In this article
Overview
You can use this Snap to implement the Slowly Changing Dimension Type 2 (SCD2) function in your Snowflake, Redshift, Azure Synapse, Databricks Lakehouse Platform, or BigQuery table. Configure the database type and the access to corresponding tables in the Configuring ELT Database Accounts for the Snap.
Internal Change in Snap behavior
Starting from November 2021, 4.27 release, the ELT SCD2 Snap performs a MERGE INTO-based SCD2 operation instead of the previous Insert-and-then-Update approach. It is important that you take notice of this change in behavior. However, if you prefer to use the Insert-and-then-Update approach for your SCD2 operation, define the Pipeline parameter SCD2_INSERTUPDATE_FALLBACK_MODE with a value greater than zero (0), before running your Pipeline.
Prerequisites
Valid accounts and access permissions to connect to the following:
Source: AWS S3, Azure Cloud Storage, or Google Cloud Storage.
Target: Snowflake, Redshift, Azure Synapse, Databricks Lakehouse Platform, or BigQuery.
Limitation
ELT Snap Pack does not support Legacy SQL dialect of Google BigQuery. We recommend that you use only the BigQuery's Standard SQL dialect in this Snap.
Known Issues
If the last Snap in the Pipeline takes 2 to 5 seconds to update the runtime, the ELT Pipeline statistics are not displayed even after the Pipeline is completed. The UI does not auto-refresh to display the statistics after the runtime.
Workaround: Close the Pipeline statistics window and reopen it to see the ELT Pipeline statistics.When you return to the Snap Statistics tab from the Extra Details tab in the Pipeline Execution Statistics pane, it contains the status bar (Pipeline execution status) instead of the Download Query Details hyperlink and the individual counts of Records Added, Records Updated, and Records Deleted.
- ELT Pipelines built using an ELT SCD2 Snap fail to perform the DROP AND CREATE TABLE and ALTER TABLE operations on Delta tables when working with a Databricks SQL persona on the AWS Cloud with the error
Operation not allowed: ALTER TABLE RENAME TO is not allowed for managed Delta tables on S3. However, the same action runs successfully with the Data Science and Engineering persona on the AWS Cloud.This is due to the limitation with the Databricks SQL Admin Console that does not allow you to add the configuration parameter
spark.databricks.delta.alterTable.rename.enabledOnAWS trueto its SQL Warehouse Settings.
Due to an issue with BigQuery table schema management (the time travel feature), an ALTER TABLE action (Add or Update column) that you attempt after deleting a column (DROP action) in your BigQuery target table causes the table to break and the Snap to fail.
As a workaround, you can consider either avoiding ALTER TABLE actions on your BigQuery instance or creating (CREATE) a temporary copy of your table and deleting (DROP) it after you use it.
When using the ELT SCD2 Snap to load your source data into a Redshift target instance, the Snap fails if you use constant values such as ‘2022-01-01’ or SQL expressions such as GETDATE() and current_time() that evaluate to constant values instead of the target table column names in the Target Table Sort Fields.
In the case of Azure Synapse, if you are configuring the Start_Date column as a Target Table Natural Key, the Snap fails in each of the following scenarios:
The source table/file contains one or more null values.
The target table is empty.
The End date of current row or End date of historical row has a static value, for example: '2021-01-01'.
- When your Databricks Lakehouse Platform instance uses Databricks Runtime Version 8.4 or lower, ELT operations involving large amounts of data might fail due to the smaller memory capacity of 536870912 bytes (512MB) allocated by default. This issue does not occur if you are using Databricks Runtime Version 9.0.
In any of the supported target databases, this Snap does not appropriately identify nor render column references beginning with an _ (underscore) inside SQL queries/statements that use the following constructs and contexts (the Snap works as expected in all other scenarios):
WHEREclause (ELT Filter Snap)WHENclauseONcondition (ELT Join, ELT Merge Into Snaps)HAVINGclauseQUALIFYclause- Insert expressions (column names and values in ELT Insert Select, ELT Load, and ELT Merge Into Snaps)
- Update expressions list (column names and values in ELT Merge Into Snap)
- Secondary
ANDcondition Inside SQL query editor (ELT Select and ELT Execute Snaps)
Workaround
As a workaround while using these SQL query constructs, you can:
- Precede this Snap with an ELT Transform Snap to re-map the '_' column references to suitable column names (that do not begin with an _ ) and reference the new column names in the next Snap, as needed.
- In case of Databricks Lakehouse Platform where CSV files do not have a header (column names), a simple query like
SELECT * FROM CSV.`/mnt/csv1.csv`returns default names such as _c0, _c1, _c2 for the columns which this Snap cannot interpret. To avoid this scenario, you can:- Write the data in the CSV file to a DLP table beforehand, as in:
CREATE TABLE csvdatatable (a1 int, b1 int,…) USING CSV `/mnt/csv1.csv`where a1, b1, and so on are the new column names. - Then, read the data from this new table (with column names a1, b1, and so on) using a simple SELECT statement.
- Write the data in the CSV file to a DLP table beforehand, as in:
- In case of Databricks Lakehouse Platform, all ELT Snaps' preview data (during validation) contains a value with precision higher than that of the actual floating point value (float data type) stored in the Delta. For example, 24.123404659344 instead of 24.1234. However, the Snap reflects the exact values during Pipeline executions.
Snap Input and Output
| View | Type of View | Number of Views | Examples of Upstream and Downstream Snaps | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Document |
|
| A document containing an SQL query that yields the historization data to load. |
| Output | Document |
|
| A document containing the status of the SCD2 Load operation along with the SQL query that you can use in downstream ELT Snaps if any. |
Snap Settings
SQL Functions and Expressions for ELT
You can use the SQL Expressions and Functions supported for ELT to define your Snap or Account settings with the Expression symbol = enabled, where available. This list is common to all target CDWs supported. You can also use other expressions/functions that your target CDW supports.
Understanding the ELT SCD2 terminology
See ELT SCD2 Scenarios | Terminology for definitions of the terms used in this Snap's configuration.
| Parameter Name | Data Type | Description | Default Value | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Label | String | Specify a name for the Snap. You can modify this to be more specific, especially if you have more than one of the same Snap in your pipeline. | N/A | Orders_SCD2_Data |
| Get preview data | Checkbox | Select this checkbox to include a preview of the query's output. The Snap performs limited execution and generates a data preview during Pipeline validation. In the case of ELT Pipelines, only the SQL query flows through the Snaps but not the actual source data. Hence, the preview data for a Snap is the result of executing the SQL query that the Snap has generated in the Pipeline. The number of records displayed in the preview (upon validation) is the smaller of the following:
Rendering Complex Data Types in Databricks Lakehouse Platform Based on the data types of the fields in the input schema, the Snap renders the complex data types like map and struct as object data type and array as an array data type. It renders all other incoming data types as-is except for the values in binary fields are displayed as a base64 encoded string and as string data type. | Not selected | Selected |
| Database Name | String/Expression | Specify the name of the database in which the target table exists. Leave this field blank if you want to use the database name specified in the Default Database Name field in the account settings. | N/A | TESTDB |
| Schema Name (Not applicable to Databricks Lakehouse Platform) | String/Expression/Suggestion | Required. Specify the name of the database schema. Alternatively, click to fetch a list of schemas associated with the database, and select the schema.
| N/A | SALES |
| Target Table Name | String/Expression/Suggestion | Required. Specify the name of the SCD2 table or view in which you want to load the data. Alternatively, click to fetch a list of table names associated with the schema, and select the required name. Only views that can be updated (have new rows) are listed as suggestions. So, Join views are not included. This also implies that the Snap account user has the Insert privileges on the views listed as suggestions.
The target table or view should have the following columns for field historization to work:
Use the ALTER TABLE command to add these columns in your target table if they are missing. | N/A | SALES_ORDERS |
| Input Source Alias | String/Expression | Specify an alias name for your source data table. | N/A | src |
| Target Table Action | Drop-down list | Select the SCD2 action to perform on the target table. Available options are:
During Pipeline Validation The Snap does not modify the existing tables during Pipeline validation, but if the specified target table does not exist, it creates a new target table. Selecting the Target Table Action
| Merge data into target table | Alter table |
| Table Columns | This field set enables you to configure the schema of the target table. You can use this field set to add or drop columns in the target table if you select the Drop and Create table or Alter table in the Target Table Action field. Click to add a new row in the field set. This field set consists of the following fields:
| |||
| Column | String/Suggestion | Specify the name of the column that you want to load in the target table. You can also specify the columns to drop if you select the Alter table option in the Target Table Action field. | N/A | ID FNAME |
| Data Type | String | Activates when you select the Drop and Create table or Alter table options in the Target Table Action field. Specify the data type for the values in the specified column. | N/A | INT VARCHAR |
| Modifier | Drop-down list | Activates when you select the Alter table option in the Target Table Action field. Select whether you want to add/drop the specified column. Available options are:
| Add | Drop |
| Null Value Behavior | Drop-down list | Select an option to specify how you want the Snap to treat rows with null values in Natural Key or Cause-Historization fields of the source table. The available options are:
Refer to the ELT SCD2 scenarios to learn more about the impact of the selection you make in this field. | Honor nulls as distinct values | Ignore nulls |
| Invalid Row Handling | Drop-down list | Select an option to specify how you want the Snap to treat invalid rows, if any, in the source data. A row is considered invalid when it does not result in a new, valid, and coherent SCD2 entry/row in the target table. The available options are:
Refer to the ELT SCD2 scenarios to learn more about the impact of the selection you make in this field. | Ignore invalid rows | Insert duplicate invalid rows |
| Target Table Natural Key(s) | Required. This field set enables you to configure the names of fields that identify a unique row in the target table. The identity key cannot be used as the Natural key, since a current row and its historical rows cannot have the same identity value. Click to add a new row in the field set. Specify the value in the following field for each new row added in this field set.
| |||
| Target Table Natural Key(s) | String/Expression/Suggestion | Specify the name of the Natural Key column from the target table. | N/A | CUSTOMER_ID |
| Target Table Cause-Historization Field(s) | Required. This field set enables you to configure the names of fields where any change in value causes the historization of an existing row and the insertion of a new 'current' row. Click to add a new row in the field set. Specify the value in the following field for each new row added in this field set.
| |||
| Target Table Cause-Historization Field(s) | String/Expression/Suggestion | Required. Specify the name of the historization-causing column from the target table. | N/A | LAST_ORDER_AMT |
| Target Table Temporal Field(s) | Required. This field set enables you to configure the historical and updated information for the Cause-historization field. Click to add SCD fields. Specify the values in the following fields for each SCD field row in the field set.
| |||
| Meaning | Drop-down list | Required. Select one from the following six permitted values for this field in each row. At the minimum, ensure that you configure appropriate values for the first three meanings, only one of the end dates, and the flag in this list.
Breaking change In 4.26 GA, we have updated the last option in this field—Invalid historical row flag—and it may cause your Pipelines to fail. See Snap Pack History for more information. | Five rows with one list item in each row . | Start date of current row |
| Field | String/Expression/Suggestion | Required. Configure the field name from the target table that would contain the historical information. Click to select an item from the suggested list of items.
See the Troubleshooting section in this document and ELT SCD2 Scenarios to ensure that you have configured these fields in your Snap's settings properly. The date fields must be configured with a field and a corresponding value. Pass null as the value to indicate the field's value is null. | N/A | Start_Date End_Date Current_Row Historical_Row |
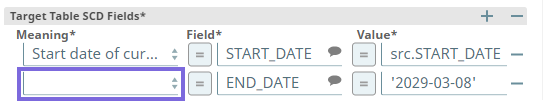
| Value or Expression | String/Expression | Required. Configure the value for each of the fields selected in the Field field. The date fields must be configured with a field and a corresponding value. Pass null as the value to indicate the field's value is null. For the End date of historical row, we recommend that you specify an appropriate expression in this field. See Expressions to use for End date of Historical Row to choose the right expression from a set of expression templates. | N/A | For date fields: For row fields: |
| Target Table Sort Field(s) | Required. This field set enables you to sort the records in the target table, by one or more historization fields (for example, by natural key). This mapping is for columns that are not part of the Target Table Temporal Fields. Click to add a sort order. Specify the values in the following fields for each sort order.
| |||
Sort Field | String/Expression | Specify the column by which to sort the target table data set. | N/A | start_date GENDER |
| Sort Order | Drop-down list | Choose either of the sort orders—ASC (ascending) or DESC (descending)—for the target table data set. | ASC | DESC |
| Null Value Sort Preference | Drop-down list | Choose the position for the null values, if any, in the selected column while sorting—NULLS FIRST (at the beginning) or NULLS LAST (at the end). This field is not applicable if you are working with an Azure Synapse target database. | NULLS LAST | NULLS FIRST |
| Target-Source Column Mapping | This field set enables you to define a one-to-one mapping between the columns in the source and target tables for inserting new rows into the target table. Click to add a new mapping row.
| |||
Target Table Column Name | String/Expression/Suggestion | Choose a column from the target table's schema to map with a column from the source data set (schema). Ensure that the target table column name you specify for mapping with a source column is not already configured as a target table SCD field. | N/A | ORD_AMT |
Source Column Mapping Expression | String/Expression | Choose a column from the source data set (schema) that corresponds to the respective column in the target table's schema. You can alternatively specify an expression for the source column name. If you have specified the target table column as a target table natural key or a target table cause-historization field already in this Snap, ensure that you specify the corresponding source column mapping expression (not null nor left blank). All other columns not mentioned in the Snap can be mapped to null. | N/A | src.ORD_AMT |
Pipeline Execution Statistics
As a Pipeline executes, the Snap shows the following statistics updating periodically. You can monitor the progress of the Pipeline as each Snap performs executes.
Records Added
Records Updated
Records Deleted
You can view more information when clicking the Download Query Details link.
Troubleshooting
| Error | Reason | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| Ambiguous SCD column mapping | You cannot map a field that is configured in Target Table SCD Fields again in the Target-Source Column Mapping field set. | Ensure that the target table column name you specify for mapping with a source column is not already configured as a target table temporal field. |
| Invalid target column - source expression mapping | You cannot map a target table column to null or a blank source column value/expression. | If you have specified the target table column as a target table natural key or a target table cause-historization field already in this Snap, ensure that you specify the corresponding source column mapping expression (not null nor left blank). All other columns not mentioned in the Snap can be mapped to null. |
Database cannot be blank. (When seeking the suggested list for Schema Name field) | Suggestions in the Schema Name and Target Table Name fields do not work when you have not specified a valid value for the Database Name field in this Snap. | Specify the target Database Name in this Snap to view and choose from a suggested list in the Schema Name and Target Table Name fields respectively. |
Invalid row flag not configured for target table | Invalid historical row flag is not defined in Target Table Temporal Field(s) field set. | Add an entry in Target Table Temporal Field(s) field set for the Meaning Invalid historical row flag with the corresponding field name in the target table and the boolean value (true or false) or an expression that resolves to a boolean true or false. Make sure that the target table contains the specified field. |
| Target table sort column %s not mapped to a source column or an expression | Target table sort fields should be mapped to a source column or an expression in one of the two places: Target Table Temporal Field(s) field set or Target-Source Column Mapping field set. | Map this column either in Target Table Temporal Field(s) field set or Target-Source Column Mapping field set before you can use it for sorting. |
| Invalid end date configuration for SCD2 | You have provided both End date of current row and End date of historical row while one of them is adequate. | Remove one of End date of current row and End date of historical row from the Target Table Temporal Field(s) field set and try again. |
Ambiguous source data (Only when you configure the Snap to check for nulls and duplicates.) | Source data contains nulls in one or more of columns you specified in the Target Table Natural Key(s) field set, Target Table Cause-Historization Field(s) field set, or the Start date of current row in Target Table Temporal Field(s) field set. | Peruse your source data to ensure that it is valid and contains valid values required to perform the SCD2 operation and try again. |
Source data has ambiguous records (Only when you configure the Snap to check for nulls and duplicates.) | Source data contains duplicate keys in one or more of columns you specified in the Target Table Natural Key(s) field set, Target Table Cause-Historization Field(s) field set, or the Start date of current row in Target Table Temporal Field(s) field set. | Peruse your source data to ensure that it is valid and contains only unique entries required for the SCD2 operation in these columns and try again. |
Incorrect start date in source data (Only when you configure the Snap to check for nulls and duplicates.) | The column you specified for the Start date of current row in Target Table Temporal Field(s) field set has one or more nulls. | Ensure that your source data or the start date SQL expression resolves to a valid start date and try again. |
Incorrect start date(s) in source data (Only when you configure the Snap to check for nulls and duplicates.) | Multiple rows for one or more Target Table Natural Keys that you defined contain the same start date. | Ensure that your source data contains only unique start dates across the rows for the same natural key. Perform this check for all natural keys you specified, before trying again. |
| Scenario: Sort order by a date column in the target table is incorrect after the SCD2 operation is complete. | Sorting the date values in a column with date data type may yield different results when compared to sorting the same date values in a column with string data type. | Ensure that the values loaded in the target table column are of the same data type as defined for the respective column/field. |
| SQL exception from Snowflake: Syntax error in one or more positions in the SQL query | Column names in Snowflake tables are case-sensitive. It stores all columns in uppercase unless they are surrounded by quotes during the time of creation in which case, the exact case is preserved. See, Identifier Requirements — Snowflake Documentation. | Ensure that you follow the same casing for the column table names across the Pipeline. |
[Simba][SparkJDBCDriver](500051) ERROR processing query/statement. Error Code: 0 Cannot create table (' (Target CDW: Databricks Lakehouse Platform) | The specified location contains one of the following:
So, the Snap/Pipeline cannot overwrite this table with the target table as needed. | Ensure that you take appropriate action (mentioned below) on the existing table before running your Pipeline again (to create another Delta table at this location). Move or drop the existing table from the schema manually using one of the following commands: Access the DBFS through a terminal and run:
OR Use a Python notebook and run:
|
Examples
Loading Historical Data From an S3 Bucket to a Snowflake Table
The following Pipeline is designed to view and capture Type 2 SCD data from a folder in S3 bucket and load it into the target table in Snowflake database.
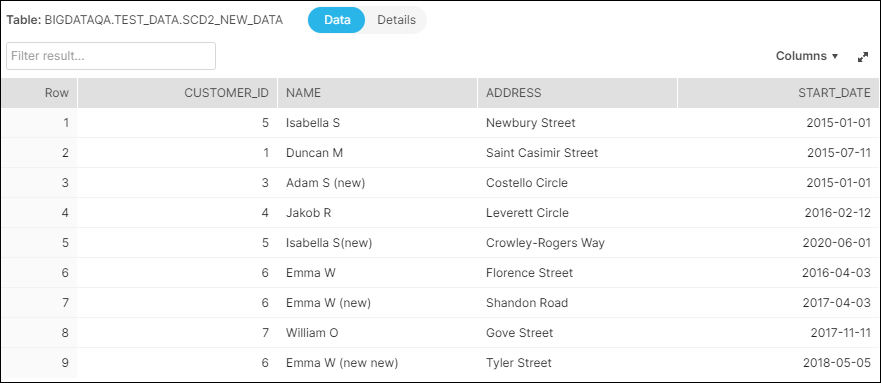
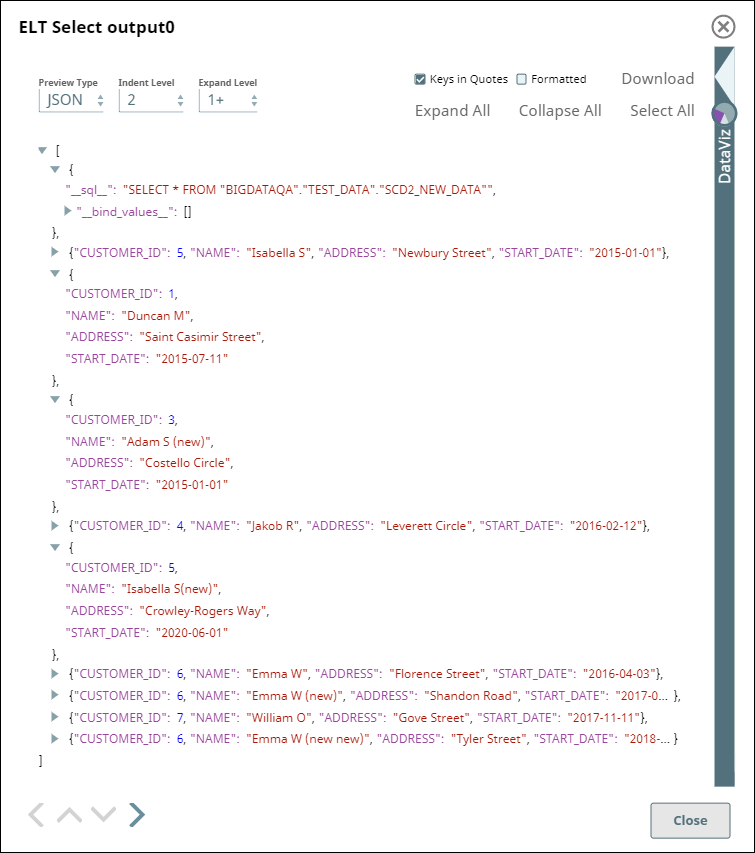
We configure an ELT Select Snap to capture SCD2 data from the source table SCD2_NEW_DATA in S3. The image below depicts the data available in the source table.
| ELT Select Snap |
|---|
| Snap Output |
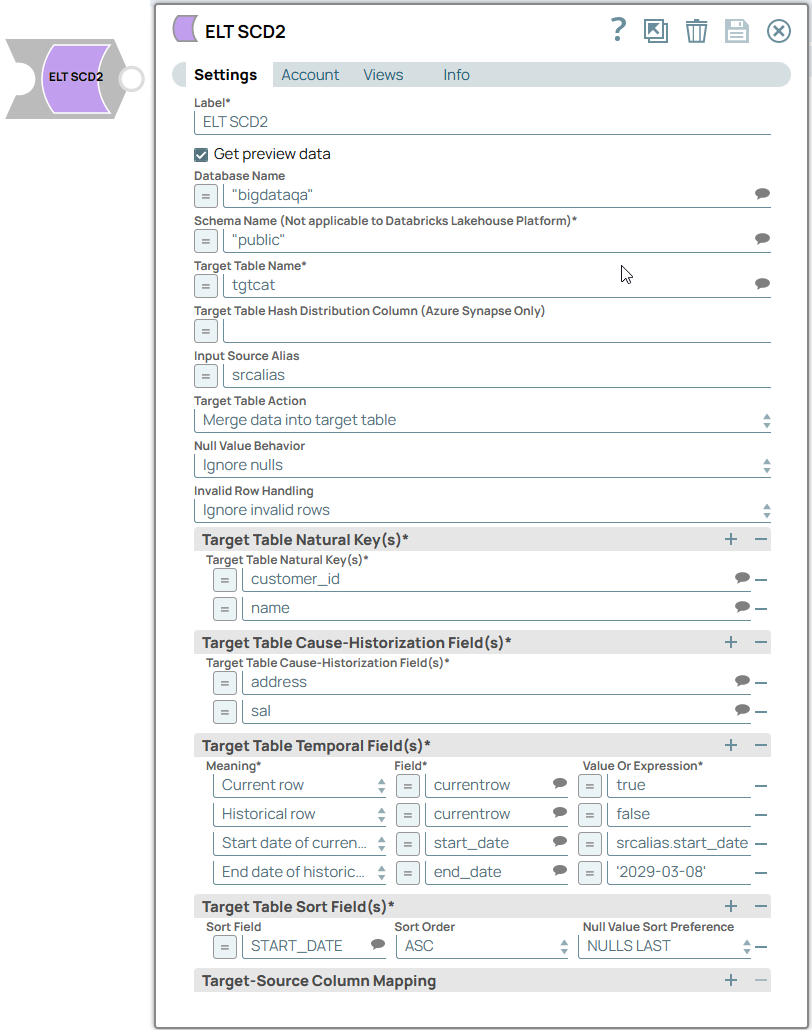
We use this Snap's output as the input to an ELT SCD2 Snap and configure this Snap to update the table SCD2_TRG_TEST5 residing in the Snowflake database.
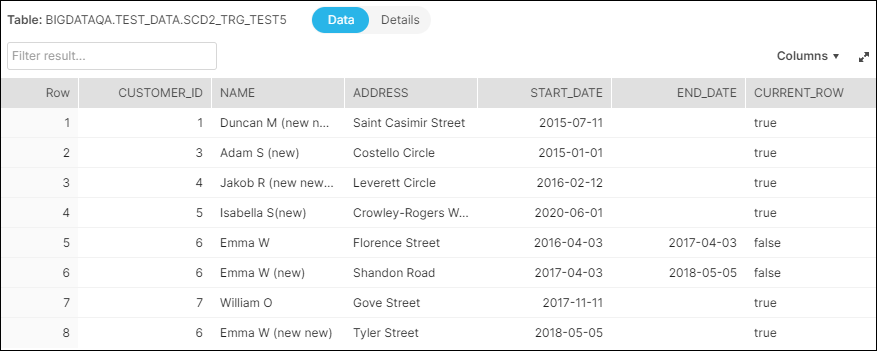
The image below depicts the data available in the target table, before the data load.
| Existing Data in Target Table |
|---|
| ELT SCD2 Snap |
Notice the difference in the number of rows and the values in the END_DATE and the CURRENT_ROW columns. There is only one row with CURRENT_ROW = true in the updated table for each unique CUSTOMER_ID.
Downloads
Important Steps to Successfully Reuse Pipelines
- Download and import the Pipeline into SnapLogic.
- Configure Snap accounts as applicable.
- Provide Pipeline parameters as applicable.


.png?version=5&modificationDate=1683730806625&cacheVersion=1&api=v2)