PostgreSQL - Execute
On this Page
Snap type: | Write | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description: | This Snap allows you to execute arbitrary SQL. This Snap works only with single queries. Valid JSON paths that are defined in the where clause for queries/statements will be substituted with values from an incoming document. Documents will be written to the error view if the document is missing a value to be substituted into the query/statement. You can drop your database with it, so be careful. | ||||||||||
| Prerequisites: | [None] | ||||||||||
| Support and limitations: |
| ||||||||||
| Behavior Change |
If you have any existing Pipelines that are mapped with status key or previous description then those Pipelines will fail. So, you might need to revisit your Pipeline design. | ||||||||||
| Account: | This Snap uses account references created on the Accounts page of SnapLogic Manager to handle access to this endpoint. See Configuring PostgreSQL Accounts for information on setting up this type of account. | ||||||||||
| Views: |
| ||||||||||
Settings | |||||||||||
Label* | Specify the name for the Snap. You can modify this to be more specific, especially if you have more than one of the same Snap in your Pipeline. | ||||||||||
SQL statement* | Specify the SQL statement to execute on the server. Scenarios to successfully execute your SQL statements You must understand the following scenarios to successfully execute your SQL statements: Scenario 1: Executing SQL statements without expressions
Examples:
Additionally, the JSON path (e.g. $myName) is allowed only in the WHERE clause. If the SQL statement starts with SELECT (case-insensitive), the Snap regards it as a select-type query and executes once per input document. If not, it regards it as write-type query and executes in batch mode. Scenario 2: Executing SQL queries with expressions
Table name and column names must not be provided as bind parameters. Only values can be provided as bind parameters. Examples:
We recommend you to add a single query in the SQL Statement field. Known Issues
Single quotes in values must be escaped Any relational database (RDBMS) treats single quotes ( For example:
Default Value: [None] | ||||||||||
| Query type | Select the type of query for your SQL statement (Read or Write). When Auto is selected, the Snap tries to determine the query type automatically. Default Value: Auto | ||||||||||
Pass through | Select this checkbox to pass the input document to the output view under the key 'original'. This property applies only to the Execute Snaps with SELECT statement. Default Value: Selected | ||||||||||
Ignore empty result | If selected, no document will be written to the output view when a SELECT operation does not produce any result. If this property is not selected and the Pass through property is selected, the input document will be passed through to the output view. Default Value: Not selected | ||||||||||
| Number of retries | Specify the maximum number of retry attempts the Snap must make in case there is a network failure and is unable to read the target file. The request is terminated if the attempts do not result in a response.
Ensure that the local drive has sufficient free disk space to store the temporary local file. Default Value: 0
| ||||||||||
| Retry interval (seconds) | Specifies the time interval between two successive retry requests. A retry happens only when the previous attempt resulted in an exception. Default Value: 1 | ||||||||||
Auto commit | Select one of the options for this property to override the state of the Auto commit property on the account. The Auto commit at the Snap-level has three values: True, False, and Use account setting. The expected functionality for these modes are:
Default Value: Use account setting 'Auto commit' may be enabled for certain use cases if PostgreSQL jdbc driver is used in either Redshift, PostgreSQL or generic JDBC Snap. But the JDBC driver may cause out of memory issues when Select statements are executed. In those cases, “Auto commit" in Snap property should be set to ‘False’ and the Fetch size in the “Account setting" can be increased for optimal performance. Behavior of DML Queries in Database Execute Snap when auto-commit is false DDL queries used in the Database Execute Snap will be committed by the Database itself, regardless of the Auto-commit setting. When Auto commit is set to false for the DML queries, the commit is called at the end of the Snap's execution. The Auto commit needs to be true in a scenario where the downstream Snap does depend on the data processed on an Upstream Database Execute Snap containing a DML query. When the Auto commit is set to the Use account setting on the Snap, the account level commit needs to be enabled. | ||||||||||
Snap execution | Select one of the three modes in which the Snap executes. Available options are:
| ||||||||||
Troubleshooting
| Error | Reason | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
Pipeline is no longer running. | When you use numerous self-joins in SQL SELECT statements with bind values, the Snap is likely to fail after the 11th statement. | Use either of the following workaround solutions to avoid Pipeline failure:
|
Examples
Inserting a record in a table using stored procedure in PostgreSQL-Execute Snap
Stored procedure:
A stored procedure is a named set of pre-written instructions or commands that are saved in a database. Instead of giving instructions whenever you want to perform an operation like inserting, updating, fetching, or deleting records, you write them down in a procedure. Then, whenever you need to do that specific task again, you call the stored procedure.
This example pipeline demonstrates how to create a stored procedure and call the stored procedure to insert a record in an existing table.
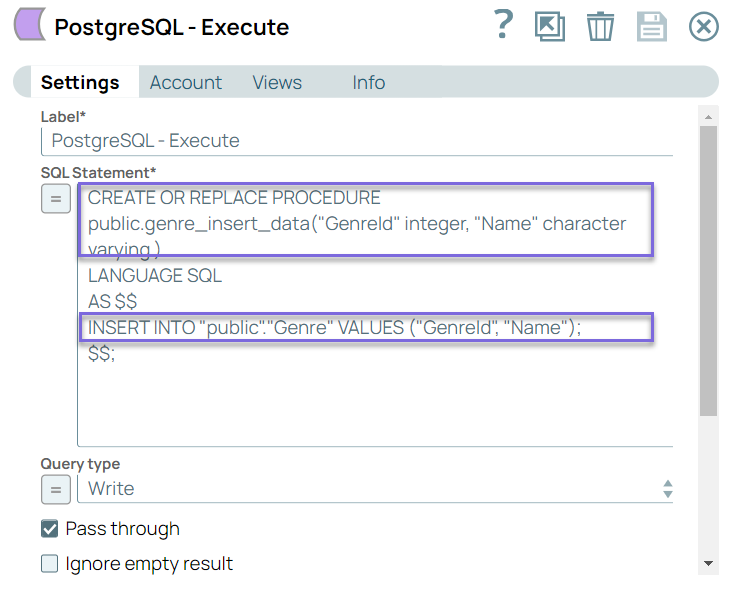
Step 1: Configure the PostgreSQL-Execute Snap with Create Procedure statement to create a stored procedure, genre_insert_data, to insert GenreId and Name in the Genre table.
a. CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE public.genre_insert_data("GenreId" integer, "Name" character varying ) statement creates a stored procedure that has INPUT parameters GenreId and Name values.
b. INSERT INTO "public"."Genre" VALUES ("GenreId", "Name"); this statement inserts the values in the Genre table.
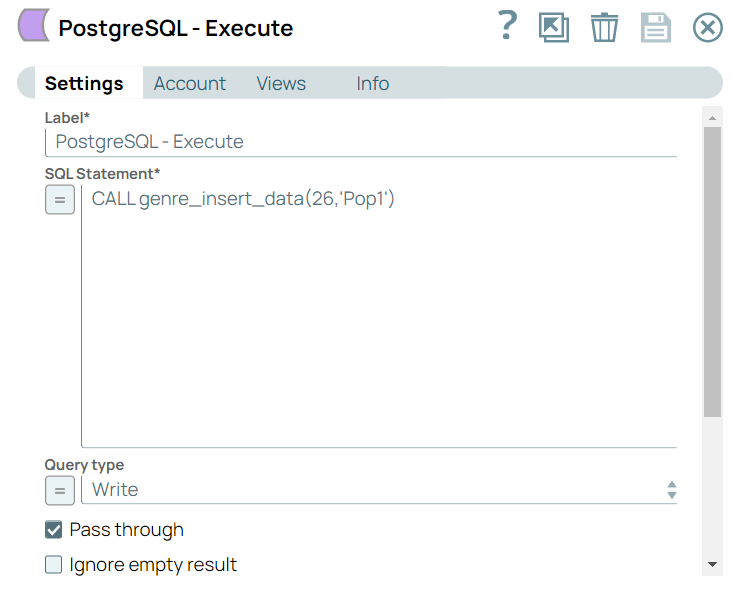
Step 2: Configure the PostgreSQL-Execute Snap with a call statement to trigger the stored procedure by passing values for GenreId and Name.
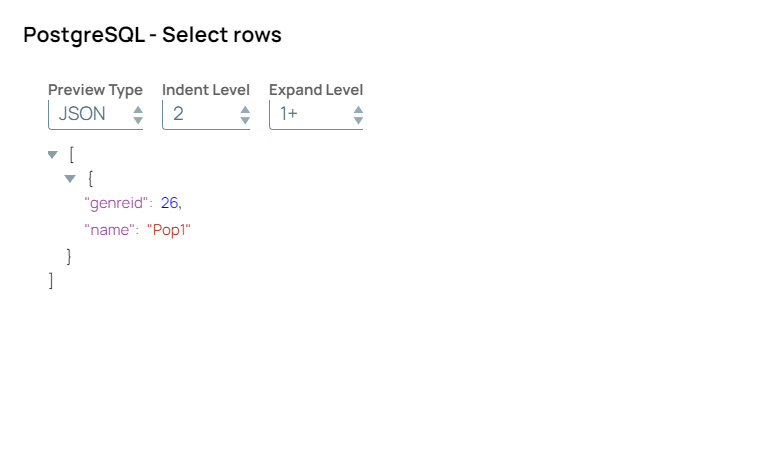
Step 3: Configure the Table Name and GenreId in the PostgreSQL-Select Snap as follows to fetch the inserted record to verify if the record has been inserted.
Step 4: On validation, the PostgreSQL-Select Snap fetches the previously inserted record.
The following single-Snap Pipeline runs an SQL query containing a JOIN command to collate data between two PostgreSQL tables.
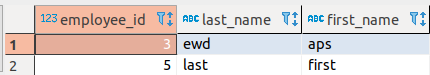
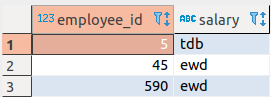
Let us consider the following tables in a PostgreSQL DB. Notice that the column employee_id is common between these tables.
| Table 1: AVemployees | Table 2: AVempsalary |
|---|---|
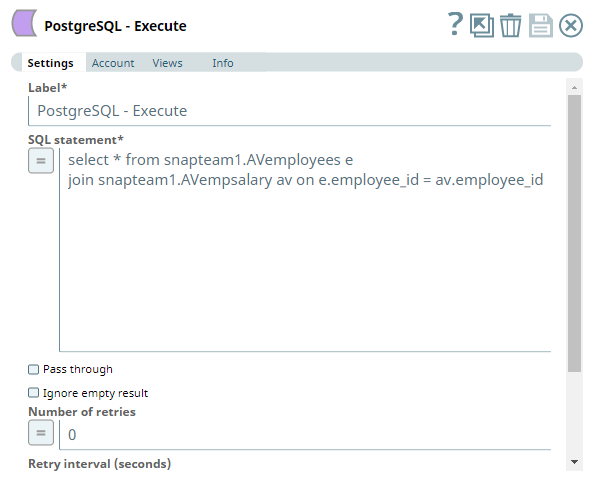
The Snap accesses the PostgreSQL tables using a valid account and runs an SQL query that contains a JOIN command based on the following settings:
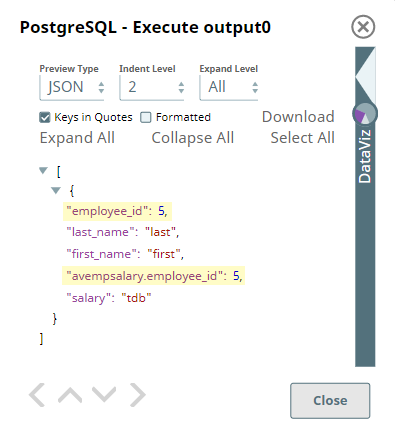
The output preview after executing this Pipeline displays the result for the SQL query.
Upon joining the two tables as defined in the SQL query, we can see the employee_id column in the second table is prefixed with its table name AVempsalary to differentiate it from the column with the same name in the AVemployees table. This is how the PostgreSQL - Execute Snap handles column with conflicting names in tables when the SQL statement contains a JOIN command.
Downloads
Important steps to successfully reuse Pipelines
- Download and import the pipeline into the SnapLogic application.
- Configure Snap accounts as applicable.
- Provide pipeline parameters as applicable.
Snap Pack History
Have feedback? Email documentation@snaplogic.com | Ask a question in the SnapLogic Community
© 2017-2025 SnapLogic, Inc.
.png?version=1&modificationDate=1489886486706&cacheVersion=1&api=v2)
.png?version=1&modificationDate=1489744292055&cacheVersion=1&api=v2)