ELT BigQuery Account
In this article
Overview
You can use the ELT Database Account to connect ELT Snaps with a target Google BigQuery instance. This account enables you to write transformed data to a target BigQuery database hosted in a Google Cloud Platform (GCP) location. The cloud location where the database is hosted is indicated in the JDBC URL for BigQuery—jdbc:bigquery://<host_URL>/bigquery.
Deprecation of Refresh Token Accounts
With Google deprecating the OAuth out-of-band (OOB) flow, the Refresh Token Accounts defined for connecting your ELT Snaps to the BigQuery instances start failing in a phased manner. We recommend that you immediately modify these Snap account configurations to switch to an Access Token Account or a Service Account from the Refresh Token Account.
The ELT Snap Pack does not support mixed accounts from different types of databases in the same Pipeline. For example, a Pipeline in which some Snaps are connecting to the BigQuery database cannot have other Snaps connecting to the Redshift database.
Prerequisites
- A valid Snowflake account.
Certified JDBC JAR File: SimbaJDBCDriverforGoogleBigQuery42_1.3.0.1001.zip. Refer to Preparing the JDBC Driver for Manual Upload if you are not selecting the Download JDBC Driver Automatically checkbox.
Using Alternate JDBC JAR File Versions
We recommend that you let the ELT Snaps use this JAR file version. However, you may use a different JAR file version of your choice.
Limitations
None.
Known Issue
- When you use the auto-fill feature in the Google Chrome browser to fill ELT Snap account credentials—such as user names, passwords, client secrets, auth codes and tokens, secret keys, and keystores, the accounts, and hence the Pipelines fail. This is because the browser overwrites the field values with its own encrypted values that the SnapLogic Platform cannot read. SnapLogic recommends that you do not auto-save your Snap account credentials in the Chrome browser, delete any credentials that the browser has already saved for elastic.snaplogic.com, and then perform ONE of the following actions:
- Option 1: Click that appears in the address bar after you submit your login credentials at elastic.snaplogic.com, and then click Never.
- Option 2: Disable the Offer to save Passwords option at chrome://settings/passwords while working with your SnapLogic Pipelines. If you disable this option, your Chrome browser will not remember your passwords on any other website.
Due to an issue with BigQuery table schema management (the time travel feature), an ALTER TABLE action (Add or Update column) that you attempt after deleting a column (DROP action) in your BigQuery target table causes the table to break and the Snap to fail.
As a workaround, you can consider either avoiding ALTER TABLE actions on your BigQuery instance using the Snap or creating (CREATE) a temporary copy of your table and deleting (DROP) it after you use it.
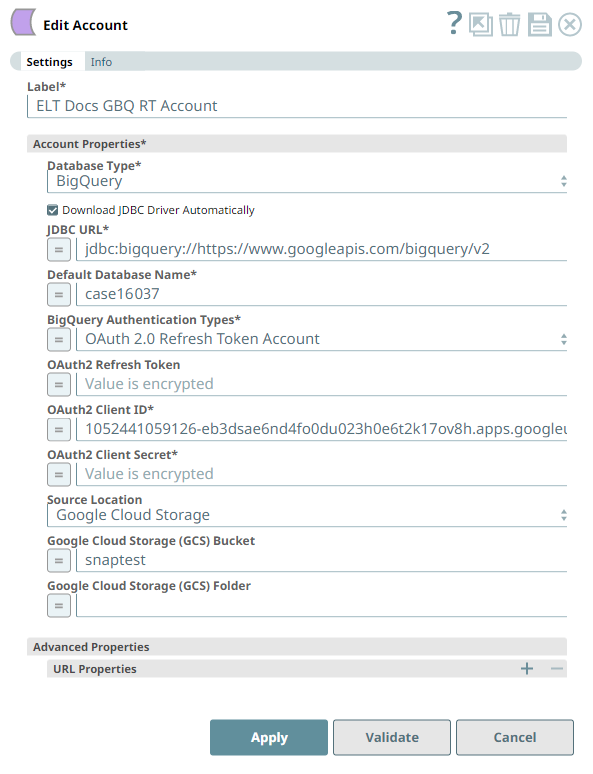
Account Settings
Asterisk ( * ) indicates a mandatory field.
Suggestion icon ( ) indicates a list that is dynamically populated based on the configuration.
Expression icon ( ) indicates whether the value is an expression (if enabled) or a static value (if disabled). Learn more about Using Expressions in SnapLogic.
Add icon () indicates that you can add fields in the fieldset.
Remove icon () indicates that you can remove fields from the fieldset.
| Parameter | Field Dependency | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Label* | None. | Unique user-provided label for the account. Default Value: N/A Example: ELT BQ RT Account AD ON | ||
| Account Properties* | Use this field set to configure the information required to establish a JDBC connection with the account. This field set consists of the following fields:
| |||
| Database Type* | None. | Select the target data warehouse into which the queries must be loaded, that is BigQuery. This activates the following fields:
Default Value: N/A Example: BigQuery | ||
| Download JDBC Driver Automatically | None. | Select this checkbox to allow the Snap account to download the certified JDBC Driver for BigQuery. The following fields are disabled when this checkbox is selected.
To use a JDBC Driver of your choice, clear this checkbox, upload (to SLDB), and choose the required JAR files in the JDBC JAR(s) and/or ZIP(s): JDBC Driver field. Use of Custom JDBC JAR version You can use a different JAR file version outside of the recommended listed JAR file versions. Default Value: Not Selected Example: Selected | ||
| JDBC JAR(s) and/or ZIP(s): JDBC Driver | Required when the Download JDBC Driver Automatically checkbox is not selected. | Upload the JDBC driver and other JAR files that you want to use into SLDB. Click to add a new row. Add each JDBC JAR file in a separate row. See Current JDBC Driver for BigQuery for more information about JDBC drivers and download the appropriate driver for your account. Default Value: N/A Example: SimbaJDBCDriverforGoogleBigQuery42_1.2.22.1026.zip | ||
| JDBC driver class* | Required when the Download JDBC Driver Automatically checkbox is not selected. | Specify the driver class to use for your application. We recommend that you use com.simba.googlebigquery.jdbc.Driver to suit your BigQuery database, as other classes and methods may change due to future enhancements. Default Value: N/A Example: com.simba.googlebigquery.jdbc.Driver, com.simba.googlebigquery.jdbc.DataSource | ||
| JDBC URL* | None. | Enter the JDBC driver connection string that you want to use, based on the Database you are connecting to. See the Installation and Configuration Guide at ODBC and JDBC drivers for BigQuery for more information.
Alternatively, you can make use of the Username, Password, and Database Name fields, along with the Advanced Properties > URL Properties fieldset to provide the parameters required for building your JDBC URL. See Passing your JDBC URL for more information. Avoid passing Password inside the JDBC URL If you specify the password inside the JDBC URL, it is saved as it is and is not encrypted. We recommend passing your password using the Password field provided, instead, to ensure that your password is encrypted. Default Value: N/A Example: jdbc:bigquery://https://www.googleapis.com/bigquery/v2:443;ProjectId=MyBigQueryProject;OAuthType=1; | ||
| Default Database Name* | None. | Enter the name of the database to use by default. This database is used if you do not specify one in the ELT Select, ELT Insert-Select, or ELT Merge Into Snaps. Default value: N/A Example: EMPLOYEEDB | ||
| BigQuery Authentication Types* | Database Type is BigQuery | Select the authentication type that you use to connect to your Google BigQuery instance. It can be one of the following:
Default value: Service Account Example: OAuth 2.0 Access Token Account | ||
| Service Account Email* | BigQuery Authentication Types is Service Account | Specify the Google email account that is associated with your Google Cloud project. You would need the associated service account key file to authenticate this account. See Creating a Service Account and Authenticating with a service account key file for more information. Default value: N/A Example: my_service_account@domain.com | ||
| Service Account Key File Path* | BigQuery Authentication Types is Service Account | Specify the SLDB location (file path) of the service account key file associated with this service account. Default value: N/A Example: /my_SA/key_file/ | ||
| OAuth 2.0 Access Token | BigQuery Authentication Types is OAuth 2.0 Access Token Account | Enter the OAuth 2.0 Access Token pertaining to your BigQuery instance. See Obtaining Access Tokens for the steps to generate and use this access token. Using OAuth2 Access Tokens from BigQuery An OAuth2 Access Token generated for Google BigQuery is valid for 60 minutes. To be able to run SQL queries after the token has expired, generate and enter another Access Token in this field. Default value: N/A Example: ya29.Ci9deZOky9V36Tz497HY1chAA2sA8J_wM8e5FnY9rJg551153GQWGbleO-y9apjLFg | ||
| OAuth2 Refresh Token | BigQuery Authentication Types is OAuth 2.0 Refresh Token Account | Deprecation of Refresh Token Accounts With Google deprecating the OAuth out-of-band (OOB) flow, the Refresh Token Accounts defined for connecting your ELT Snaps to the BigQuery instances start failing in a phased manner. We recommend that you immediately modify these Snap account configurations to switch to an Access Token Account or a Service Account from the Refresh Token Account. Provide the OAuth2 Refresh Token string that the Snap can use to automatically generate a valid access token—that you need to run SQL queries in BigQuery—whenever an access token expires. This method of authentication helps you to avoid repetitive manual updates to your Snap accounts in BigQuery ELT Snaps. OAuth2 Refresh Tokens Refresh tokens do not expire until the administrator revokes them. You can use the Refresh Token as many times as necessary to request access tokens. Default value: N/A Example: AA2sA8J_wM8e5FnY9rJg551153GQWGbleO-y9apjLFgya29.Ci9deZOky9V36Tz497HY1ch | ||
| OAuth2 Client ID* | BigQuery Authentication Types is OAuth 2.0 Refresh Token Account | Enter the OAuth2 client ID associated with your BigQuery application. The Snap uses this value along with Secret Key and OAuth2 Refresh Token to generate the required Access Token. Default value: N/A Example: 1055912624410-6a29rmvnogteqt99781q0gm4vp2k7v9a.apps.googleusercontent.com | ||
| OAuth2 Client Secret* | BigQuery Authentication Types is OAuth 2.0 Refresh Token Account | Enter the OAuth2 client secret associated with the OAuth2 client ID entered in the above field. Default value: N/A Example: bOqUqFQdusfInjfDlh2FDtbD | ||
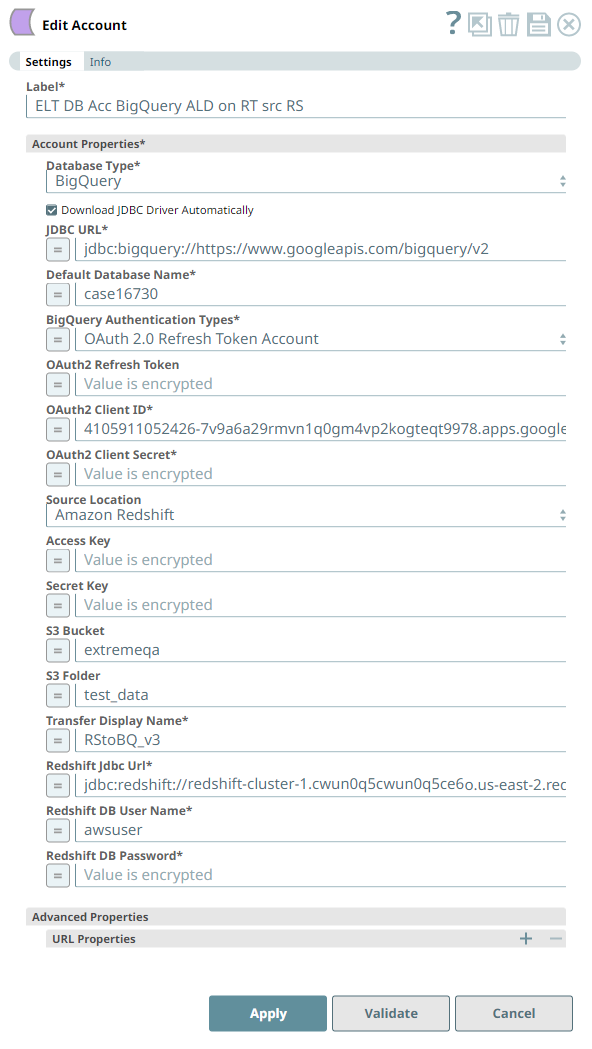
| Source Location* | Database Type is BigQuery | Select the source data warehouse from which to load data into the target database. You must configure this field if you want to use the ELT Load Snap. Available options are:
Default value: None Example: S3, Azure, Google Cloud Storage | ||
| Access Key | Source Location is S3 or Amazon Redshift, and Authentication is Source Location Credentials. | Enter the access key ID associated with your AWS S3 account. Default value: N/A Example: ABCDEFGHIJKL1MNOPQRS | ||
| Secret Key | Source Location is S3 or Amazon Redshift, and Authentication is Source Location Credentials. | Enter the client secret key associated with your AWS S3 account. Default value: N/A Example: aBcdeFGhiJKLM/N1OPQRS/tUvWxyZABCDEFGHIJKLMN | ||
| S3 Bucket | Source Location is S3 or Amazon Redshift. | Enter the name of the bucket from which to load the data. Default value: N/A Example: employeedata | ||
| S3 Folder | Source Location is S3 or Amazon Redshift. | Enter the name of the folder in the S3 bucket specified above where the source files are located. Default value: N/A Example: hrdepartment | ||
| Transfer Display Name* | Source Location is Amazon Redshift | Specify the display name for the data transfer configuration you created for the load operation. Default value: N/A Example: rs_bq_transfer_one | ||
| Redshift Jdbc Url* | Source Location is Amazon Redshift | Specify the JDBC URL needed to locate and connect to the Redshift source data.
Default value: N/A Example: jdbc:redshift://endpoint:port/<databaseName> | ||
| Redshift DB User Name* | Source Location is Amazon Redshift | Enter the user name to access your Redshift database. SnapLogic appends this user name to build the final JDBC URL. Default value: N/A Example: rs_user_johndoe | ||
| Redshift DB Password* | Source Location is Amazon Redshift | Enter the password associated with the above user name. SnapLogic appends this password to build the final JDBC URL. Default value: N/A Example: SJvcsDjhfASD%^ | ||
| Google Cloud Storage (GCS) Bucket | Source Location is Google Cloud Storage | Enter the name of the GCS bucket from which to load the data to your Snowflake database. Default value: N/A Example: elt_gcs_bucket_1 | ||
| Google Cloud Storage (GCS) Folder | Source Location is Google Cloud Storage | Enter the name of the folder in the GCS bucket where the source files are located. Default value: N/A Example: elt_gcs_bucket_1_CSV_Files | ||
| Advanced Properties | Other parameters that you want to specify as URL properties. See Connector Configuration Options in Simba Google BigQuery JDBC Connector Install and Configuration Guide (PDF) for the list of parameters that you can define in this field set. This field set consists of the following fields:
| |||
| URL Properties | None. | The account parameter's name and its corresponding value. Click + to add more rows. Add each URL property-value pair in a separate row. Specify the name of the parameter in the URL Property Name field and its value in the URL Property Value field. | ||
Click Validate after entering the required details to ensure that all fields have been filled accurately. Click Apply to save the settings.
Account Validation when using Pipeline parameters
If you have used Pipeline parameters or expressions to define values for the account fields above, the account validation (done by clicking the Validate button) is not supported. However, the Snaps that use this account may connect to the endpoint successfully depending on the accuracy and validity of the expressions and parameters used.
Passing your JDBC URL
Order of Precedence
The parameter values for the URL used to connect to your target database are governed by the following order of precedence:
- JDBC URL field
- Snap Properties (including Advanced Properties)
- Default values
Default Properties set internally
No properties are internally passed in the JDBC URL, by default.
Specific Scenarios
When setting default values for the Database Name, Username, and Password fields:
As a best practice, ensure that the Default Database Name provided in the Snap's properties and the database name in the JDBC URL field match.
Else, make sure that both the database names exist.
However, the username and password from the JDBC URL take precedence over the values provided in the respective fields.
Preparing the Simba JDBC Driver for Manual Upload
Following are the instructions to prepare the JDBC Driver ZIP archive if you choose to manually upload and use the SimbaJDBCDriverforGoogleBigQuery42_1.3.0.1001.zip for your ELT BigQuery Account:
Download the JDBC4.2-compatible driver from the official source.
Open the downloaded SimbaJDBCDriverforGoogleBigQuery42_1.3.0.1001.zip archive and extract its contents to your local drive, for example:
C:\SimbaJDBCDriverforGoogleBigQuery42_1.3.0.1001.Open the
...\libsfolder from the extracted contents.Move all the jar files from this folder to one level up (to the same folder as the GoogleBigQueryJDBC42.jar file).
Compress the SimbaJDBCDriverforGoogleBigQuery42_1.3.0.1001 folder to SimbaJDBCDriverforGoogleBigQuery42_1.3.0.1001.zip.
Use/upload this Zip file as the JDBC driver for your ELT BigQuery Account.
The instructions provided above are OS-agnostic. Use the file operation commands specific to your OS for extracting, moving, and archiving these files and folders.
Troubleshooting
None.
Example
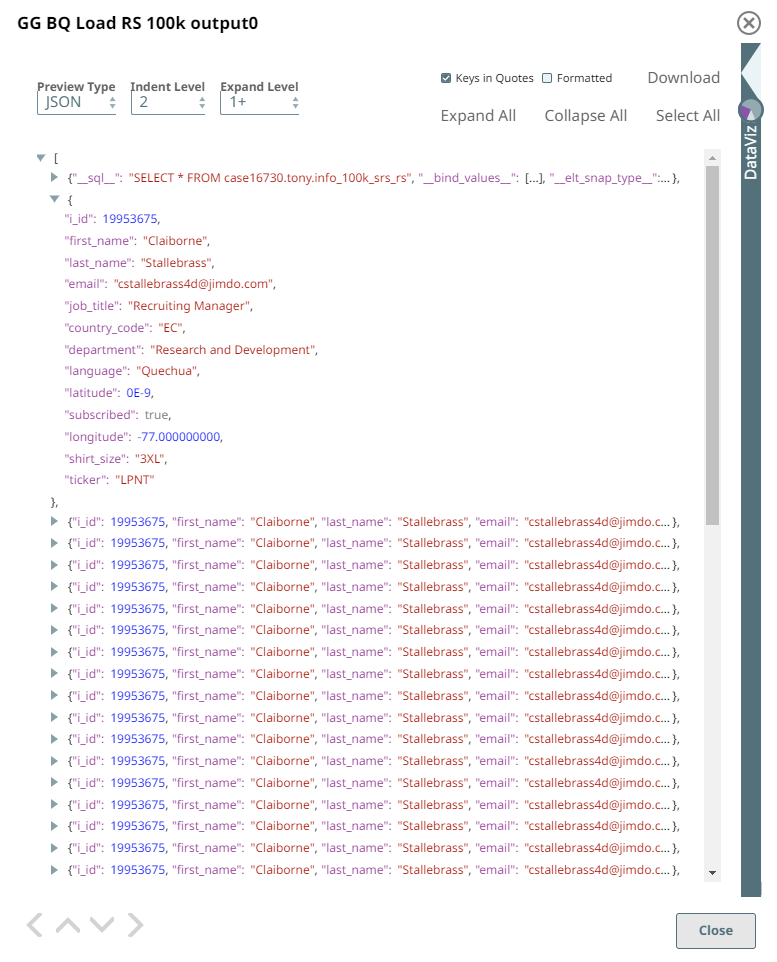
Configuring the ELT Database Account for connecting to a Google BigQuery Database
The following Pipeline is designed to extract data from a Redshift table and load it into a new table in the BigQuery database.
Snap Settings
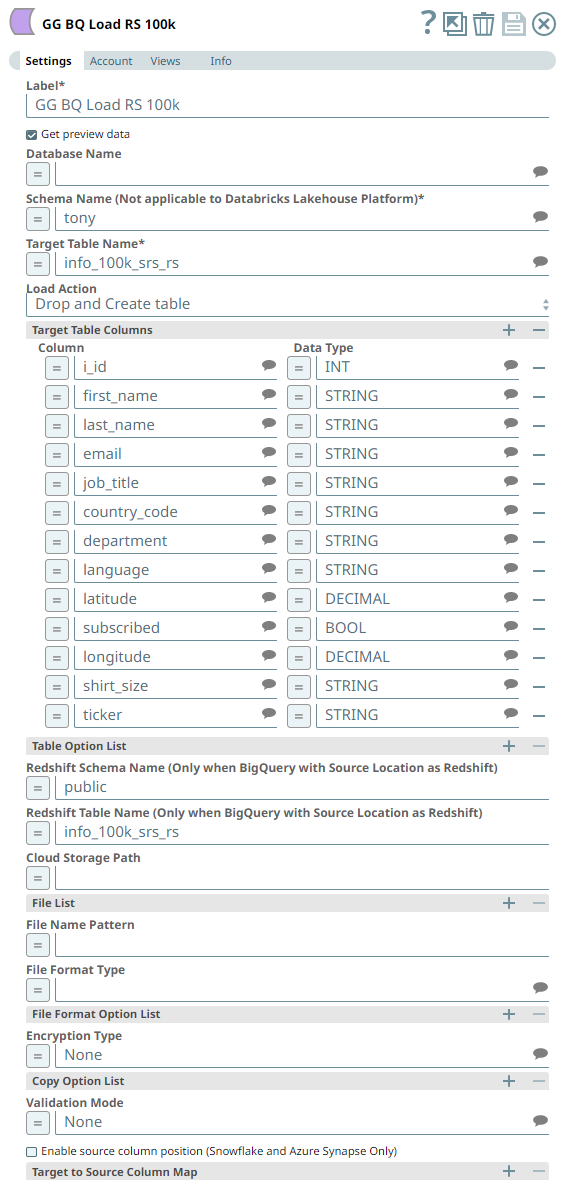
The Pipeline uses an ELT Load Snap to define the source table in Redshift database and is configured to perform the following functions.
- Create a new table info_100k_srs_rs in the specified target database (BigQuery).
- Load the data from the test_data folder to this newly-created target table based on the 13 table columns specified.
Account Settings
The Pipeline accesses the Parquet file using the Storage Account Key mode of authentication.
The schema of the new table in BigQuery can be visualized through the Snap's output preview as follows:
See Also
Have feedback? Email documentation@snaplogic.com | Ask a question in the SnapLogic Community
© 2017-2025 SnapLogic, Inc.