Active Directory List Users
On this Page
Snap type: | Write | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Description: | This Snap lists the user with the specified Distinguished Name in Active Directory.
| |||||||
| Prerequisites: | [None] | |||||||
| Support and limitations: | Works in Ultra Tasks. | |||||||
| Account: | This Snap uses account references created on the Accounts page of SnapLogic Manager to handle access to this endpoint. See Active Directory Basic Auth Account for information on setting up this type of account. | |||||||
| Views: |
| |||||||
Settings | ||||||||
Label | Required. The name for the Snap. You can modify this to be more specific, especially if you have more than one of the same Snap in your pipeline. | |||||||
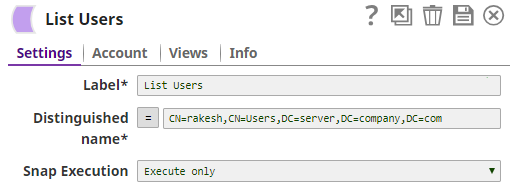
Distinguished name | Required. The LDAP API references an LDAP object by its distinguished name (DN). A DN is a sequence of relative distinguished names (RDN) connected by commas. An RDN is an attribute with an associated value in the form attribute=value, normally expressed in a UTF-8 string format. The typical RDN attribute types include: DC = domainComponent, CN = commonName, OU = organizationalUnitName,O = organizationName, STREET = streetAddress, L = localityName,ST = stateOrProvinceName, C = countryName, UID = userid. This field is applicable only to existing users. If the user does not exist, create an entry using the Create Entry Snap first. Example: A distinguished name for an LDAP entry can be represented as: CN=AbcUser,CN=Users,DC=server,DC=company,DC=com. In this example, to refer to the entire user list, you can remove the initial attribute, CN=AbcUser. Default value: [None] You can also use special characters in the distinguished name. See the section Using Special Characters in Distinguished Name below. | |||||||
| Pass through | Select to include the entire input data in the Snap's output. The Snap includes this data within the $original field in the output. Default value: Not selected | |||||||
Loading | Loading | |||||||
Examples
The following table provides some examples of the data returned for varying Distinguished name values.
| Distinguished name value | Returns |
|---|---|
CN=user,CN=Users,DC=server,DC=company,DC=com | Details about that user. |
| CN=Users,DC=server,DC=company,DC=com | Details about all items in "Users" under that domain. |
| DC=server,DC=company,DC=com | Details about all objects on that server domain. |
Using Special Characters in Distinguished Name
You can include special characters in the Distinguished name and Existing distinguished name fields. As of Patch activedirectory8789, the fields do not require the following special characters to be prefixed with an escape character:
- Forward slash (/)
- Backward slash (\)
- Plus (+)
- Double-quote (")
- Less than symbol (<)
- Greater than symbol (>)
- Semi-colon (;)
If an escape character is prefixed, the Snap reads it, else, it prefixes it to the special character to correctly process the data.
Comma (,) and Equals (=) have a special meaning in the distinguished name, as comma (,) is used to separate RDNs and equals (=) is used for designating key value pairs (key=value). Therefore, these must still be prefixed with an escape character to be passed as special characters. For example, \, or \=.
Example: Using Special Characters
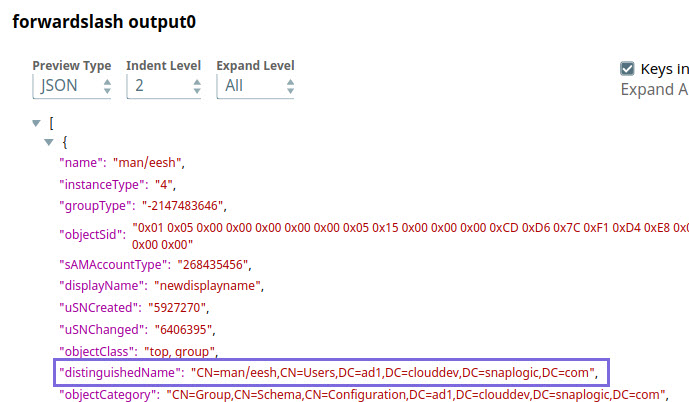
Let us say you need to specify a distinguished name like CN=man/eesh,CN=Users,DC=ad1,DC=clouddev,DC=snaplogic,DC=com, where the common name man/eesh contains a special character.
The Snap supports both scenarios:
- If the special character is prefixed with an escape character. For example, CN=man\/eesh.
- If no escape character is used. For example, CN=man/eesh,
In both cases, the Snap generates the same output during Pipeline validation, as shown in the image below. This ensures existing Pipelines do not break in either case.
Using the pass-through functionality
In certain scenarios, the Snap may be unable to process the entire input due to limitations imposed by the endpoint's API. In such cases, we recommend that you select the Pass through checkbox to ensure that the unprocessed input is not lost. You can process the remaining input data using more of the same Snap in the Pipeline. Alternatively, you can also write the original data into a separate file using a combination of the Mapper Snap and the File Writer Snap.
Snap Pack History
Have feedback? Email documentation@snaplogic.com | Ask a question in the SnapLogic Community
© 2017-2025 SnapLogic, Inc.