Available options are:
| |
Durable Exchange Default | |
|---|---|
...
Value: |
|---|
...
Whether or not the exchange is durable.
Default Value: Selected
Queue
...
Selected | Checkbox | None | Select this checkbox to enable the exchange to be durable. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Queue Default Value: N/A | String/Expression | None | Conditional. Specify a name of the RabbitMQ queue from which messages have to be consumed. If there is no queue with given queue name on RabbitMQ, then a new queue is created and consumer starts listening. If the exchange name and routing key are also specified, then the queue is bound to the exchange with the given routing key.
| |||
Auto delete Default Value: Deselected | Checkbox | None | Select this check box to indicate that the RabbitMQ autoDelete property associated with the existing queue is set to | |||
Routing Key Default | ||||||
...
Routing Key
...
Value: N/A | String/Expression | None | Specify the routing key to be used for binding the queue with the exchange. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Processing Mode | ||||
...
Specifies the mode of message processing. The options available include Synchronous and Asynchronous.
...
Default Value: Synchronous | Dropdown list | None | Select one of the following modes for processing messages: Synchronous: In synchronous mode, the consumer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
...
processes messages from the destination one at a time until a STOP is read or the Message Count is reached.
Asynchronous: |
...
In asynchronous mode, the consumer reads the messages from the destination whenever the message arrives until a 'STOP' is read or the Message Count is reached. The consumer registers a messagelistener asynchronously. It does not block, but calls (the processmessage) immediately once a message is available. | |
Message Acknowledge Mode* Default | |
|---|---|
...
Message Acknowledge Mode
...
Value: AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE | Dropdown list | None | Select one of the following modes of message acknowledgement for non-transacted sessions | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
...
:
|
...
|
...
|
...
| |||
Acknowledge type Default value: | |||
...
Acknowledge Message | Dropdown list | Appears on selecting Auto_Acknowledgment from the Message Acknowledge Mode dropdown list. | Select one of the following acknowledge types for the message.
| |
x-match | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
...
Default Value: all | Dropdown list | None | Specify the x-match value to be submitted for binding. The available options are:
| |
|---|---|---|---|---|
...
|
...
|
...
| ||
Header properties |
|---|
...
Use this fieldset to define header properties | ||||
...
Header key
...
to bind the queue with an exchange as arguments.
| |||||
Only one Header can be specified in each row. Click to add a new row in this table and specify the values accordingly.
This fieldset comprises the following fields:
- Header key
- Header value
Header key Default Value: N/A | String/Expression | None | Specify the name of the header that is being used for the binding. |
|---|---|---|---|
Header value |
...
Default Value: N/A | String/Expression | None | Specify the header value corresponding to the respective header key. |
|---|---|---|---|
Argument properties |
...
Use this field set to define custom argument properties to ensure all declarations for the queues use the same configuration/options/arguments. |
...
This fieldset comprises the following fields:
Argument key |
...
Specifies the name of the argument used for declaration. See Optional Arguments in RabbitMQ documentation for more information.
Default value: N/A |
...
Default value: None.
...
| String/Expression | None | Specify the name of the argument used for declaration. Learn more about Optional Arguments in RabbitMQ documentation. |
Argument value Default value: N/A |
...
, quorum | String/Expression | None | Specify the value corresponding to the argument key.
| ||
Message Count Default value: -1 | Integer/Expression | None | Controls the number of messages to be consumed from the destination queue before the consumer is stopped. Negative integer | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
...
value, that is the default value of -1 makes the consumer run indefinitely. |
Possible values include:
|
...
|
...
| Info |
|---|
The Consumer Snap processes one document only when the Message Count property is configured to a negative integer (for example, -1). |
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
| |
Maximum connection attempts | |
|---|---|
...
Default Value: 3 | Integer | None | Specify the maximum number of connection attempts in case of a connection failure. The Snap retries for the configured number of attempts for establishing the connection. If it exceeds the configured value, and the Route connection errors property is enabled, the messages are routed to the error view with the error information along with the original. When the Route connection errors property is disabled, the Snap displays the number of published messages along with the error information, however, the Snap fails. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Default value: 3
Connection retry interval Default Value: 10 | Integer | None | Specify the time taken in seconds to wait before retrying for another connection. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Route connection errors Default | ||||
...
Value: |
|---|
...
Deselected | Checkbox | None | Select this checkbox to route the connection errors to the error view displaying the error information along with the original. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
...
If |
...
you deselect this checkbox, the Snap fails to execute. | |
Snap Execution Default | |
|---|---|
...
Value: Validate & Execute | Dropdown list | None | Indicates how the Snap must be executed. Available options are:
| |
|---|---|---|---|---|
...
Default value: Validate & Execute
...
| Multiexcerpt include macro | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
...
| name | Snap_Execution_Introduced |
|---|---|
| page | Anaplan Read |
Examples
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
|
...
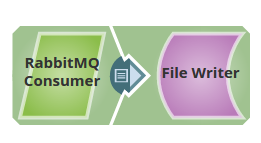
This example Pipeline demonstrates how to consume messages from a specified queue and |
...
write them to the output view. The RabbitMQ Consumer Snap, consumes the messages from the queue |
...
DemoQueue |
...
either in synchronous or asynchronous mode. Note that the Consumer creates the Exchange and Queue if they are |
...
unavailable in the RabbitMQ server, and binds them based on the properties configured such as Routing key, Header Properties, x-match etc., and then starts consuming the messages from the server. |
...
Successful execution of the |
...
Pipeline displays the message properties in the output preview: |
...
| Expand | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
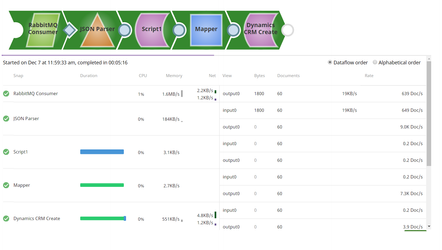
In the below |
...
Pipeline, the RabbitMQ Consumer Snap reads the messages from a queue and sends them to the CRM instance. The JSON Parser parses the messages and maps the messages to the CRM instance. The Script Snap is configured for a time delay |
...
to process all the messages configured in the queue |
...
. |
...
Snap Pack History
| Insert excerpt | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
.png?version=1&modificationDate=1489658399918&cacheVersion=1&api=v2&width=612)