In this article
Overview
Use this Snap to load files/data from AWS S3 buckets or Azure Cloud Storage containers to a Snowflake, Azure Synapse database, or Databricks Lakehouse Platform (DLP). You can also use this Snap to transfer files from the AWS S3 buckets to the Redshift database, and to load data from Amazon Redshift or Google Cloud Storage to BigQuery. See ELT Source-Target-Hosting Support Matrix for complete information.
If you want to use the COPY INTO command in ELT Execute Snap for loading data into the target database, you need to pass (expose) these account credentials inside the SQL statement. You can use the ELT Load Snap to prevent this security issue.
Prerequisites
Valid accounts and access permissions to connect to the following:
Source: AWS S3, Azure Cloud Storage, or Google Cloud Storage
Target: Snowflake, Redshift, Azure Synapse, Databricks Lakehouse Platform, or BigQuery
Limitations
- ELT Snap Pack does not support Legacy SQL dialect of Google BigQuery. We recommend that you use only the BigQuery's Standard SQL dialect in this Snap.
- Unlike other Write-type Snaps, the Snap does not display the end SQL query in its output preview when connected to a BigQuery instance. This is because BigQuery makes use of APIs instead of an SQL query to load data.
- If the CSV file you want to load into a DLP instance contains null values, you need to define the Format Option in the File Format Option List fieldset as sep = ',' without which the load operation does not succeed.
- Due to a limitation in Snowflake in inferring the source files (and thereby the source schema) based on file name patterns in a Storage Integration-based session, the Snap fails to load data from any supported source location into your Snowflake target instance based on any File Name Pattern that you specify. As a workaround, we recommend that you use the File List field set to define the source data file locations for the Snap to load the data.
Snowflake does not support COPY statements that result in data transformation in any of the validation modes it allows. Therefore, the ELT Load Snap fails during Pipeline validation when the number of columns you define in the Target to Source Column Map field set is not the same as the number of columns in the target table. But the same Pipeline runs successfully because this limitation does not apply to Pipeline execution.
As a workaround for this limitation, ensure that you specify error_on_column_count_mismatch=false in the Format Option field under the File Format Option List field set.
Known Issues
Due to an issue with the Redshift COPY INTO SQL for PARQUET input files table schema management, the Snap fails to perform ALTER TABLE actions before loading data from a PARQUET source file to the target table in Redshift. This issue does not occur when the source file is in CSV or another format.
- ELT Pipelines built using an ELT Load Snap fail to perform the DROP AND CREATE TABLE and ALTER TABLE operations on Delta tables when working with a Databricks SQL persona on the AWS Cloud with the error
Operation not allowed: ALTER TABLE RENAME TO is not allowed for managed Delta tables on S3. However, the same action runs successfully with the Data Science and Engineering persona on the AWS Cloud.This is due to the limitation with the Databricks SQL Admin Console that does not allow you to add the configuration parameter
spark.databricks.delta.alterTable.rename.enabledOnAWS trueto its SQL Warehouse Settings.
Because BigQuery does not support Automatic Schema Inferencing (ASI) from source files in Amazon S3, the ELT Load Snap fails to produce the required output when you choose Drop and Create table as the Load Action and define the Target to Source Column Map in the Snap’s settings. However, the same configuration works fine for Pipeline validation purposes.
The ELT Load Snap cannot automatically infer schema from GZIP-compressed source files located in an ADLS Gen2 storage location for loading the data into Snowflake target tables.
The ELT Load Snap fails to complete the load operation on the target Snowflake instance when you choose to automatically infer the schema from the source data available in Microsoft Azure Storage Blob (WASB), specified as a File Name Pattern, and accessed using the Source Location Credentials. The Snap returns the error:
Azure null Storage Account incorrectly configured. But the same Snap configuration with the source files specified using File List instead of a File Name Pattern succeeds without any issues.Due to an issue with BigQuery table schema management (the time travel feature), an ALTER TABLE action (Add or Update column) that you attempt after deleting a column (DROP action) in your BigQuery target table causes the table to break and the Snap to fail.
As a workaround, you can consider either avoiding ALTER TABLE actions on your BigQuery instance or creating (CREATE) a temporary copy of your table and deleting (DROP) it after you use it.
Due to an issue with the Simba Spark JDBC driver for DLP, you cannot insert a NULL value in the nullable columns of Boolean data type in your DLP instance using any of the Write-type Snaps—ELT Load, ELT SCD2, ELT Insert Select, ELT Merge Into, and ELT Execute.
The only workaround currently available for this issue is to upgrade your JDBC driver to databricks-jdbc-2.6.25-1.jar, and use the corresponding JDBC driver class (com.databricks.client.jdbc.Driver) and JDBC URL in your Snap account.
This latest JDBC driver for DLP uses a JDBC URL structure and driver class that is different from the Simba Spark JDBC driver.
You cannot add a column to your BigQuery target table with a deleted column name using the ELT Load Snap, as BigQuery reserves deleted column names and data until the pre-configured time travel duration (from 2 through 7 days).
When loading data from a CSV file to a target DLP table, the header names in the file must exactly match the column names in the target table. Otherwise, the Snap returns the error—
Column names should be the same in the target table and CSV fileand aborts the load operation.When you are enclosing the column names within backticks (
`<Column_Name>`) for creating a new target table in a DLP instance using the ELT Load Snap—typically to ensure that the column names are used verbatim—you may encounter the error:ERROR processing query/statement: no viable alternative at input 'FROM'(line X, pos XX). To prevent this error, edit the header in your source file to exclude any special characters, thereby avoiding the use of backticks in the target table column names.- When your Databricks Lakehouse Platform instance uses Databricks Runtime Version 8.4 or lower, ELT operations involving large amounts of data might fail due to the smaller memory capacity of 536870912 bytes (512MB) allocated by default. This issue does not occur if you are using Databricks Runtime Version 9.0.
- ELT Pipelines created prior to 4.24 GA release using one or more of the ELT Insert Select, ELT Merge Into, ELT Load, and ELT Execute Snaps may fail to show expected preview data due to a common change made across the Snap Pack for the 4.26 GA release. In such a scenario, replace the Snap in your Pipeline with the same Snap from the Asset Palette and configure the Snap's Settings again.
- When loading data from a JSON file into a target Databricks Lakehouse Platform (DLP) instance using this Snap, if you choose the Drop and Create Table option as the Load Action and specify an additional column (that is not available in the JSON file) for the new table, it results in one more column null added to the new target table. In case of CSV files, this Snap behaves the same way as mentioned above, but only when the CSV file uses a comma separator.
- Suggestions displayed for the Schema Name field in this Snap are from all databases that the Snap account user can access, instead of the specific database selected in the Snap's account or Settings.
For Redshift and Azure Synapse databases, the ELT Load Snap displays JSON values for fields with datatypes Date and Time, when validating the Pipeline.
Snowflake Redshift Azure Synapse ”time_data” : “09:23:56”,”time_data” : {“time”: “09:23:56”},”time_data” : {“time”: “09:23:56”},”date_data” : “2020-12-20”,”date_data” : “2020-12-20”,”date_data” : {“date”: “2020-12-20”},However, the ELT Load Snap outputs the correct date and time values when executing the Pipeline.
To prevent these values from showing up in JSON format in the previews and ELT Transform Snap, you can cast the time or date values to a VARCHAR type in your custom query as follows:
CAST (<time_column_type_name> AS VARCHAR(<size_based_on_precision_required>)).
Example:CAST (time_data AS VARCHAR(20)).If you have dropped one or more columns from your target table outside of the Snap and then use it again to add these columns back and load data into the table, the Snap adds the new columns to the target table, but not the corresponding data from the source file.
- The ELT Load Snap does not infer accurate Date & Timestamp data types for Redshift.
In any of the supported target databases, this Snap does not appropriately identify nor render column references beginning with an _ (underscore) inside SQL queries/statements that use the following constructs and contexts (the Snap works as expected in all other scenarios):
WHEREclause (ELT Filter Snap)WHENclauseONcondition (ELT Join, ELT Merge Into Snaps)HAVINGclauseQUALIFYclause- Insert expressions (column names and values in ELT Insert Select, ELT Load, and ELT Merge Into Snaps)
- Update expressions list (column names and values in ELT Merge Into Snap)
- Secondary
ANDcondition Inside SQL query editor (ELT Select and ELT Execute Snaps)
Workaround
As a workaround while using these SQL query constructs, you can:
- Precede this Snap with an ELT Transform Snap to re-map the '_' column references to suitable column names (that do not begin with an _ ) and reference the new column names in the next Snap, as needed.
- In case of Databricks Lakehouse Platform where CSV files do not have a header (column names), a simple query like
SELECT * FROM CSV.`/mnt/csv1.csv`returns default names such as _c0, _c1, _c2 for the columns which this Snap cannot interpret. To avoid this scenario, you can:- Write the data in the CSV file to a DLP table beforehand, as in:
CREATE TABLE csvdatatable (a1 int, b1 int,…) USING CSV `/mnt/csv1.csv`where a1, b1, and so on are the new column names. - Then, read the data from this new table (with column names a1, b1, and so on) using a simple SELECT statement.
- Write the data in the CSV file to a DLP table beforehand, as in:
- In case of Databricks Lakehouse Platform, all ELT Snaps' preview data (during validation) contains a value with precision higher than that of the actual floating point value (float data type) stored in the Delta. For example, 24.123404659344 instead of 24.1234. However, the Snap reflects the exact values during Pipeline executions.
Snap Input and Output
| Input/Output | Type of View | Number of Views | Examples of Upstream and Downstream Snaps | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | None |
| N/A | This Snap does not require any input from upstream Snaps. |
| Output | Document |
|
| A document containing the status of the load operation and an SQL query that you can use in downstream ELT Snaps if any. |
Snap Settings
SQL Functions and Expressions for ELT
You can use the SQL Expressions and Functions supported for ELT to define your Snap or Account settings with the Expression symbol = enabled, where available. This list is common to all target CDWs supported. You can also use other expressions/functions that your target CDW supports.
| Parameter Name | Data Type | Description | Default Value | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Label | String | Specify a name for the Snap. You can modify this to be more specific, especially if you have more than one of the same Snap in your pipeline. | ELT Load | S3 Load |
| Get preview data | Check box | Select this checkbox to include a preview of the query's output. The Snap performs limited execution and generates a data preview during Pipeline validation. In the case of ELT Pipelines, only the SQL query flows through the Snaps but not the actual source data. Hence, the preview data for a Snap is the result of executing the SQL query that the Snap has generated in the Pipeline. The number of records displayed in the preview (upon validation) is the smaller of the following:
Rendering Complex Data Types in Databricks Lakehouse Platform Based on the data types of the fields in the input schema, the Snap renders the complex data types like map and struct as object data type and array as an array data type. It renders all other incoming data types as-is except for the values in binary fields are displayed as a base64 encoded string and as string data type. | Not selected | Selected |
| Database Name | String | Enter the name of the database in which the target table exists. Leave this blank if you want to use the database name specified in the Default Database Name field in the account settings. | N/A | TESTDB |
| Schema Name (Not applicable to Databricks Lakehouse Platform) | String | Required. Enter the name of the database schema. In case the schema name is not defined, then the suggestion for the schema name retrieves all schema names in the specified database when you click the suggest button.
| N/A | SALES |
| Target Table Name | String | Required. Enter the name of the table or view in which you want to perform the load operation. Only views that can be updated (have new rows) are listed as suggestions. So, Join views are not included. This also implies that the Snap account user has the Insert privileges on the views listed as suggestions.
| N/A | SALES_ORDERS |
| Target Table Hash Distribution Column (Azure Synapse Only) | String/Expression | Specify the hash distribution column name for the target table in Azure Synapse, if you choose the Load Action as Drop and Create table. This field is applicable only for Azure Synapse. Azure Synapse needs a table to be always hash-distributed for improved query performance. If the target table is created outside the Snap, you need not specify the target table column name. | N/A | var table |
| Load Action | Drop-down list | Select the load action to perform on the target table. Available options are:
The Snap does not modify the existing tables during Pipeline validation, but if you choose the Drop and Create table option in the Load Action field and the target table does not exist, it creates a new (empty) target table based on the schema specified in the Snap. | Append rows to existing table | Alter table |
| Table Option List | This field set enables you to define the table options for creating the target table before performing the load operation. You must specify each table option in a separate row. Click to add a new row.
| |||
| Table Option | Expression/Suggestion | Click the Suggest icon () and choose a table option that you want to use, from the suggested values. Specify the required values for the selected option. The table options you can use are:
| N/A | OPTIONS(custID=03761) |
| Table Columns | This field set enables you to configure the schema of the target table. You can use this field set to add/drop columns in the target table if you select the Drop and Create table or Alter table options in the Load Action field. This field set consists of the following fields:
| |||
| Column | String | Enter the name of the column that you want to load in the target table. You can also specify the columns to drop if you select the Alter table option in the Load Action field. | N/A | ID FNAME |
| Data Type | String | Activates when you select the Drop and Create table or Alter table options in the Load Action field. Enter the data type of the values in the specified column. | N/A | INT VARCHAR |
| Modifier | String | Activates when you select the Alter table option in the Load Action field. Select whether you want to add/drop the specified column. Available options are:
| Add | Drop |
| Redshift Schema Name (Only when BigQuery with Source Location as Redshift) | String/Expression | Applicable only when you are loading data from a Redshift source to a BigQuery target. Specify the schema name of the source table in Redshift. | N/A | PUBLIC, DEF_SCHEMA |
| Redshift Table Name (Only when BigQuery with Source Location as Redshift) | String/Expression | Applicable only when you are loading data from a Redshift source to a BigQuery target. Specify the name of the Redshift source table (from the schema selected above). | N/A | DataLoad_Source01 |
| Cloud Storage Path | String/Expression | Specify the fully-qualified path to the folder in the Cloud storage in this field, if you want to override the default path defined in the Snap's Account settings. For example:
| N/A | s3://bigbucket/app_data |
| File List | This field set enables you to specify the staged files to load. You must specify each file in a separate row. Click + to add a new row. Use File List for up to 2 files For the best performance of your load operation, we recommend that you use the File Name Pattern field to load data from multiple files at a source location (S3 or Redshift) instead of specifying the individual file names/paths in the File List fieldset. This field set consists of the following field:
| |||
| File | String | Enter the name of the staged file to load. | N/A | TestData.csv |
| File Name Pattern | String | Enter the pattern to use to match the file name and/or absolute path. You can specify this as a regular expression pattern string, enclosed in single quotes. For Redshift tables
Using Wildcard Patterns in BigQuery BigQuery has its own set of rules to resolve wildcard patterns like *.* (that you provide in this field). Refer Batch loading data > Load Wildcards in BigQuery documentation for the rules around using wildcards in BigQuery. See Loading Using Pattern Matching for details on Snowflake regular expressions, Examples of COPY INTO (Delta Lake on Databricks) for DLP, or Regular Expressions and the Java Programming Language for using regular expressions with Redshift, Azure Synapse, or BigQuery in this field. | N/A | Snowflake: '.*key.*[.]csv' Redshift: './key.*csv' |
| File Format Type | String/Expression/Suggestion | Select the format for the file. The options vary based on the database type (Snowflake/Redshift/Azure Synapse) in your account settings. The supported file formats are:
| None | AVRO |
| File Format Option List | This field set enables you to define the file format options for the load operation. You must specify each file format option in a separate row. Click + to add a new row.
See Snowflake Data Loading Commands, Redshift Data Format Parameters, or COPY INTO (Transact-SQL) for Azure Synapse Analytics for the list of of options that you can use based on the target database. Auto-Inferencing Source Table Schema ELT Load Snap allows you to infer the table schema from the source files and then apply the auto-inferred schema to your target tables. As of the July 2022 release, this feature is supported on the Redshift target CDW and with the source files in an S3 location. Learn more at Automatic Schema Inference with ELT Load Snap. | |||
| Format Option | String/Expression/Suggestion | Click the Suggest icon ( and choose a file format option that you want to use during the load operation, from the suggested values. Specify the required value for the selected option. Loading a CSV file with nulls into DLP If the CSV file you want to load into a DLP instance contains null values, ensure that you define the Format Option in the File Format Option List fieldset as sep = ',' without which the load operation does not succeed. | N/A | SKIP_HEADER = 1 |
| Encryption Type | Drop-down list | Select the encryption type that you want to use for the loaded data and/or files. Available options are:
Server-side encryption is available only for S3 accounts and Snowflake. | None | Server-Side Encryption |
| KMS Key | String | Activates when you select the Server-side KMS Encryption option in the Encryption Type field. Enter the KMS key to use to encrypt the files. Not required for Redshift databases. The load operation automatically recognizes and loads the encrypted files. See Loading encrypted files from Amazon S3 for details. | N/A | <require input> |
| Copy Option List | This field set enables you to define the COPY options for the load operation. You must specify each COPY option in a separate row. Click + to add a new row. This field set comprises the following field:
See COPY Options for Snowflake, COPY Parameter Reference for Redshift, or COPY INTO (Transact-SQL) for Azure Synapse Analytics. | |||
| Copy Option | String/Expression/Suggestion | Click the Suggest icon ( and choose a COPY option that you want to use if there is an error during the load operation, from the suggested values. Specify the required value for the selected option. | N/A | ON_ERROR = ABORT_STATEMENT |
| Validation Mode | String | Select an output preview type for the data validation performed as part of the Pipeline validation. The options vary based on the database type (Snowflake/Redshift) in your account settings. Available options for Snowflake are:
Available options for Redshift are:
No specific validation modes are available for Azure Synapse. For more details, see Validating Staged Files for Snowflake and Validating Input Data for Redshift. | None | RETURN_n_ROWS |
| Rows To Return | Integer | Activates when you select the RETURN_n_ROWS option in the Validation Mode field. Enter the number of records to retrieve from the target table to validate whether the load operation was successful. | N/A | 20 |
| Enable source column position (Snowflake and Azure Synapse Only) | Checkbox | Select this checkbox to include the column position from the source table in the case of Snowflake or Azure Synapse. In the case of other target CDWs (Redshift, DLP, and BigQuery), you can leave this checkbox unchecked. | Not selected | Selected |
| Target to Source Column Map | This field set enables you to define the mapping between the columns in the target table and the corresponding columns in the source file. You must define each mapping in a separate row. Click to add a new row. The available options are:
| |||
| Target Table Column Name | String/Expression/Suggestion | Click the Suggest icon ( and choose a column from the list of target table columns displayed. Ensure that you have defined the Schema Name or the Target Table Name to see the list of columns in this field's suggestions. | N/A | ORDER_ID |
| Source File Column Name | String/Expression/Suggestion | Click the Suggest icon ( and choose a column from the list of source file columns displayed. Ensure that you have defined the Schema Name or source file path) to see the list of columns in this field's suggestions. | N/A | ORD_ID |
Snap Behavior During Pipeline Validation
This Snap's behavior during Pipeline validation varies for each Load Action selected.
| Load Action | Target Table exists? | Validation Result | Action on Target Table# |
|---|---|---|---|
| Append rows to existing table | No | Success | Creates an empty target table based on the schema information available in the Snap settings. |
| Yes | Success | No updates made. | |
| Overwrite existing table | No | Success | Creates an empty target table based on the schema information available in the Snap settings. |
| Yes | Success | No updates made. | |
| Drop and Create table | No | Success | Creates an empty target table based on the schema information available in the Snap settings. |
| Yes | Success | No updates made. | |
| Alter table | No | Success | Creates an empty target table based on the schema information available in the Snap settings. |
| Yes | Success | No updates made. | |
| # Bulk load operations are not carried out during Pipeline validation. | |||
Snowflake
The data is not loaded into the Snowflake table. It is just validated using the RETURN_n_ROWS validation mode. The number of records in the output is determined by the preview count set in the Pipeline settings. The Snap creates the target table (if not existing already) in the database when you select Load Action as Drop and Create the table. For all other load actions, the Snap verifies if the specified target table exists in the database.
Redshift
The data is not loaded into the Redshift table. The files in S3 are just validated using the NOLOAD validation mode to verify data integrity of the files. The target table is also affected based on your selection in the Load Action field. The Snap creates the target table (if not existing already) in the database when you select Load Action as Drop and Create table. For all other load actions, the Snap verifies if the specified target table exists in the database.
Azure Synapse
The data is not loaded into the Azure Synapse table. The Snap creates the target table (if not existing already) in the database when you select Load Action as Drop and Create table. For all other load actions, the Snap verifies if the specified target table exists in the database.
Troubleshooting
| Error | Reason | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| Time '"01:01:23"' is not recognized. | The CSV file you are trying to load into the Snowflake database contains single or double quotes for time and/or date values. Hence, the ELT Load Snap is unable to read and insert these values into the target table. | After you specify the CSV files in the ELT Load Snap’s settings, add an entry in the File Format Options field set as FIELD_OPTIONALLY_ENCLOSED_BY='\'' or FIELD_OPTIONALLY_ENCLOSED_BY='\”' to match the quotes used in the CSV files for date and/or time values in it. The Snap would then ignore these quotes used for the values in the CSV files. |
| File read error while uploading data from a CSV file | This can happen when the source CSV file contains a header row which the target database cannot recognize/interpret. | Depending on your target database, use the respective File Format Option in the ELT Load Snap.
|
Invalid DBFS folder name (Target CDW: Databricks Lakehouse Platform) | You have not specified an appropriate DBFS path in the DBFS Folder path field in the Snap's (DLP) account settings. | Edit the Snap's account settings to ensure that you have provided a valid DBFS Folder path. |
Database cannot be blank. (when seeking the suggested list for Schema Name field) | Suggestions in the Schema Name and Target Table Name fields do not work when you have not specified a valid value for the Database Name field in this Snap. | Specify the target Database Name in this Snap to view and choose from a suggested list in the Schema Name and Target Table Name fields respectively. |
Unknown Source / Not found: <path> (Target CDW: BigQuery) | BigQuery has a unique way of resolving wildcard patterns like | Make sure that the file name pattern you provide conforms to the rules defined in Batch loading data > Load Wildcards section of BigQuery documentation. |
Loading data into a Redshift table using the RegEx pattern *.* in File Name Pattern field results in the operation being performed twice. | Since the Redshift Copy Into SQL does not natively support File Pattern option unlike the other CDWs, SnapLogic supports this externally through Java Regular Expressions (RegEx). The RegEx | Use the RegEx csv/person/.+\..+ in the File Name Pattern field to load data from all the files available in a specific source folder. |
Keyword RANGE is not acceptable as a column name. (CDW: Databricks Lakehouse Platform) | This can happen with any reserved keyword if it is used as a column/field name in the table to be created. | Ensure the enclose such column names (reserved keywords) between backticks (`). For example: `RANGE' STRING. |
Keyword ORDER is not acceptable as a column name in the JSON file. (Target CDW: BigQuery) | This can happen with any reserved keyword if it is used as a column/field name in the table to be created. | Ensure that you enclose such column names (reserved keywords) between backticks (`). For example: `ORDER`. |
| Column names in Snowflake tables are case-sensitive. It stores all columns in uppercase unless they are surrounded by quotes during the time of creation in which case, the exact casing is preserved. See, Identifier Requirements — Snowflake Documentation. | Ensure that you follow the same casing for the column table names across the Pipeline. | |
[Simba][SparkJDBCDriver](500051) ERROR processing query/statement. Error Code: 0 Cannot create table (' (Target CDW: Databricks Lakehouse Platform) | The specified location contains one of the following:
So, the Snap/Pipeline cannot overwrite this table with the target table as needed. | Ensure that you take appropriate action (mentioned below) on the existing table before running your Pipeline again (to create another Delta table at this location). Move or drop the existing table from the schema manually using one of the following commands: Access the DBFS through a terminal and run:
OR Use a Python notebook and run:
|
Column names should be the same in the target table and CSV file. (Target: DLP) | One or more header names in your source CSV file do not match with the corresponding target table column names. | Ensure that each of the column names in your target table exactly matches the corresponding header name used in the CSV file or vice versa before you retry running the Pipeline. |
Error code 400: Column <column_name> was recently deleted in the table <table_name>. | BigQuery reserves deleted column names for up to the time travel duration (2 through 7 days) as set by your DBA. | Use a different column name to complete your Load action. |
Examples
To skip the header row while uploading data from a CSV file, use the following File Format Options that suit your target database.
| Target | File Format Options to use |
|---|---|
| Azure Synapse | FIRSTROW = 2 |
| Databricks Lakehouse Platform | 'header' = 'true' |
| Google BigQuery | skip_leading_rows = 1 |
| Redshift | IGNOREHEADER 1 |
| Snowflake | SKIP_HEADER = 1 |
Loading Files from S3 Bucket to Snowflake
We need to perform Snowflake ELT transformations upon a file present in an S3 bucket. Therefore, we must first load the file into the Snowflake database from the source location. This Pipeline shows how we can use the ELT Load Snap to accomplish this task.
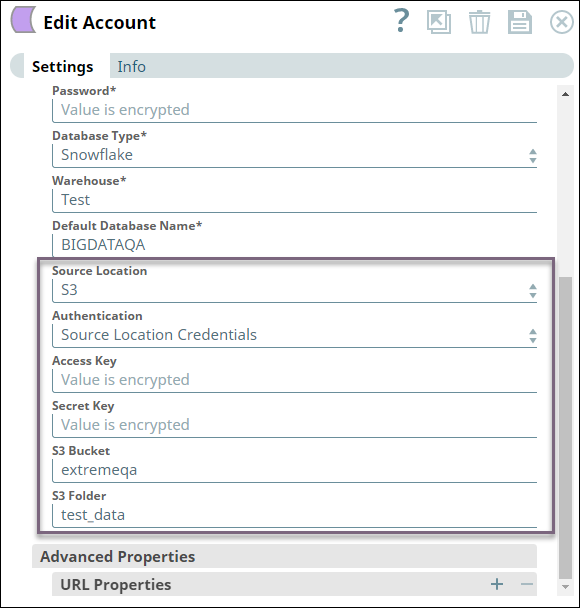
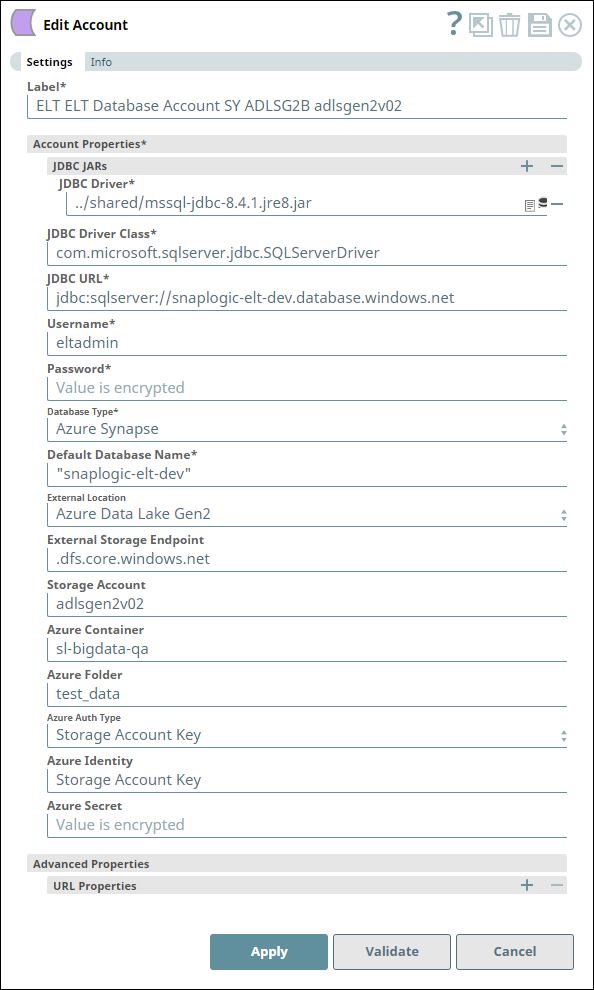
Before we can load the file, we must configure the ELT account to read from the source S3 bucket by configuring the Source Location, Authentication, Access Key, Secret Key, S3 Bucket, and S3 Folder fields. The fields vary based on the source location and authentication. See Configuring ELT Database Accounts for details.
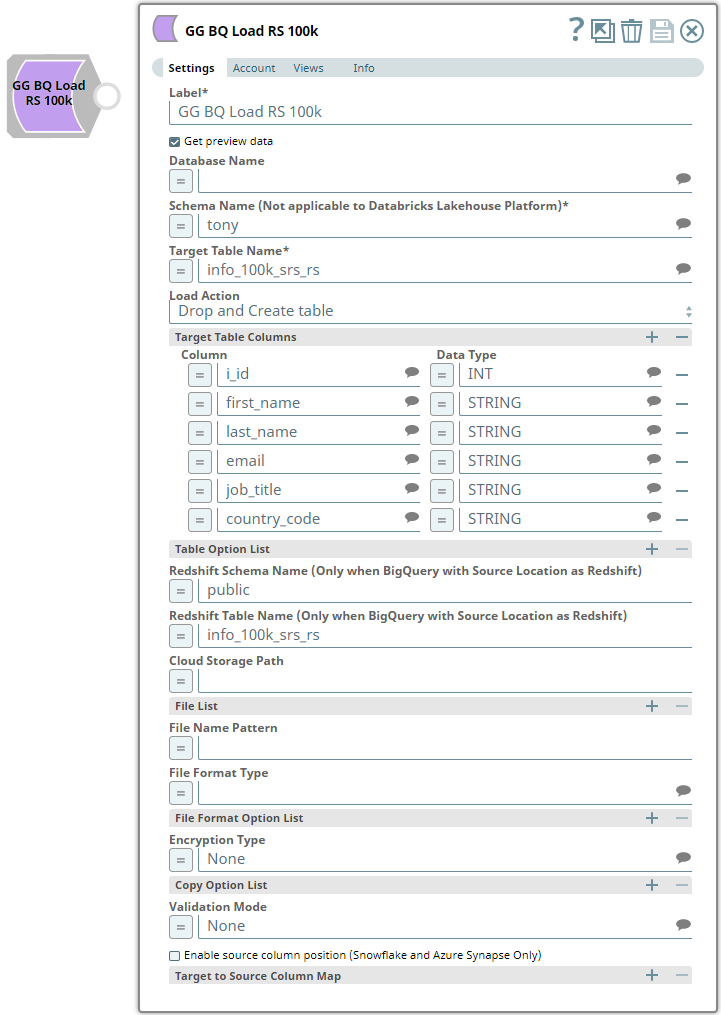
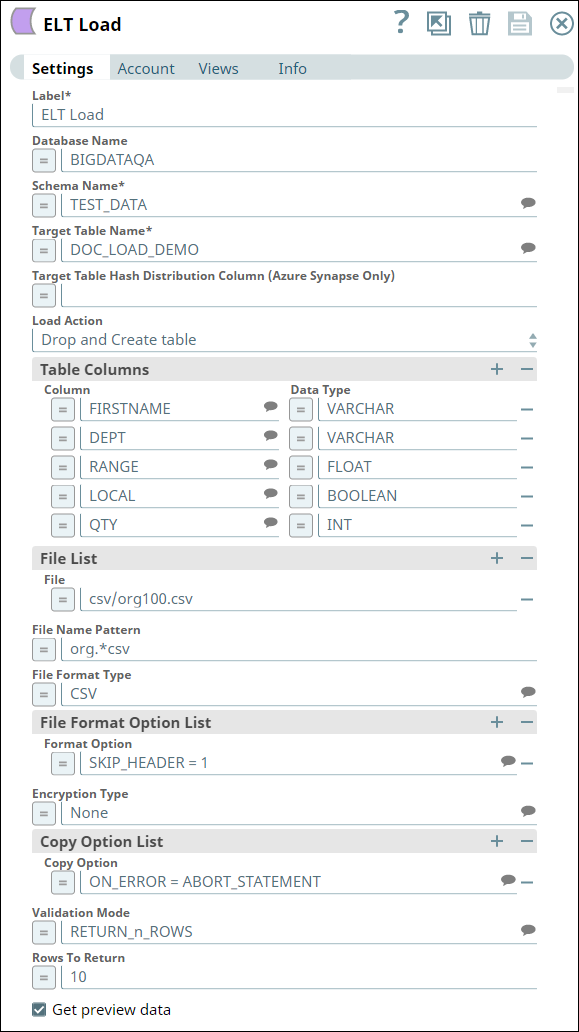
We configure the ELT Load Snap as shown below:
Let us understand the Snap's configuration:
- The Database Name, Schema Name, and Target Table Name specify the target database, schema, and table into which we want to write the file's data.
- Table Action indicates that if a table with the same name exists, we configure the Snap to drop the table and create a new one in its place.
- Since this is a new table, the Table Columns field set specifies the table's schema.
- The File List field set specifies the source file's path in the S3 bucket and the file's format.
- The Format Option field set specifies that the Snap must ignore the file's header. Otherwise, the header is also loaded into the target table.
- The Copy Option field set specifies that the Snap must abort the loading operation if it encounters an error.
- The Validation Mode and Rows to Return fields specify that 10 rows from the target table be retrieved upon successful completion.
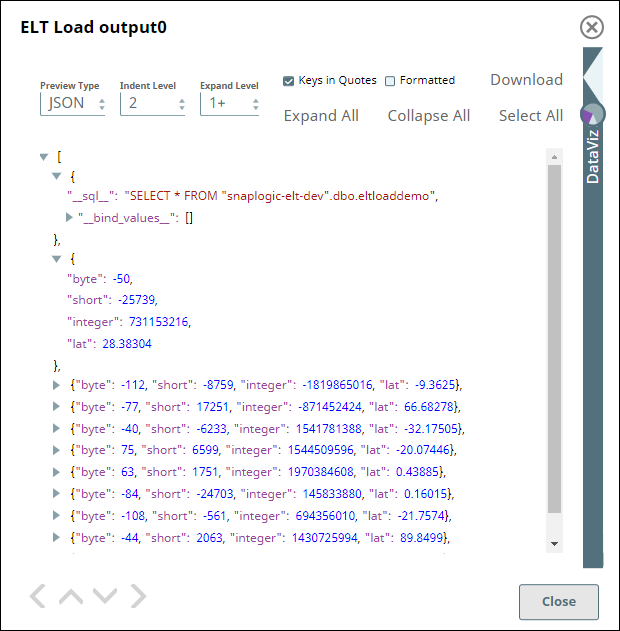
To validate a successful execution, the ELT Load Snap executes a SELECT * command on the target table and returns 10 rows:
We can either create a separate Pipeline to perform ELT operations on the table or add appropriate Snaps downstream of the ELT Load Snap in the same Pipeline.
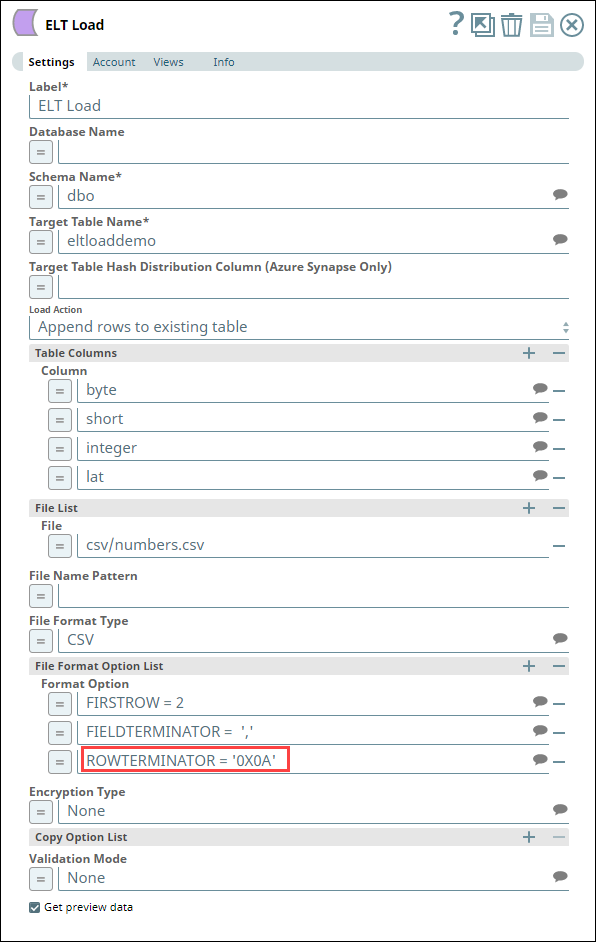
Uploading data from a CSV File in Azure Data Lake Gen2 Storage to Azure Synapse
The following one-Snap (ELT Load) Pipeline connects to an Azure Data Lake Gen2 Storage using an ADLS Gen2 Basic Auth account to upload a CSV file from the storage to an Azure Synapse database. This CSV file is created on MacOS with the default line endings.
| Account Configuration | Snap Configuration |
|---|---|
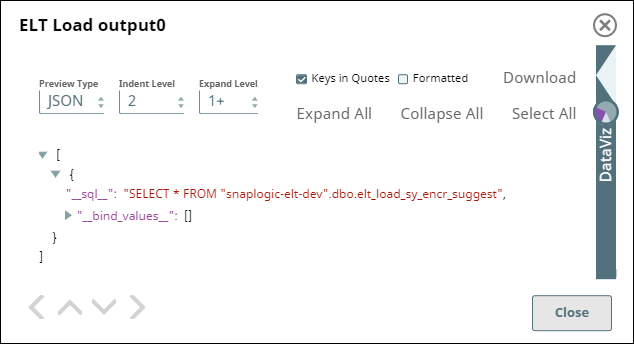
For the Pipeline to work as expected in case of the CSV file created on MacOS with the default (MacOS) line endings, define the value for the file format option ROWTERMINATOR as '0X0A' instead of the usual '\n'. With '\n' as ROWTERMINATOR, the Pipeline runs successfully, but does not insert the data from the CSV file into the newly-created table in Azure Synapse.
| Snap Output with ROWTERMINATOR = '\n' |
|---|
| Snap Output with ROWTERMINATOR = '0X0A' |
Downloads
Important Steps to Successfully Reuse Pipelines
- Download and import the Pipeline into SnapLogic.
- Configure Snap accounts as applicable.
- Provide Pipeline parameters as applicable.