Snap type | Write
|
|---|
Description | info |
This Snap works only with single queries.This Snap allows you to execute a Teradata statement/query. This Snap works only with single queries. | Note |
|---|
| You can drop your database with it, so be cautious. |
Valid JSON paths that are defined in the where clause for queries/statements will be substituted with values from an incoming document. Documents will be written to the error view if the document is missing a value to be substituted into the query/statement. If a select query is executed, the query's results are merged into the incoming document and any existing keys will have their values overwritten. On the other hand, the original document is written if there are no results from the query.
| Note |
|---|
The Teradata Execute Snap is for simple DML (SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE) type statements. |
|
|---|
| Prerequisites | None
|
|---|
| Support and limitations | Works in Ultra Task Pipelines. |
|---|
| Behavior Change | In 4.26, when the stored procedures were called using the Database Execute Snaps, the queries were treated as write queries instead of read queries. So the output displayed message and status keys after executing the stored procedure.
In 4.27, all the Database Execute Snaps run stored procedures correctly, that is, the queries are treated as read queries. The output now displays message key, and OUT params of the procedure (if any). The status key is not displayed. If the stored procedure has no OUT parameters then only the message key is displayed with value success.
| Note |
|---|
If you have any existing Pipelines that are mapped with status key or previous description then those Pipelines will fail. So, you might need to revisit your Pipeline design. |
|
|---|
| Account | This Snap uses account references created on the Accounts page of SnapLogic Manager to handle access to this endpoint. See Configuring Teradata Database Accounts for information on setting up this type of account. |
|---|
| Views |
| Input | This Snap has at most one document input view. If the input view is defined, then the where clause can substitute incoming values for a given expression. |
|---|
| Output | This Snap has at most one document output view. If an output view is available and an update/insert/merge/delete statement was executed, then the original document that was used to create the statement will be output with the status of the statement executed. |
|---|
| Error | This Snap has at most one document error view and produces zero or more documents in the view. | Note |
|---|
| Database write Snaps output all records of a batch (as configured in your account settings) to the error view if the write fails during batch processing. |
|
|---|
|
|---|
Settings |
|---|
Label*
| Specify the name for the Snap. You can modify this to be more specific, especially if you have more than one of the same Snap in your Pipeline. Default Value: Teradata Execute
Example: Teradata Execute |
|---|
SQL statement*
| Specify the SQL statement to execute on the server. There are two possible scenarios that you encounter when working with SQL statements in SnapLogic. You must understand the following scenarios to successfully execute your SQL statements: | Info |
|---|
| title | Scenarios to successfully execute your SQL statements |
|---|
| Scenario 1: Executing SQL statements without expressions
If the expression toggle of the SQL statement field is disabled: - The SQL statement must not be within quotes.
- The $<variable_name> parts of the SQL statement are expressions. In the below example, $id and $book.
For example: 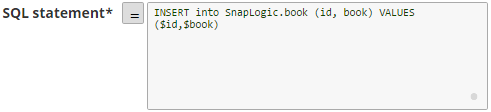
Additionally, the JSON path is allowed only in the WHERE clause. If the SQL statement starts with SELECT (case-insensitive), the Snap regards it as a select-type query and executes once per input document. If not, it regards it as write-type query and executes in batch mode. Scenario 2: Executing SQL queries with expressions
If the expression toggle of the SQL statement field is selected: - The SQL statement must be within quotes.
- The + $<variable_name> + parts of the SQL statement are expressions, and must not be within quotes. In the below example, $tablename.
- The $<variable_name> parts of the SQL statement are bind parameter, and must be within quotes. In the below example, $id and $book.
|
| Note |
|---|
Table name and column names must not be provided as bind parameters. Only values can be provided as bind parameters. |
For example: 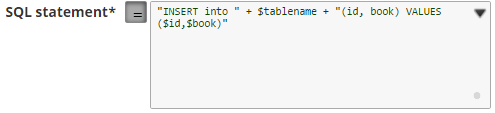
| Info |
|---|
We recommend you to add a single query in the SQL Statement field. |
Known issue: When the SQL statement property is an expression, the Pipeline parameters are shown in the suggest, but not the input schema.
| Note |
|---|
- The non-expression form uses bind parameters, so it is much faster than executing N arbitrary SQL expressions.
With the SQL statement property set as an expression, the Snap can be exposed to SQL injection. Please use this feature with caution. - The '$' sign and identifier characters, such as double quotes (“), single quotes ('), or back quotes (`), are reserved characters and should not be used in comments or for purposes other than their originally intended purpose.
|
| Warning |
|---|
| title | Single quotes in values must be escaped |
|---|
| Any relational database (RDBMS) treats single quotes (') as special symbols. So, single quotes in the data or values passed through a DML query may cause the Snap to fail when the query is executed. Ensure that you pass two consecutive single quotes in place of one within these values to escape the single quote through these queries. For example: | If String | To pass this value | Use |
|---|
| Has no single quotes | Schaum Series | 'Schaum Series'
| | Contains single quotes | O'Reilly's Publication
| 'O''Reilly''s Publication' |
|
Default Value: [None] |
|---|
| Query type | Select the type of query for your SQL statement (Read or Write). When Auto is selected, the Snap tries to determine the query type automatically.
If the execution result of the query is not as expected, you can change the query type to Read or Write. Default Value: Auto
Example: Read |
|---|
Pass through
| Select this checkbox to pass the input document to the output view under the key 'original'. This property applies only to the Execute Snaps with SELECT statement. Default Value: Selected |
|---|
Ignore empty result
| Select this checkbox to ignore empty result; no document will be written to the output view when a SELECT operation does not produce any result.
If you deselect this checkbox and select the Pass through checkbox, the input document will be passed to the output view. Default Value: Not selected |
|---|
| Multiexcerpt macro |
|---|
| Number of retries |
|
| Multiexcerpt macro |
|---|
| name | ME_Number_of_retries_Desc |
|---|
| Specify the maximum number of reconnection attempts that the Snap must perform, in case of connection failure or timeout. Default Value: 0 |
|
|---|
| Multiexcerpt macro |
|---|
| Retry interval (seconds)
|
|
| Multiexcerpt macro |
|---|
| name | ME_Retry_Interval_Desc |
|---|
| Enter in seconds the duration for which the Snap must wait between two reconnection attempts, until the number of retries is reached. Default Value: 1 |
|
|---|
Auto commit | Select one of the options for this property to override the state of the Auto commit property on the account. The Auto commit at the Snap-level has three values: True, False, and Use account setting. The expected functionality for these modes are: - True - The Snap will execute with auto-commit enabled regardless of the value set for Auto commit in the Account used by the Snap.
- False - The Snap will execute with auto-commit disabled regardless of the value set for Auto commit in the Account used by the Snap.
- Use account setting - The Snap will execute with Auto commit property value inherited by the Account used by the Snap.
Default Value: Use account setting
Example: False | Note |
|---|
'Auto commit' may be enabled for certain use cases if PostgreSQL jdbc driver is used in either Redshift, PostgreSQL or generic JDBC Snap. But the JDBC driver may cause out of memory issues when Select statements are executed. In those cases, “Auto commit" in Snap property should be set to ‘False’ and the Fetch size in the “Account setting" can be increased for optimal performance. |
| Multiexcerpt include macro |
|---|
| name | DDL Auto Commit |
|---|
| page | PostgreSQL - Execute |
|---|
|
|
|---|
| Advanced options | Select the option ‘Timestamp with microsecond precision’ to support the microsecond precision for TIMESTAMP data type. The SELECT query for TIMESTAMP columns produces string values with microsecond precision in the output documents. Default Value: None |
|---|
| Multiexcerpt include macro |
|---|
| name | Snap Execution |
|---|
| page | SOAP Execute |
|---|
|
| | Multiexcerpt include macro |
|---|
| name | Execution_Detail_Write |
|---|
| page | SOAP Execute |
|---|
|
|
|---|


.png?version=1&modificationDate=1489644645122&cacheVersion=1&api=v2)
.png?version=1&modificationDate=1489644905603&cacheVersion=1&api=v2&width=1000)