In this article
| Table of Contents | ||
|---|---|---|
|
...
On this page
| Table of Contents | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
List of articles in this section
| Child pages (Children Display) |
|---|
Overview
You can configure your Groundplex nodes through the Create Snaplex or Update Snaplex dialogs in SnapLogic Manager or directly through the Snaplex properties file. Additionally, you can customize your Groundplex configuration through the global.properties fields.
For defining network settings in your Grounplex, refer to Groundplex Network Setup.
Node Property Configuration
Do not make changes to your configuration without consulting your SnapLogic
...
The various configuration options for the Snaplex process are documented here. These options can be added (or the existing value updated) in the Updating a Snaplex dialog. Java Component Container (JCC) configuration updates takes effect when the Snaplex process is restarted by running /opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh restart or c:\opt\snaplogic\bin\jcc.bat restart.
The various configuration options for the Snaplex process are documented in this page. These options can be added (or the existing value updated) using the SnapLogic Manager, Updating a Snaplex dialog, Node Properties tab.
Java Component Container (JCC) configuration updates take effect when the Snaplex is restarted by running the command: /opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh restart OR c:\opt\snaplogic\bin\jcc.bat restart.
Logs
SnapLogic logs are written to the /opt/snaplogic/run/log directory. Two types of processes write events and errors to the logs – JCC and Monitor. The JCC process tracks events, while the Monitor process monitors the health of the JCC. FeedMaster logs are also included.
jcc_json–Main log for tracking SnapLogic application event and error messages.- j
cc_error.json–As errors are encountered, verbose error messages are written to this log. jcc.output.log–As the JCC is booting up, any informational, debugging, and error messages are written to this log.- j
cc_access.log–All requests to the node are written to this log. jcc.status.log–JCC status is periodically written to this log.monitor.log–As the status of the monitor process initializes, events and errors are written to this log during boot up.monitor.json–The main log for tracking the monitoring application.monitor_error.json–Verbose error messages are written to this log, such as the stack traces.feed_master.json—The log for tracking FeedMaster event and error messages.feed_master_error.json—As errors are encountered, verbose error messages are written to this log.feed_master_access.log—All requests to the node are written to this log.
The logs are rotated based on file size into the /opt/snaplogic/run/log/backup directory.
All logs rotate after they become 50MB in size. The logs are compressed and written to the backup directory. Ten of the latest backup files are maintained, while the older files are automatically deleted.
Understanding Distribution of Data Processing across Snaplex Nodes
When a Pipeline or Task is executed, the work is assigned to one of the JCC nodes in the Snaplex. Depending on a number of variables, the distribution of work across JCC nodes is determined by number of threads in use, the amount of memory available, and the average system load.
| Note |
|---|
To ensure that requests are being shared across JCC nodes, we recommend that you set up a load balancer to distribute the work across JCC nodes in the Snaplex. |
Node Cluster
Starting multiple nodes with the JCC service pointing to the same Snaplex configuration automatically forms a cluster of nodes, as long as you follow these requirements for nodes in a Snaplex:
- The nodes need to communicate to each other on the following ports: 8081, 8084, and 8090.
- The nodes should have a reliable, low-latency network connection between them.
- The nodes should be homogeneous in that they should have similar CPU and memory configurations, as well as access the same network endpoints.
Heap Space
...
CSM.
Various configuration options can be added, or the existing values updated, in the Node Properties tab on the Update Snaplex dialog in SnapLogic Manager.
Making Snaplex Configuration Changes
Snaplex nodes are typically configured using the slpropz configuration file located in the $SL_ROOT/etc folder.
If you use the slpropz file as your Snaplex configuration, then you can expect the following:
After a Snaplex node is started with the slpropz configuration, subsequent configuration updates are applied automatically.
Changing the Snaplex properties in Manager causes each Snaplex node to download the updated
slpropzand do a rolling restart with no downtime on Snaplexes with more than one node.Some configuration changes, such as an update to the logging properties, do not require a restart and are applied immediately.
Some configuration properties, like the Environment value, cannot be changed without doing manual updates for the
slpropzfiles on the Snaplex nodes.
The Groundplex nodes must be set up to use a slpropz configuration file before changes to these properties take effect. If you make changes that affect the software configuration, but there are nodes in the Snaplex that are not set up to use a slpropz configuration file, a warning dialog appears with a listing of the unmanaged nodes. Learn more about setting up a node to use this configuration mechanism when you add a node to your Snaplex. for more information on setting up a node to use this configuration mechanism.
Restarting the Groundplex Nodes
To restart the Snaplex process on your Groundplex nodes, run the following commands, depending on your OS:
Linux:
/opt/snaplogic/bin/jcc.sh restart
Windows:
c:\opt\snaplogic\bin\jcc.bat restart.
Managing Older Groundplex Installations
If you have an older Snaplex installation with a configuration defined in the global.properties file, then the Environment value must match the jcc.environment value In the JCC global.properties file. To migrate your Snaplex configuration to the slpropz mechanism, see Migrating Older Snaplex Nodes.
You should always configure your Snaplex instances using the slpropz file because you do not have to edit the configuration files manually. Changes to the Snaplex done through Manager are applied automatically to all nodes in that Snaplex.
Temporary Folder
The temporary folder stores unencrypted data. These temporary files are deleted when the Snap/Pipeline execution completes. You can update your Snaplex to point to a different temporary location in the Global properties table by entering the following:
jcc.jvm_options = -Djava.io.tmpdir=/new/tmp/folder
The following Snaps write to temporary files on your local disk:
Anaplan: Upload, Write
Binary: Sort, Join
Box: Read, Write
Confluent Kafka: All Snaps that use either Kerberos and SSL accounts
Database: When using local disk staging for read-type Snaps
Data Science (Machine Learning) Snaps: Profile, AutoML, Sample, Shuffle, Deduplicate, Match
Email: Sender
Hadoop: Read, Write (Parquet and ORC formats)
JMS: When the user provides a JAR file
Salesforce: Bulk Query, Snaps that process CSV data
Script: PySpark
Snowflake: When using internal staging
Teradata: TPT FastExport
Transform: Aggregate, Avro Parser, Excel Parser, Join, Unique, Sort
Vertica: Bulk Load
Workday Prism Analytics: Bulk Load
Heap Space
To change the maximum heap space used by your Snaplex,
...
edit the Maximum Heap Size
...
field setting in the
...
Snaplex dialog.
Default Auto Setting Behavior
The default is auto, meaning that SnapLogic automatically sets the maximum heap size based on the available memory. The auto setting uses the optimum fraction of physical memory available to the system and leaves sufficient memory for operating system usage, as follows:
For RAM up to
...
4 GB, 75% is allocated to Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
For RAM over
...
4 GB and up to
...
8 GB, 80% is allocated to JVM.
For RAM over
...
8 GB and up to
...
32 GB, 85% is allocated to JVM.
For RAM over
...
32 GB, 90% is allocated to JVM
...
.
Custom Heap Setting
If you
...
enter your own heap space value, one method is
...
to set the value to approximately
...
1 GB less than the amount of RAM available on
...
Guidelines
...
the machine.
We recommend that you appropriately set the heap space for optimum Snaplex performance.
If the heap space value is excessively high, this can cause the machine to swap memory to disk, degrading performance.
...
If the heap space value is excessively low, this can cause pipelines that require higher memory to fail or degrade in performance.
Compressed Class Space
In Java,
...
objects are instantiations of
...
classes. Object data is stored on the heap, and class data is stored in
...
nonheap space for memory allocation.
The default compressed class space size is
...
automatically raised to 2 GB to prevent pipeline preparation errors when the JVM heap space size is more than
...
10 GB.
If
...
a Pipeline Failed to Prepare error displays related to compressed class space,
...
you can customize this setting in the Snaplex Global Properties.
To override the default, add the following global property, where N is the custom size of the compressed class space.
Key | Value |
|---|---|
|
...
|
...
HTTP Proxy Configuration
Refer to the Node Proxies section for information about configuring through an HTTP proxy.
HTTP Port
The HTTP port used by the JCC is configurable in the Update Snaplex dialog, Node Properties tab, HTTP Port property.
Default value is 8090 for JCC, 8091 for FeedMaster.
Updating this option modifies the global.properties file by setting the port number to the following value:
| Code Block |
|---|
jcc.jetty_port = 8090 |
HTTPS Port
The HTTPS port is configurable in the Update Snaplex dialog, Node Properties tab, HTTPS Port property.
Default value is 8081 for JCC, 8084 for FeedMaster.
Updating this option modifies the global.properties file by setting the port number to the following value:
| Code Block |
|---|
jcc.cc_secure_port = 8888 |
FeedMaster Broker Port
The FeedMaster uses port 8089 by default for the message broker. To change this, add the following entry:
...
jcc.broker_service_uri = ssl://0.0.0.0:8089?transport.enabledProtocols=TLSv1,TLSv1.1,TLSv1.2&transport.enabledCipherSuites=TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256,TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA,TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA
in the Update Snaplex dialog, Node Properties tab, Global properties table. The port used should be unique, it cannot be the same as used for the HTTP and HTTPS services.
Temporary Folder
This section explains what data traversing the SnapLogic platform is encrypted or unencrypted. The temporary folder stores unencrypted data.
Encrypted data:
Transit data – Is always encrypted, assuming the endpoint supports encryption.
Preview and Account data – Is always encrypted.
Unencrypted data:
Snaplex – Data processing on Groundplex, Cloudplex, and eXtremeplex nodes occur principally in-memory as streaming, which is unencrypted.
Larger dataset – When larger datasets are processed that exceed the available compute memory, some Snaps like Sort and Join, which process multiple documents, writes Pipeline data to the local disk as unencrypted during Pipeline execution to help optimize the performance. These temporary files are deleted when the Snap/Pipeline execution completes. You can update your Snaplex to point to a different temporary location in the Global properties table of the Node Properties tab in the Update Snaplex dialog:
| Code Block |
|---|
jcc.jvm_options = -Djava.io.tmpdir=/new/tmp/folder |
The following Snaps write to temporary files on your local disk:
Anaplan: Upload, Write
Binary: Sort, Join
Box: Read, Write
Confluent Kafka: All Snaps that use either Kerberos and SSL accounts
Database: When using local disk staging for read-type Snaps
Email: Sender
Hadoop: Read, Write (Parquet and ORC formats)
JMS: When the user provides a JAR file
Salesforce: Bulk Query, Snaps that process CSV data
Script: PySpark
Snowflake: When using internal staging
Teradata: TPT FastExport
Transform: Aggregate, Avro Parser, Excel Parser, Join, Unique, Sort
Vertica: Bulk Load
Workday Prism Analytics: Bulk Load
Data Science (Machine Learning) Snaps: Profile, AutoML, Sample, Shuffle, Deduplicate, Match
Snaplex Network Binding
By default, the Snaplex starts and binds to the localhost network interface on port 8090. Any clients can connect to the JCC only if the client is also running on the same machine. This default is chosen since the Snaplex is not be receiving any inbound requests normally. It instead uses an outbound WebSocket connection to receive its requests from the SnapLogic cloud services. If requests need to be sent to the Snaplex from the customer network, then the Snaplex should be configured to listen on its network interfaces. This would be required when a feed URL Pipeline execution request is done by pointing directly at the Snaplex host instead of pointing at the cloud URL. To do this, set (default is 127.0.0.1):
| Code Block |
|---|
jcc.jetty_host = 0.0.0.0 |
...
If the hostname used by the Snaplex needs to be configured to be a different value than the machine name (for example newname.mydomain.com), add:
| Code Block |
|---|
jcc.jvm_options = -DSL_INTERNAL_HOST_NAME=newname.mydomain.com -DSL_EXTERNAL_HOST_NAME=newname.mydomain.com |
in the etc/global.properties by adding it to the Update Snaplex dialog, Node Properties tab, Global properties table.
Automatic Updates
The Snaplex process automatically updates itself to run the same version as running on the SnapLogic cloud. If there is a mismatch in the versions, the Snaplex cannot be used to run Pipelines.
When the Snaplex service is started, two Java processes are started. First is the Monitor process, which then starts the actual Snaplex process. The Monitor keeps track of the Snaplex process state, restarting it in case of failure. The Snaplex by default upgrades itself to run the same binaries as running on the SnapLogic cloud. The monitor process continues running always, running from the binary which was used when the Monitor was originally started. Running jcc.sh restart or jcc.bat restart restarts both the Monitor and the Snaplex processes.
In case a custom Snaplex patch is provided for a customer, it is provided as a jcc.war file. If this is copied into the /opt/snaplogic/run/lib directory and the JCC is restarted, the JCC again downloads the latest version of the war file. To prevent the Snaplex from going back to the default binaries, the Snaplex can be setup to disable downloading the current version from the SnapLogic cloud. To do this, check the value of build_tag as returned by https://elastic.snaplogic.com/status. For example, if the build tag is mrc27, adding
| Code Block |
|---|
jcc.skip_version = mrc27 |
...
The download of latest binaries and automatic updates can be disabled on the Snaplex. If so, the next time there is a new version available on the SnapLogic cloud, the Snaplex is no longer be usable since there would be a version mismatch. The automatic download would have to be re-enabled for the Snaplex to be usable again. To avoid such issues, the skip_version approach above is the recommended method to run with a custom version of the Snaplex binaries.
To prevent the new binaries from being downloaded, set (default is True):
| Code Block |
|---|
jcc.enable_auto_download = False |
To disable the automatic restart of the Snaplex after new binaries are downloaded, set (default is True):
| Code Block |
|---|
jcc.auto_restart = False |
JCC Debug
If the Snaplex is being used for Snap development and needs to be put in debug mode, the monitor process can be configured to start the JVM with debug options enabled. To do this, set:
| Code Block |
|---|
jcc.jvm_options = -agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=n,address=8000 |
in etc/global.properties. This starts the Snaplex process with debug port set to 8000, to which the debugger can be connected. Any Pipeline executions to the Snaplex would hit breakpoints set in the Snap code.
Snaplex Outbound Connections
The Snaplex process creates outbound WebSocket connections to the SnapLogic cloud to be able to process incoming requests from the cloud. If running several nested Pipelines, or Pipelines using ForEach, there could be timeout errors if no connection is available to process an inbound request. By default, 20 connections are created. This can be increased if a higher number of cloud triggered Pipelines need to be run concurrently on the Snaplex node. The maximum allow value is 60. Setting this too high causes increased network overhead. If this has to be set to a larger value, it is an indication that more nodes need to be added to the Snaplex. Pipeline execution requests is automatically be load balanced across the available nodes.
To increase this limit, set (default is 20):
| Code Block |
|---|
jcc.websocket_connection_count = 30 |
in the etc/global.properties by adding it to the Update Snaplex dialog, Node Properties tab, Global properties table.
HTTP Connection Pooling
Outbound HTTP connections created to the SnapLogic cloud or to any other HTTP endpoints are placed in a connection pool by default. The properties for the pool can be configured in etc/global.properties by adding it to the Update Snaplex dialog, Node Properties tab, Global properties table.
To increase the maximum number of connection which can be created at a time (default is 100)
| Code Block |
|---|
jcc.http_client_max_connections = 300 |
To set the TCP connection timeout for an outbound connection (in seconds, default is 60, zero is infinite timeout)
| Code Block |
|---|
jcc.http_client_tcp_connection_timeout = 120 |
To set the inactivity timeout for a socket connection (in seconds, default is 3600, zero is infinite timeout).
| Code Block |
|---|
jcc.http_client_socket_timeout = 300 |
The http_client_socket_timeout must be set to higher than the maximum child Pipeline execution time.
Ring Buffer
The size of the buffer between Snaps is configured by setting the jcc.disruptor_ring_buffer_size in the global.properties. The default value is 1024.
Clearing Node Cache Files
A clearcache option is added to the jcc.sh/jcc.bat file to clear the cache files from the node.
| Warning |
|---|
You must ensure that the JCC is stopped before running the |
...
N |
Configure Snaplex Memory for Dynamic Workloads
If you either expect the Snaplex workload to be ad-hoc or cannot plan for the memory requirements, then the default heap memory settings on the Snaplex might not be appropriate. For example, these scenarios might require customizing the settings:
The Pipeline data volume to process varies significantly based on input data.
The Pipeline development or execution is performed by multiple teams, which makes capacity planning difficult.
The resources available in your test or development environment are lower than the production Snaplex.
In all these scenarios, setting the maximum heap size to a lower value than the available memory can result in memory issues. Because the workload is dynamic, if your existing Pipelines that are running use additional memory, then the JCC node might hit your configured maximum memory limit. When this limit is reached, the JCC displays an OutOfMemory exception error and restarts, causing all Pipelines that are currently running to fail.
To allow the JCC to manage memory limits optimally, you can use the swap configuration on the Snaplex nodes. Doing so allows your JCC node to operate with the configured memory in normal conditions, and if memory is inadequate, the JCC node can use the swap memory with minimal degradation in Pipeline performance.
For Linux-based Groundplexes, we recommend that you use the following swap values:
Node Name | Node Type | Minimum Swap | Recommended Swap |
|---|---|---|---|
Medium Node | 2 vCPU 8 GB memory, 40 GB storage | 8 GB | 8 GB |
Large Node | 4 vCPU 16 GB memory, 60 GB storage | 8 GB | 8 GB |
X-Large Node | 8 vCPU 32 GB memory, 300 GB storage | 8 GB | 16 GB |
2X-Large Node | 16 vCPU 64 GB memory, 400 GB storage | 8 GB | 32 GB |
Medium M.O. Node | 2 vCPU 16 GB memory, 40 GB storage | 8 GB | 8GB |
Large M.O. Node | 4 vCPU 32 GB memory, 60 GB storage | 8 GB | 16 GB |
X-Large M.O. Node | 8 vCPU 64 GB memory, 300 GB storage | 8 GB | 32 GB |
2X-Large M.O. Node | 16 vCPU 128 GB memory, 400 GB storage | 8 GB | 64 GB |
Linux gives you two options for allocating swap space: a swap partition or a swap file. Configure a swap file, and you do not have to restart the node. Learn more about using a swap file on Linux machines and configuring swap in AWS.
Performance Implications
When enabling the swap, the IO performance of the volume is critical to achieve an acceptable performance when the swap is utilized.
On AWS, we recommend that you use Instance Store instead of EBS volume to mount the swap data. Refer to Instance store swap volumes for details.
When your workload exceeds the available physical memory and the swap is utilized, the JCC node can become slower because of additional IO overhead caused by swapping. Therefore, configure a higher timeout for
jcc.status_timeout_secondsandjcc.jcc_poll_timeout_secondsfor the JCC node health checks.Even after configuring the swap, the JCC process can still run out of resources if all the available memory is exhausted. This scenario triggers the JCC process to restart, and all running Pipelines are terminated. We recommend that you use larger nodes with additional memory for the workload to complete successfully.
We recommend that you limit setting the swap to the maximum swap to be used by the JCC node. Using a larger swap configuration causes performance degradation during the JRE garbage collection operations.
Best Practices
Memory swapping can result in performance degradation because of disk IO, especially if the Pipeline workload also utilizes local disk IO.
When the pipeline workload is dynamic and capacity planning is difficult, we strongly recommend the minimum swap configuration.
Swap Memory Configuration Workflow
To utilize swap for the JCC process, you can use this workflow:
Enable swap on your host machine. The steps depend on your operating system (OS). For example, for Ubuntu Linux, you can use the steps in this tutorial.
Update your Maximum memory Snaplex setting to a lower percentage value, such that the absolute value is lower than the available memory. The load balancer uses this value when allocating Pipelines. The default is to set to 85%, which means that if the node memory usage is above 85% of the maximum heap size, then additional pipelines cannot start on the node.
Add the following two properties in the Global properties section of the Node Properties tab in the Update Snaplex dialog:
jcc_poll_timeout_secondsis the timeout (default value is 10 seconds) for each health check poll request from the Monitor.status_timeout_secondsis the time period (default value is 300 seconds) that the Monitor process waits for before the JCC is restarted if the health check requests continuously fail.
Example:
Key | Value |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Ring Buffer
The size of the buffer between Snaps is configured by setting the feature flags on the org com.snaplogic.cc.jstream.view.publisher.AbstractPublisher.DOC_RING_BUFFER_SIZE, where the default value is 1024 and com.snaplogic.cc.jstream.view.publisher.AbstractPublisher.BINARY_RING_BUFFER_SIZE, where the default value is 128.
| Code Block |
|---|
com.snaplogic.cc.jstream.view.publisher.AbstractPublisher.DOC_RING_BUFFER_SIZE=1024
com.snaplogic.cc.jstream.view.publisher.AbstractPublisher.BINARY_RING_BUFFER_SIZE=128 |
Clearing Node Cache Files
A clearcache option is added to the jcc.sh/jcc.bat file to clear the cache files from the node.
| Note |
|---|
You must ensure that the JCC is stopped before running the |
Customizing Version Updates
The Snaplex process automatically updates itself to run the same version as running on the SnapLogic cloud. If there is a mismatch in the versions, the Snaplex cannot be used to run Pipelines.
When the Snaplex service is started, two Java processes are started. First is the Monitor process, which then starts the actual Snaplex process. The monitor keeps track of the Snaplex process state, restarting it in case of failure. The Snaplex by default upgrades itself to run the same binaries that are running on the SnapLogic cloud. The monitor process continues running always, running from the binary which was used when the Monitor was originally started. Running jcc.sh restart or jcc.bat restart restarts both the monitor and the Snaplex processes.
In case a custom Snaplex patch is provided for a customer, it is provided as a jcc.war file. If this is copied into the /opt/snaplogic/run/lib directory and the JCC node is restarted, the JCC again downloads the latest version of the war file. To prevent the Snaplex from going back to the default binaries, you can setup the Snaplex to disable downloading the current version from the SnapLogic cloud. To do this, check the value of build_tag as returned by https://elastic.snaplogic.com/status. For example, if the build tag is mrc27, adding the following line in etc/global.properties prevents the Snaplex from downloading the mrc27 version from the cloud.
|
When the next release is available on the cloud and the custom patch is no longer required, the Snaplex automatically downloads the next version.
The download of latest binaries and automatic updates can be disabled on the Snaplex. If so, the next time there is a new version available on the SnapLogic cloud, the Snaplex is no longer be usable since there would be a version mismatch. The automatic download would have to be re-enabled for the Snaplex to be usable again.
To avoid such issues, the skip_version approach above is the recommended method to run with a custom version of the Snaplex binaries.
To prevent the new binaries from being downloaded, set (default is True):
jcc.enable_auto_download = False
To disable the automatic restart of the Snaplex after new binaries are downloaded, set (default is True):
jcc.auto_restart = False
JCC Node Debug Mode
If you are using the Snaplex for Snap development and it needs to be put in debug mode, you can configure the monitor process to start the JVM with debug options enabled. Add the following line in etc/global.properties
jcc.jvm_options = -agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=n,address=8000
This starts the Snaplex process with the debug port set to 8000. Otherwise, any Pipeline executions sent to the Snaplex would hit breakpoints set in the Snap code.
Configuring Bouncy Castle as the first Security Provider in your Snaplex
The JCC node contains a list of security providers to enable Snaps to work with SSL or private keys. SUN is the default and the main security provider. However, the SUN provider might not handle some private keys, resulting in an InvalidAlgorithmException error. In such cases, you must ensure that the
...
Bouncy Castle security provider is used as the main security provider; otherwise, the Pipelines fail.
You can enable a flag in the node properties to make
...
Bouncy Castle the first security provider.
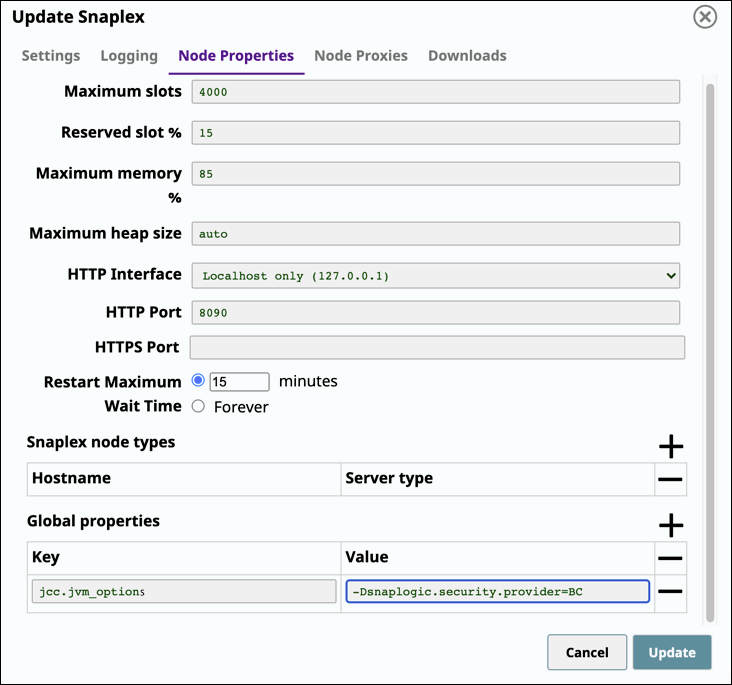
In the Node Properties tab of your target Snaplex, add the following key/value pair under Global Properties:
Key:
jcc.jvm_optionsValue:
-Dsnaplogic.security.provider=BC
...
Click Update, and then restart the Snaplex node.
...
| Info |
|---|
If you switch to |
...
Bouncy Castle as the main security provider, then Redshift accounts working with Amazon Redshift JDBC Driver fail if the driver version is below 2.0.0.4. As a |
...
workaround, use the Redshift driver 2.0.0.4 or later and provide the JDBC URL. |