PySpark
On this Page
| Snap type: | Write | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description: | This Snap executes a PySpark script. It formats and executes a 'spark-submit' command in a command line interface, and then monitors the execution status. If the script executes successfully with an exit code 0, the Snap produces output documents with the status. If the script is coded to produce a standard output, it is also included in the output document. If the script fails (with an exit code other than 0), the Snap produces an error document in the error view. For more details on the 'spark-submit' command, refer to the Apache Spark document. Input & Output
Modes
| ||||||
| Prerequisites: | The Snap must be executed in a Groundplex on a Spark cluster node or an edge node. | ||||||
| Limitations and Known Issues: | None at this time. | ||||||
| Configurations: | Account & AccessNo account is required. Views
| ||||||
| Troubleshooting: | The Snap produces an error document if a given PySpark script fails to execute. It may be helpful in troubleshooting to execute the script in a command line interface of a Goundplex where the Snap is executed. | ||||||
Settings | |||||||
Label | Required. The name for the Snap. You can modify this to be more specific, especially if you have more than one of the same Snaps in your pipeline. | ||||||
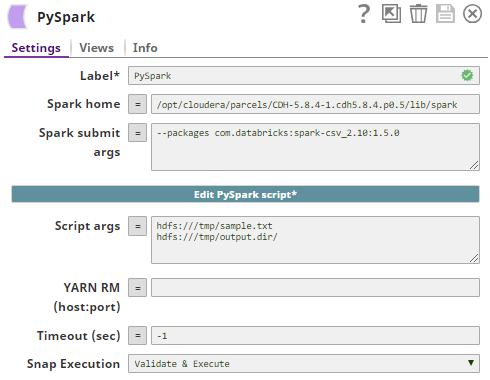
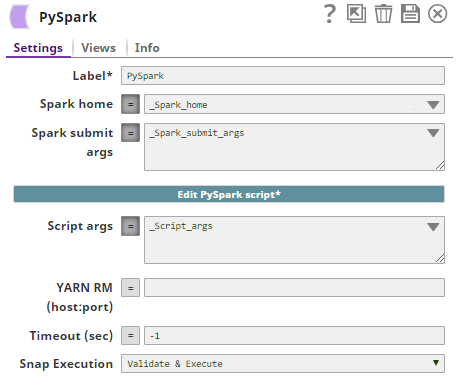
| Spark home | The Spark home directory where spark-submit command is located under the bin/ subdirectory. If this property is empty, the Snap tries to find a value for "SPARK_HOME" or "CDH_SPARK_HOME" in the environment variables or system properties. Example: /opt/cloudera/parcels/CDH-5.8.4-1.cdh5.8.4.p0.5/lib/spark Default value: [None] | ||||||
| Spark submit args | The arguments for the spark-submit command if any. Example: $sparkSubmitArgs _sparkSubmitArgs --master yarn --deploy-mode cluster (to submit the PySpark script to YARN) --principal snaplogic/admin@cloudev.snaplogic.com --keytab /snaplogic.keytab.new (to submit the PySpark script to Kerberos-enabled cluster) Default value: [None] | ||||||
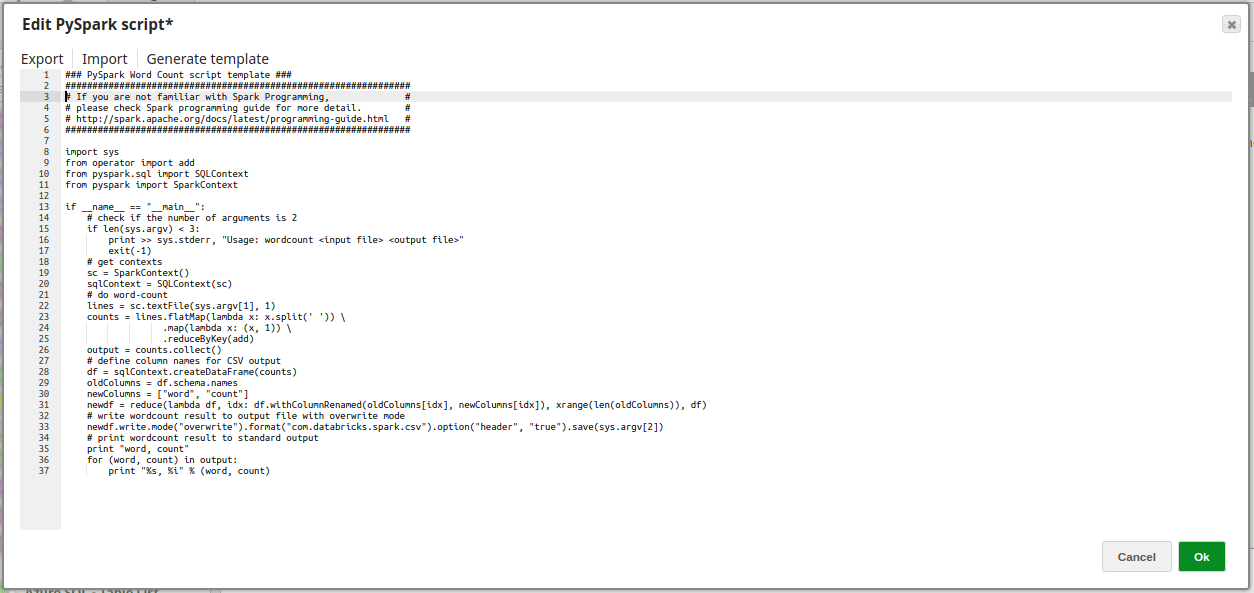
| Edit PySpark script | Required. This property enables you to edit a PySpark script. A 'word-count' sample script is included with the Snap. Click to open an editor and save. To try the sample script, enter a file path to an input text file in the Script args property. In the script editor, a script can be exported, imported, or a template can be generated as required. Default value: 'wordcount' sample script | ||||||
| Script args | The arguments for the PySpark script. Example: hdfs:///tmp/sample.txt hdfs:///tmp/output.dir/ (input file and output directory for 'wordcount' sample script) Default value: [None] | ||||||
YARN RM (host:port) | The hostname and port number of the Yarn Resource Manager in the 'host:port' format. This property is needed to be able to stop a PySpark job in progress. Default value: [None] If YARN is not used to submit PySpark script, stopping the Snap will not stop the job submitted to Spark. | ||||||
| Timeout (sec) | Timeout limit in seconds. If negative or empty, the Snap will not time out until spark-submit returns the result. Example: 600 (10 minutes) Default value: -1 | ||||||
Snap execution | Select one of the three modes in which the Snap executes. Available options are:
| ||||||
Temporary Files
During execution, data processing on Snaplex nodes occurs principally in-memory as streaming and is unencrypted. When larger datasets are processed that exceeds the available compute memory, the Snap writes Pipeline data to local storage as unencrypted to optimize the performance. These temporary files are deleted when the Snap/Pipeline execution completes. You can configure the temporary data's location in the Global properties table of the Snaplex's node properties, which can also help avoid Pipeline errors due to the unavailability of space. For more information, see Temporary Folder in Configuration Options.Examples
Basic Use Case
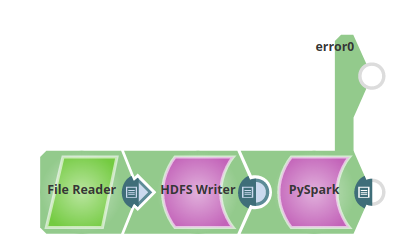
Below is a sample pipeline to demonstrate how the PySpark Snap executes the PySpark script:
The PySpark Snap is configured as:
The following PySpark Script is executed:
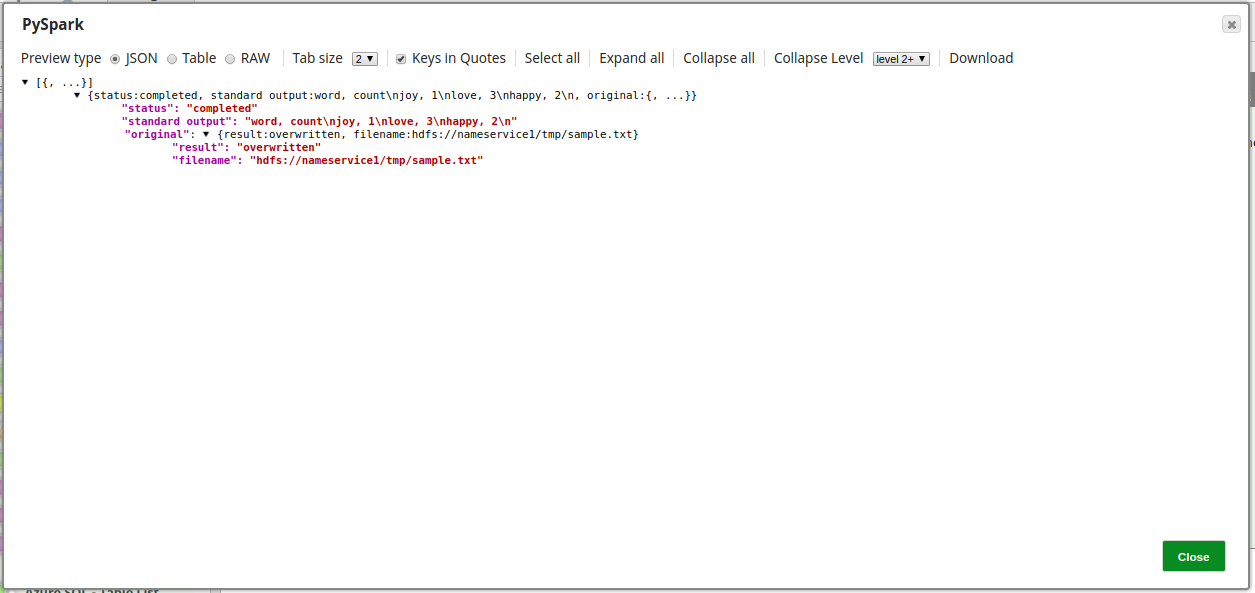
A preview of the output upon successful execution of the Snap:
Exported pipeline is available in the Downloads section below.
Typical Configuration
Key configuration of the Snap lies in how the values are passed. Values can be passed to the Snap:
- Without Expressions:
Values are passed to the Snap directly.
- With Expressions:
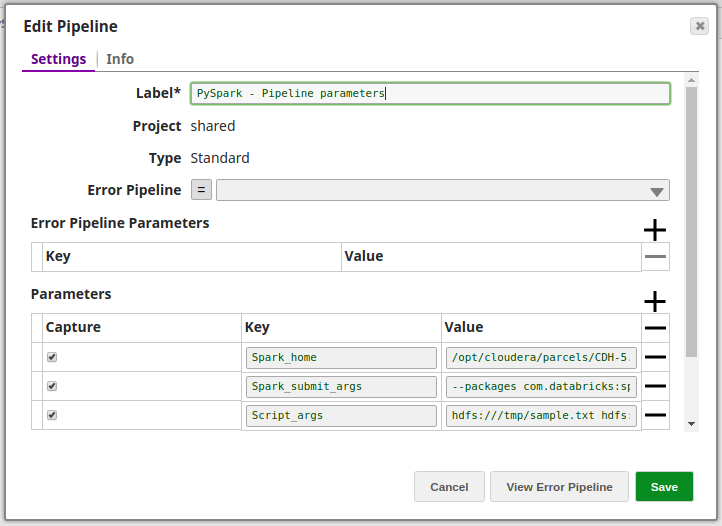
- Using Pipeline parameters:
Values are passed as pipeline parameters:
Downloads
Important steps to successfully reuse Pipelines
- Download and import the pipeline into the SnapLogic application.
- Configure Snap accounts as applicable.
- Provide pipeline parameters as applicable.
Snap Pack History
Have feedback? Email documentation@snaplogic.com | Ask a question in the SnapLogic Community
© 2017-2024 SnapLogic, Inc.