XML Parser
Lakshmi Manda (Deactivated)
Aparna Tayi (Unlicensed)
Kalpana Malladi
On this Page
Snap type: | Parse | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Description: | This Snap parses the incoming XML data into SnapLogic document objects. | |||||||||
| Prerequisites: | [None] | |||||||||
| Support: | Works in Ultra Tasks. | |||||||||
| Limitations | Mixed content such as below is not supported. XML data with mixed content may contain attributes, elements, and text. | |||||||||
| Account: | Accounts are not used with this Snap. | |||||||||
| Views: |
| |||||||||
Settings | ||||||||||
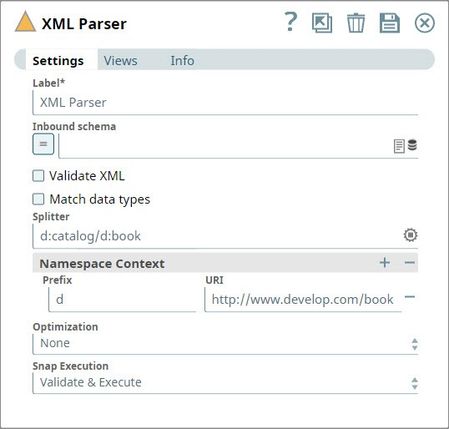
Label | Required. The name for the Snap. You can modify this to be more specific, especially if you have more than one of the same Snap in your pipeline. | |||||||||
Inbound Schema | XSD schema definition file url for the incoming data. The currently supported url protocols are SLDB, HDFS, S3. If you enter an Inbound schema, then you must select Validate XML and Match data types properties to derive the output as per the defined schema. Example: sldb:///foo/bar/customer.xsd Default value: [None] | |||||||||
| Validate XML | Required. If selected, the incoming data will be validated against the provided XSD schema definition. If you enter an Inbound schema, then you must select Validate XML and Match data types properties to derive the output as per the defined schema. Example: False Default value: False | |||||||||
| Splitter | Splits the incoming XML document into multiple smaller documents using the XPath expression. This expression must be of the form a/b/c/d or ns1:a/ns2:b/ns3:c/ns4:d where the prefixes ns1 to 4 can be the same or different. Example 1: Splitter Expression without prefix Default namespace can be accessed by giving a unique prefix in the splitter expression followed by a colon and the tag value. Provide its corresponding namespace value in the Prefix URI table.
The output view is:
Default value: [None] | |||||||||
Namespace Context optional | Namespace context for the expression provided in the Splitter property. Namespaces are typically defined in the format of xmlns prefix:URI | |||||||||
Prefix | Prefixes included in the expression provided in the Splitter property. | |||||||||
URI | URIs associated with the prefixes. | |||||||||
Match data types | Specifies the values in the input document as specified in the Inbound schema property.
| |||||||||
| Optimization | Select the parameter that you want to optimize during Snap execution. Available options:
Default value: None | |||||||||
Snap Execution | Select one of the three modes in which the Snap executes. Available options are:
Default Value: Execute only | |||||||||
Schema language supported : W3C XML Schema 1.0
Examples
Splitting XML
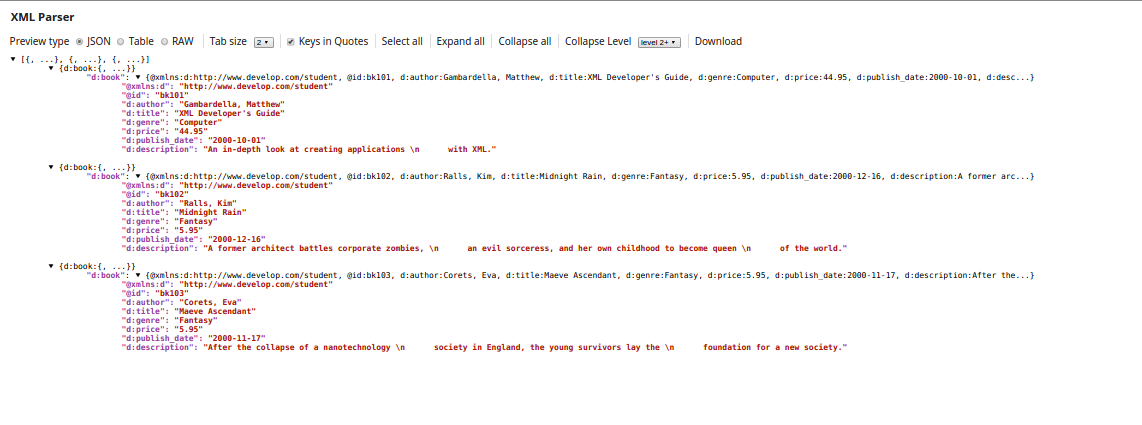
In this example, XML that contains multiple purchase orders is split into individual orders.
The incoming XML looks something like this:
<po:PurchaseOrders xmlns:po="http://www.example.com">
<po:PurchaseOrder po:PurchaseOrderNumber="23578" po:OrderDate="2015-01-20">
<po:Address po:Type="Shipping">
<po:Name>Full Name</po:Name>
<po:Street>123 Maple Street</po:Street>
<po:City>City Name</po:City>
<po:State>CA</po:State>
<po:Zip>10101</po:Zip>
<po:Country>USA</po:Country>
</po:Address>
<po:Address po:Type="Billing">
<po:Name>Another Name</po:Name>
<po:Street>456 Oak Avenue</po:Street>
<po:City>Town Name</po:City>
<po:State>NJ</po:State>
<po:Zip>99999</po:Zip>
<po:Country>USA</po:Country>
</po:Address>
<po:DeliveryNotes>Please leave packages on side porch.</po:DeliveryNotes>po
<po:Items>
<po:Item po:PartNumber="123456">
<po:ProductName>Product</po:ProductName>
<po:Quantity>1</po:Quantity>
<po:USPrice>89.90</po:USPrice>
<po:Comment>Refurbished</po:Comment>
</po:Item>
</po:Items>
</po:PurchaseOrder>
<po:PurchaseOrder po:PurchaseOrderNumber="23579" po:OrderDate="2015-01-20">
...
</po:PurchaseOrder>
</po:PurchaseOrders>
Each PurchaseOrder contains the shipping address, billing address and the items purchased.
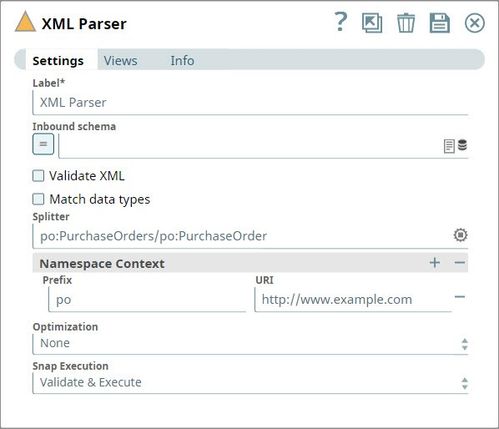
To split these into individual orders, the Splitter field should contain the hierarchy down to where you want the split to occur, including any specified prefix. In this case, the value is: po:PurchaseOrders/po:PurchaseOrder.
You will also need to specify the Namespace Context, which is defined in the sample as xmlns:po="http://www.example.com".
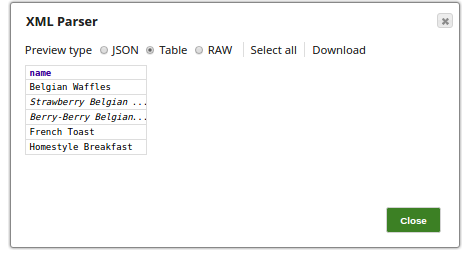
This will result in separating the orders into individual documents.
[{, ...}, {, ...}, {, ...}]
{po:PurchaseOrder:{, ...}}
{po:PurchaseOrder:{, ...}}
{po:PurchaseOrder:{, ...}}
| Release | Snap Pack Version | Date | Type | Updates | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| February 2025 | 440patches30186 | Latest | Fixed an issue with the CSV Parser Snap when a multichar delimiter is used and data has a single column with multi-line value. | |||||||
| February 2025 | 440patches29909 | Latest | Updated the Apache POI library from 4.1.2v to 5.2.5v in the Excel Parser Snap to fix the null pointer exception issue. | |||||||
February 2025 | main29887 | | Stable | Updated and certified against the current SnapLogic Platform release. | ||||||
| November 2024 | 439patches29700 | Latest | Improved Join Snap’s resource management to detect output stream closure failures, throwing an exception at the debug log level for better diagnostics. | |||||||
| November 2024 | 439patches29416 | Latest | Minimized the possibility of | |||||||
| November 2024 | 439patches29078 | Latest | Fixed an issue with the CSV Parser Snap that introduced unexpected characters into the records and output data because of incorrect handling of the delimiter. | |||||||
| November 2024 | main29029 | Stable | Updated and certified against the current SnapLogic Platform release. | |||||||
| August 2024 | 438patches28073 | Latest | Fixed an issue with the JSON Generator and XML Generator Snaps that caused unexpected output displaying '__at__' and '__h__' instead of '@' and '-' respectively because the Snap could not update them to their original values after the Velocity library upgrade. | |||||||
| August 2024 | 438patches27959 | Latest | Fixed an issue with the Sort where the Snap could not sort files larger than 52 MB. This fix applies to Join Snap also. | |||||||
| August 2024 | main27765 | Stable | Upgraded the org.json.json library from v20090211 to v20240303, which is fully backward compatible. | |||||||
| May 2024 | 437patches26643 | Latest |
| |||||||
| May 2024 | 437patches26453 | Latest |
| |||||||
| May 2024 | main26341 | Stable |
| |||||||
| February 2024 | 436patches25564 | Latest | Fixed an issue with the JSON Formatter Snap that generated incorrect schema. | |||||||
| February 2024 | 436patches25292 | Latest | Fixed an If the input documents are unsorted and GROUP-BY fields are used, you must use the Sort Snap upstream of the Aggregate Snap to presort the input document stream and set the Sorted stream field Ascending or Descending to prevent the Learn more about presorting unsorted input documents to be processed by the Aggregate Snap. | |||||||
| February 2024 | main25112 | Stable | Updated and certified against the current SnapLogic Platform release. | |||||||
| November 2023 | 435patches24802 | Latest | Fixed an issue with the Excel Parser Snap that caused a null pointer exception when the input data was an Excel file that did not contain a StylesTable. | |||||||
| November 2023 | 435patches24481 | Latest | Fixed an issue with the Aggregate Snap where the Snap was unable to produce the desired number of output documents when the input was unsorted and the GROUP-BY fields field set was used. | |||||||
| November 2023 | 435patches24094 | Latest | Fixed a deserialization issue for a unique function in the Aggregate Snap. | |||||||
| November 2023 | main23721 | Stable | Updated and certified against the current SnapLogic Platform release. | |||||||
| August 2023 | 434patches23076 | Latest | Fixed an issue with the Binary to Document Snap where an empty input document with Ignore Empty Stream selected caused the Snap to stop executing. | |||||||
| August 2023 | 434patches23034 | Latest | ||||||||
| August 2023 | 434patches22705 | Latest | Fixed an issue with the JSON Splitter Snap that caused the pipeline to terminate with excessive memory usage on the Snaplex node after the 4.33 GA upgrade. The Snap now consumes less memory. | |||||||
| August 2023 | main22460 | Stable | Updated and certified against the current SnapLogic Platform release. | |||||||
| May 2023 | 433patches22431 | Latest |
| |||||||
| May 2023 | 433patches21779 | Latest | The Decrypt Field and Encrypt Field Snaps now support CTR (Counter mode) for the AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) block cipher algorithm. | |||||||
| May 2023 | 433patches21586 | Latest | The Decrypt Field Snap now supports the decryption of various encrypted fields on providing a valid decryption key. | |||||||
| May 2023 | 433patches21461 | Latest | The following Transform Snaps include new fields to improve memory management: Aggregate, Group By Fields, Group By N, Join, Sort, Unique. | |||||||
| May 2023 | 433patches21336 | Latest | Fixed an issue with the AutoPrep Snap where dates could potentially be rendered in a currency format because currency format options were displayed for the DOB column. | |||||||
| May 2023 | 433patches21196 | Latest | Enhanced the In-Memory Lookup Snap with the following new fields to improve memory management and help reduce the possibility of out-of-memory failures:
These new fields replace the Maximum memory % field. | |||||||
| May 2023 | main21015 | Stable | Upgraded with the latest SnapLogic Platform release. | |||||||
| February 2023 | 432patches20535 | Latest | Fixed an issue with the Encrypt Field Snap, where the Snap failed to support an RSA public key to encrypt a message or field. Now the Snap supports the RSA public key to encrypt the message. | |||||||
| February 2023 | 432patches20446 | Latest | The Join Snap is enhanced with the following:
| |||||||
| February 2023 | 432patches20250 | Latest |
| |||||||
| February 2023 | 432patches20151 | Stable/Latest | Fixed an issue that occurred with the JSON Splitter Snap when used in an Ultra pipeline. The request was acknowledged before it was processed by the downstream Snaps, which caused a 400 Bad Request response. | |||||||
| February 2023 | 432patches20062 | Stable/Latest | Fixed the behavior of the JSON Splitter Snap for some use cases where its behavior was not backward compatible with the 4.31 GA version. These cases involved certain uses of either the Include scalar parents feature or the Include Paths feature. | |||||||
| February 2023 | 432patches19974 | Stable/Latest | Fixed the Review your pipelines where this error occurred to check your assumptions about the input to the JSON Splitter and whether the value referenced by the JSON Path to Split field will always be a list. If the input is provided by an XML-based or SOAP-based Snap like the Workday or NetSuite Snaps, a result set or child collection that’s an array when there's more than one result or child will be an object when there's only one result or child. In these cases, we recommend using a Mapper Snap and the | |||||||
| February 2023 | 432patches19918 | Stable/Latest |
| |||||||
| February 2023 | main19844 | Stable | Upgraded with the latest SnapLogic Platform release. | |||||||
| November 2022 | 431patches19441 | Stable | The Encrypt Field Snap supports decryption of encrypted output in Snowflake Snaps. | |||||||
| November 2022 | 431patches19385 | Latest | The Transform Join Snap now doesn’t fail with the | |||||||
| November 2022 | 431patches19359 | Latest | The JSON Splitter Snap includes memory improvements and a new Exclude List from Output Documents checkbox. This checkbox enables you to prevent the list that is split from getting included in output documents, and this also improves memory usage. | |||||||
| November 2022 | main18944 | Stable |
| |||||||
| October 2022 | 430patches18800 | Latest | The Sort and Join Snaps now have improved memory management, allowing used memory to be released when the Snap stops processing. | |||||||
| October 2022 | 430patches18610 | Latest | The CSV Formatter and CSV Parser Snaps now support shorter values of Unicode characters. | |||||||
| October 2022 | 430patches18454 | Latest |
| |||||||
The CSV Parser Snap now parses data with empty values in the columns when using a multi-character delimiter. | ||||||||||
| September 2022 | 430patches18119 | Latest | The Transcoder Snap used in a low-latency feed Ultra Pipeline now acknowledges the requests correctly. | |||||||
| September 2022 | 430patches17802 | Latest | The Avro Parser Snap now displays the decimal number correctly in the output view if the column’s logical type is defined as a decimal. | |||||||
| September 2022 | 430patches17737 | Stable/Latest | AutoPrep now enables you to handle empty or null values. | |||||||
| September 2022 | 430patches17643 | Latest | The CSV Parser and CSV Formatter Snaps now support either \ or \\ for a single backslash delimiter which were failing earlier. | |||||||
| September 2022 | 430patches17589 | Latest | The CSV Formatter Snap does not hang when running in specific situations involving multibyte characters in a long field. If you notice the CSV Formatter Snap is hung, we recommend that you update to the 430patches17589 version and restart your Snaplex. | |||||||
| August 2022 | main17386 | Stable |
| |||||||
| 4.29 Patch | 429patches16990 | Latest |
| |||||||
| 4.29 Patch | 429patches16923 | Latest |
| |||||||
| 4.29 Patch | 429patches16521 | Latest |
| |||||||
| 4.29 Patch | 429patches16026 | Latest | Enhanced the Excel Parser Snap with the Custom Locale dropdown list that allows you to select a user-defined locale to format numbers as per the selected locale. | |||||||
| 4.29 | main15993 | Stable |
| |||||||
| 4.28 patch | 428patches14370 | Latest | Fixed an issue with the XML Generator Snap, where the Snap failed with an invalid UTF-8 sequence error when running on the Windows Snaplex. | |||||||
| 4.28 | main14627 | Stable | Upgraded with the latest SnapLogic Platform release. | |||||||
| 4.27 Patch | 427patches12966 | Latest | Enhanced the Avro Formatter Snap to display meaningful error message while processing invalid and null values from the input. | |||||||
| 4.27 | main12989 | Stable and Latest | Fixed an issue in the Group by Fields Snap that caused the Snap to abort with an error when executed with zero input documents. | |||||||
| 4.27 | main12833 | Stable |
| |||||||
| 4.26 Patch | 426patches12086 | Latest | Fixed an issue with the Join Snap, where it exhausted the memory while buffering millions of objects. | |||||||
| 4.26 Patch | 426patches11780 | Latest | Fixed an issue in the XML Formatter Snap, where the Map input to first repeating element in XSD checkbox is selected, while no XSD is specified for mapping the input. | |||||||
| 4.26 Patch | 426patches11725 | Latest | Fixed an issue with the Join Snap where the upstream document flow of the right view is blocked by the left view, which hung the Join Snap. | |||||||
| 4.26 | main11181 | Stable |
| |||||||
| 4.25 Patch | 425patches10663 | Latest | Fixed an issue in the CSV Formatter Snap, where even if the Ignore empty stream checkbox is not enabled, the Snap did not produce an empty binary stream output in case there is no input document. | |||||||
| 4.25 Patch | 425patches10152 | Latest |
| |||||||
| 4.25 Patch | 425patches9815 | Latest | Fixed a | |||||||
| 4.25 Patch | 425patches9749 | Latest | Enhanced XML Parser Snap to recognize input headers when defining inbound schema. | |||||||
| 4.25 Patch | 425patches9638 | - | Latest | Reverts the Join Snap to the 4.24 release behavior. This is in response to an issue encountered in the Join Snap in the 4.25 release version (main9554), which can result in incorrect outputs from all Join Types. 425patches9638 is the default version for both stable and latest Transform Snap Pack versions for orgs that are on the 4.25 release version. No action is required by customers to receive this update and no impact is anticipated. | ||||||
| 4.25 | main9554 | Stable | Enhanced the Group By N Snap with the following settings:
| |||||||
| 4.24 Patch | 424patches8938 | Latest |
| |||||||
| 4.24 | main8556 | Stable | Upgraded with the latest SnapLogic Platform release. | |||||||
| 4.23 Patch | 423patches7958 | Latest | Fixes an issue in the JSON Splitter Snap by logging an error when the matcher does not find a pattern. | |||||||
| 4.23 Patch | 423patches7898 | Latest |
| |||||||
| 4.23 Patch | 423patches7792 | Latest | Fixes an issue in the XML Formatter Snap when it fails to convert input JSON data, with JSON property having a special character as its prefix, to XML format by sorting the elements. | |||||||
| 4.23 Patch | 423patches7753 | Latest | Fixes an issue with the JSON Splitter Snap's behavior in Ultra Pipelines that prevents processed requests to be acknowledged and removed from the FeedMaster queue, resulting in retries of requests that are already processed successfully. | |||||||
| 4.23 | main7430 | Stable | Enhances the JSON Formatter Snap to render groups output from upstream (Group by) Snaps with one document per group and a new line per group element. You can now select the Format each document and JSON lines check boxes simultaneously. | |||||||
| 4.22 Patch | 422patches6395 | Latest | Fixes the JSON Splitter Snap data corruption issue by copying the data in JSON Splitter Snap before sending it to other downstream Snaps. | |||||||
| 4.22 Patch | 422patches6505 | Latest | Fixes the XML Generator Snap issue reflecting empty tags and extra space by removing the extra space in the XML output. | |||||||
| 4.22 | main6403 | Latest | Upgraded with the latest SnapLogic Platform release. | |||||||
| 4.21 Patch | 421patches5901 | Latest | Enhances the JSON Generator Snap to include pass-through functionality where the Snap embeds the upstream input document under the | |||||||
| 4.21 Patch | 421patches5848 | Latest |
| |||||||
| 4.21 | snapsmrc542 | - | Stable | Adds support in the Mapper Snap to display schemas with complex nesting. For example, if Snaps downstream from the | ||||||
| 4.20 Patch | transform8792 | - | Latest | Resolves the | ||||||
| 4.20 Patch | transform8788 | - | Latest | Resolves the NullPointerException in the Join Snap on Windows Snaplex instances. | ||||||
| 4.20 Patch | transform8760 | - | Latest |
The JSON Formatter Snap output now includes only those fields from the input file that are specified in the Content field under Settings. If your Pipelines use the JSON Formatter Snap with the JSON lines field selected, they may fail to execute correctly if the Content field mentions a specific object or field but the downstream Snap is expecting the entire data. Hence, for backward compatibility, you must review the entries in the Content field based on the desired output, as follows:
The behavior of the Snap when the JSON lines field is not selected is correct and remains unchanged. The Example: Filtering Output Data Using the JSON Formatter Snap's Content Setting further illustrates the corrected vs the old behavior.
XML Generator Snap behavior might break existing Pipelines The XML Generator Snap now gives precedence to any custom XML data that is provided over data coming from upstream Snaps, to generate the output. Existing Pipelines using the XML Generator Snap may fail in the following scenarios. Use the resolution provided to update the Snap settings based on the XML data you want to pass to downstream Snaps.
| ||||||
| 4.20 Patch | transform8738 | - | Latest |
| ||||||
| 4.20 | snapsmrc535 | - | Stable | Upgraded with the latest SnapLogic Platform release. | ||||||
| 4.19 Patch | transform8280 | - | Latest | Fixed an issue with the Excel Parser Snap wherein the Snap incorrectly outputs Unformatted General Number format. | ||||||
| 4.19 | snaprsmrc528 | - | Stable | The output of the AVG function in the Aggregate Snap now rounds up all numeric values that have more than 16 digits. | ||||||
| 4.18 Patch | transform8199 | - | Latest | Fixed an issue with the Excel Multi Sheet Formatter Snap wherein the Snap fails to create sheets in the expected order. | ||||||
| 4.18 Patch | transform7994 | - | Latest | Added a field, Round dates, to the Excel Parser Snap which enables you to round numeric excel data values to the closest second. | ||||||
| 4.18 Patch | transform7780 | - | Latest |
| ||||||
| 4.18 Patch | transform7741 | - | Latest | Fixed an issue with the Sort and Join Snaps wherein the platform removes all temp files at the end of Pipeline execution. | ||||||
| 4.18 Patch | transform7711 | - | Latest | Fixed an issue with the XML Parser Snap wherein a class cast exception occurs when the Snap is configured with a Splitter and Namespace Context. | ||||||
| 4.18 | snapsmrc523 | - | Stable |
| ||||||
| 4.17 Patch | Transform7431 | - | Latest | Added a new field, Ignore empty stream, to the Avro Formatter Snap that writes an empty array in the output in case of no input documents. | ||||||
| 4.17 Patch | Transform7417 | - | Latest | Added a new field, Format as canonical XML, to the XSLT Snap that enables canonical XML formatting. | ||||||
| 4.17 Patch | ALL7402 | - | Latest | Pushed automatic rebuild of the latest version of each Snap Pack to SnapLogic UAT and Elastic servers. | ||||||
| 4.17 | snapsmrc515 | - | Stable |
| ||||||
| 4.16 Patch | transform7093 | - | Latest | Fixed an issue with the XSLT Snap failure by enhancing the Saxon version. | ||||||
| 4.16 Patch | transform6962 | - | Latest |
| ||||||
| 4.16 Patch | transform6869 | - | Latest | Fixed an issue with the XML Parser Snap wherein XSD with annotations were incorrectly interpreted. | ||||||
| 4.16 | snapsmrc508 | - | Stable | Upgraded with the latest SnapLogic Platform release. | ||||||
| 4.15 Patch | transform6736 | - | Latest | Fixed an issue wherein the XML Generator Snap was unable to escape some of the special characters. | ||||||
| 4.15 Patch | transform6680 | - | Latest | Fixed an issue with the Excel Parser Snap wherein headers were not parsed properly and header columns were also maintained in an incorrect order. | ||||||
| 4.15 Patch | transform6402 | - | Latest | Fixed an issue with an object type in the Fixed Width Formatter Snap. | ||||||
| 4.15 Patch | transform6386 | - | Latest | Fixed an issue with the Fixed Width Parser Snap wherein Turkish characters caused incorrect parsing of data on Windows plex. | ||||||
| 4.15 Patch | transform6321 | - | Latest | Fixed an issue with the XML Parser Snap wherein the Snap failed to get data types from XSD. | ||||||
| 4.15 Patch | transform6265 | - | Latest | Fixed an issue with the XML Parser wherein XML validation was failing if the XSD contained | ||||||
| 4.15 | snapsmrc500 | - | Stable | Added a new property, Binary header properties, to the Document to binary Snap that enables you to specify the properties to add to the binary document's header. | ||||||
| 4.14 Patch | transform6098 | - | Latest | Fixed an issue wherein the XML Parser Snap was not maintaining the datatype mentioned in the XSD file. | ||||||
| 4.14 Patch | transform6080 | - | Latest | Fixed an issue with the Avro Formatter Snap wherein the Snap was failing for a complex JSON input. | ||||||
| 4.14 Patch | MULTIPLE5732 | - | Latest | Fixed an issue with S3 file reads getting aborted intermittently because of incomplete consumption of input stream. | ||||||
| 4.14 Patch | transform5684 | - | Latest | Fixed the JSON Parser Snap that causes the File Reader Snap to fail to read S3 file intermittently with an | ||||||
| 4.14 | snapsmrc490 | - | Stable | Upgraded with the latest SnapLogic Platform release. | ||||||
| 4.13 Patch | transform5411 | - | Latest | Fixed an issue in the CSV Formatter Snap where the output showed extra values that were not provided in the input. | ||||||
| 4.13 | snapsmrc486 | - | Stable | Upgraded with the latest SnapLogic Platform release. | ||||||
| 4.12 Patch | transform5005 | - | Latest | Fixed an issue with the Excel Parser Snap that drops columns when the value is null at the end of the row. | ||||||
| 4.12 Patch | transform4913 | - | Latest | Fixed an issue in the Excel Formatter Snap, wherein opening an output stream prematurely causes the Box Write Snap to fail. Excel Formatter now awaits the first input document, before opening an output stream. | ||||||
| 4.12 Patch | transform4747 | - | Latest | Fixed an issue that caused the Join Snap to go out of memory. | ||||||
| 4.12 | snapsmrc480 | - | Stable |
| ||||||
| 4.11 Patch | transform4558 | - | Latest | Enforced UTF-8 character encoding for the Fixed Width Formatter Snap. | ||||||
| 4.11 Patch | transform4343 | - | Latest | Enhanced enum labels on the Binary to Document and the Document to Binary Snaps for the Encode or Decode property with DOCUMENT and NONE options. | ||||||
| 4.11 Patch | transform4361 | - | Latest | Fixed a sorting issue with the Join and Sort Snaps where the end of the file was not detected correctly. | ||||||
| 4.11 Patch | transform4281 | - | Latest | Added support on the Kryo serialization for UUID and other types to the Sort, Join and In-Memory Lookup Snaps. | ||||||
| 4.11 | snapsmrc465 | - | - |
| ||||||
| 4.10 Patch | transform4058 | - | - | Addressed an issue with the Excel Parser Snap that failed with out of memory when using large input Data (eg. 191 MB). | ||||||
| 4.10 Patch | transform3956 | - | - | Conditional Snap: fixed an issue with the "Null-safe access" Snap Setting not being respected for return values. | ||||||
| 4.10 | snapsmrc414 | - | - |
| ||||||
| 4.9.0 Patch | transform3343 | - | - | Join Snap - All input documents from all input views should be consumed before the end of Snap execution. | ||||||
| 4.9.0 Patch | transform3281 | - | - | Made all four output views in Diff snap as mandatory. | ||||||
| 4.9.0 Patch | transform3264 | - | - | Made all four output views in Diff snap as mandatory. | ||||||
| 4.9.0 Patch | transform3220 | - | - | CSV Parser Snap - A new Snap property Ignore empty data with true default is added | ||||||
| 4.9.0 Patch | transform3019 | - | - | Addressed an issue with the transform2989 build. | ||||||
| 4.9.0 Patch | transform2989 | - | - | Addressed an issue with Excel Parser not displaying the most recent cached value for vlookups containing missing external references. | ||||||
| 4.9.0 | - | - | Introduced Encrypt Field and Decrypt Field Snaps. | |||||||
| 4.8.0 Patch | transform2956 | - | - | [CSVParser] Fixed an issue where an empty Quote Character config field was defaulting to the unicode quote character U+0000 (null). This caused issues if the input CSV had U+0000 characters in it. | ||||||
| 4.8.0 Patch | transform2848 | - | - |
| ||||||
| 4.8.0 Patch | transform2768 | - | - | Addressed an issue with CSV Parser causing a spike in CPU usage. | ||||||
| 4.8.0 Patch | transform2736 | - | - | Addressed an issue with Excel Formatter dropping the first record when Ignore empty stream is selected. | ||||||
| 4.8.0 | - | - |
| |||||||
| 4.7.0 Patch | transform2549 | - | - | Addressed an issue with Excel Formatter altering decimal numbers to text. | ||||||
| 4.7.0 Patch | transform2344 | - | - | Resolved an issue with validation of pipelines taking more time than executing a pipeline when a large amount of data is used. | ||||||
| 4.7.0 Patch | transform2335 | - | - | Resolved an issue with XML Parser failing with error: 'Maximum attribute size (524288) exceeded'. | ||||||
| 4.7.0 Patch | transform2206 | - | - | Resolved an issue with JSON Generator failing with an "Invalid UTF-8 middle byte 0x70" error on Windows. | ||||||
| 4.7.0 | - | - |
| |||||||
| 4.6.0 Patch | transform2018 | Resolved an issue where Excel Parser did not reliably set header row when "contains headers" is checked | ||||||||
| 4.6.0 Patch | transform1905 | Resolved an issue in Sort Snap where buffer size should not be fixed for optimal performance | ||||||||
| 4.6.0 Patch | transform1901 |
| ||||||||
| 4.6.0 Patch | transform1871 | Resolved a performance issue in Excel Multi Sheet Formatter. | ||||||||
| 4.6.0 |
| |||||||||
| 4.5.1 |
| |||||||||
| 4.5.0 |
| |||||||||
| 4.4.1 |
| |||||||||
| 4.4 |
| |||||||||
| 4.3.2 |
| |||||||||
| 4.3.1 |
| |||||||||
| 4.3.0 |
| |||||||||
| 4.2.2 |
| |||||||||
| August 7, 2015 (2015.25/4.2.1) |
| |||||||||
| June 27, 2015 (2015.22) |
| |||||||||
| June 6, 2015 (2015.20) |
| |||||||||
| May 2, 2015 |
| |||||||||
| March 2015 |
| |||||||||
| January 2015 |
| |||||||||
December 20, 2014 |
| |||||||||
| November 2014 | Aggregate now provides 2 new functions: concat and unique_concat | |||||||||
| October 18, 2014 |
| |||||||||
| Fall 2014 |
| |||||||||
| August 2014 |
| |||||||||
| July/Summer 2014 |
| |||||||||
| June 30, 2014 |
| |||||||||
| May 2014 |
| |||||||||
| April 2014 |
| |||||||||
| March 2014 |
| |||||||||
| January 2014 |
| |||||||||
| December 2013 |
| |||||||||
| November 2013 |
| |||||||||
| August 2013 |
| |||||||||
| July 2013 | JSON Splitter: The JSON Splitter Snap splits a list of values into separate documents. | |||||||||
| Initial release |
|
Have feedback? Email documentation@snaplogic.com | Ask a question in the SnapLogic Community
© 2017-2025 SnapLogic, Inc.
.png?version=1&modificationDate=1491454352204&cacheVersion=1&api=v2&width=765&height=492)
.png?version=1&modificationDate=1491454350249&cacheVersion=1&api=v2)