BigQuery Execute
On this Page
Snap type: | Write | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Description: | This Snap allows you to execute queries on BigQuery easily leveraging the jobs and query APIs. This Snap works only with single queries. A complete list of supported queries as well as examples are documented here: https://cloud.google.com/bigquery/query-reference.
Snaps in Google BigQuery Snap Pack
So, ensure that you include the time zone in all the datetime values that you load into Google BigQuery tables using this Snap. For example: "2020-08-29T18:38:07.370 America/Los_Angeles", “2020-09-11T10:05:14.000-07:00", “2020-09-11T17:05:14.000Z” | |||||||
| Prerequisites: | [None] | |||||||
| Support and limitations: | Works in Ultra Tasks. | |||||||
| Known Issues | Google BigQuery does not support very large exponential values—larger than EXP(700). So, while displaying values of such high exponential order in the validation preview, this Snap routes to the error view, and displays the following error: | |||||||
| Account: | This Snap uses account references created on the Accounts page of SnapLogic Manager to handle access to this endpoint. See Google BigQuery Account for information on the type of account to use. | |||||||
| Views: |
| |||||||
Settings | ||||||||
Label | Specify a name for the Snap. You can modify this to be more specific, especially if you have more than one of the same Snap in your pipeline. | |||||||
Project ID | Required. This drop-down shows you a list of all the available projects that your user Account has access to. Clicking on the the drop-down always pulls the latest list of available projects. The project on which the query should be executed should be selected. | |||||||
| Location | Specify or select a region from the list of suggested locations on which you want to execute BigQuery. | |||||||
Query | The query that you want to execute on BigQuery for the selected project. For a full list of supported functions and operators for your queries, see Legacy SQL Functions and Operators and Standard SQL Functions and Operators.
This setting also supports expressions that can be enabled to parameterize a specific section of the query like table names or columns to be selected. | |||||||
| Standard SQL | Select this checkbox if you want to use the Standard SQL dialect in the Query field. It is crucial that you understand how the Snap interprets the dialect used in the Query field. Do not select this check box if the query contains Default value: Not selected | |||||||
| Destination dataset ID | Dataset ID of the dataset where the destination table has to be created in case of the query returning large query results. | |||||||
| Destination table ID | Table ID of the destination table to write the query results to in case of the query returning large query results. | |||||||
| Action on destination table | This option specifies the action that has to be taken if the destination table already exists. Options available include OVERWRITE, APPEND, and ERROR. Default value: OVERWRITE | |||||||
Loading | Loading | |||||||
Troubleshooting
| Error | Reason | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
Failure: Query execution failed., Reason: 404 Not Found GET <URL> { "code": 404, "errors": [ { "domain": "global", "message": "Not found: Job <>, | This error occurs when you refer to a resource (a dataset, a table, or a job) that doesn't exist or when the location in the request does not match the location of the resource. | Fix the resource names, correctly specify the location, or wait at least 6 hours after streaming before querying a deleted table. |
Implicit retries in BigQuery Snaps
The BigQuery Snaps handle all retriable BigQuery errors (BigQuery exception, IO exception, and Runtime exception) internally.
429 (Too Many Requests):
Retry attempts: Maximum of 5 retries.
Delay Between Retries: Backoff strategy with jitter (random variation) is applied to prevent synchronized retries and reduce load.
401 (Unauthorized):
Retry attempts: Maximum of 3 retries.
Delay Between Retries: Backoff strategy is applied.
Additional Actions: Reloads the BigQuery account on the retry event.
IOException and 500, 502, 503, 504 (Server Errors):
Retry attempts: Maximum of 3 retries.
Delay Between Retries: Backoff strategy is applied.
Interpreting the SQL Query Dialect
The Snap determines the SQL dialect used in the query based on the following flags:
- Dialect specified as prefix within the Query field (
#standardSQLor#legacySQL) - Default Standard SQL check box at account level
- Standard SQL check box at Snap level
The prefix specified in the query ignores the other two flags.
- When the prefix is not specified,
- The user must select either one of the check boxes at the account level and at the Snap level to specify that the query uses Standard SQL dialect.
- Else, the query is considered to be written in Legacy SQL.
- The user must select either one of the check boxes at the account level and at the Snap level to specify that the query uses Standard SQL dialect.
The following matrix depicts all the possible real-time scenarios for resolving the query dialect:
| Prefix in Query | Check box at account level | Check box at Snap level | Query Dialect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Not specified | Legacy SQL | ||
| Not specified | Standard SQL | ||
| Not specified | Standard SQL | ||
| Not specified | Standard SQL | ||
#legacySQL | Legacy SQL | ||
#legacySQL | Legacy SQL | ||
#legacySQL | Legacy SQL | ||
#legacySQL | Legacy SQL | ||
#standardSQL | Standard SQL | ||
#standardSQL | Standard SQL | ||
#standardSQL | Standard SQL | ||
#standardSQL | Standard SQL |
For existing Pipelines
- If the prefix is defined in the Query field, the query is interpreted accordingly.
- Else, the query is treated as using Legacy SQL dialect.
- To mark a query without prefix as using Standard SQL, select the Standard SQL check box at the Snap level.
- To update all Pipelines for an account to use Standard SQL, select the Default Standard SQL checkbox at the account level.
Sample Queries
Here are some SQL statements in each of the two SQL dialects, that the BigQuery Execute Snap can execute:
| SQL Operation | Standard SQL | Legacy SQL |
|---|---|---|
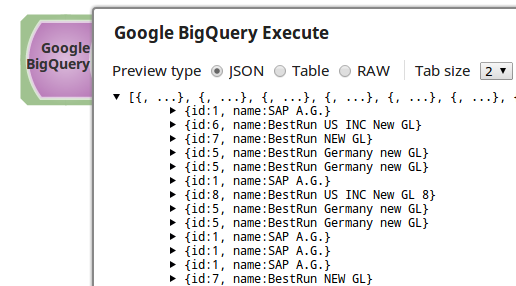
| Select | SELECT id, name FROM `project-123.testKamal.TestTablet` LIMIT 5000 | SELECT id, name FROM [project-123:testKamal.TestTablet] LIMIT 5000 |
| Create (DDL) table with nested array | CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE `project-123.testKamal.TestTable2` ( x INT64, y STRUCT< a ARRAY<STRING>, b BOOL > ) | Not allowed in Legacy SQL. |
| Insert (DML) | INSERT INTO `project-123.testKamal.TestTable2` (x, y) VALUES (1, (['1', '2', '3'], true)), (2, (['a', 'b'], false)) | Not allowed in Legacy SQL. |
| Row count | SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT x) FROM `project- 123.testKamal.TestTable2` | SELECT EXACT_COUNT_DISTINCT(x) FROM [project- 123:testKamal.TestTable2] |
| Convert an Array into Table rows (Flattening) | SELECT x, a, y.b as b FROM `project-123.testKamal.TestTable2`, UNNEST(y.a) as a | SELECT x, y.a as a, y.b as b FROM FLATTEN([project- 123:testKamal.TestTable2], y.a) |
| DROP (DDL) | DROP TABLE `project-123.testKamal.TestTable2` | Not allowed in Legacy SQL. |
After the execution of query, the results are written to the output view. The sample output of Execute Snap looks as follows.
Snap Pack History
Have feedback? Email documentation@snaplogic.com | Ask a question in the SnapLogic Community
© 2017-2025 SnapLogic, Inc.