Redshift - Bulk Load
On this Page
| Snap type: | Write | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description: | This Snap executes a Redshift bulk load. The input data is first written to a staging file on S3. Then the Redshift copy command is used to insert data into the target table. Table CreationIf the table does not exist when the Snap tries to do the load, and the Create table property is set, the table will be created with the columns and data types required to hold the values in the first input document. If you would like the table to be created with the same schema as a source table, you can connect the second output view of a Select Snap to the second input view of this Snap. The extra view in the Select and Bulk Load Snaps are used to pass metadata about the table, effectively allowing you to replicate a table from one database to another. ETL Transformations & Data FlowThis Snap executes a Load function with the given properties. The documents that are provided on the input view will be inserted into the provided table on the provided database. Input & Output:
| ||||||
| Prerequisites: | IAM Roles for Amazon EC2The 'IAM_CREDENTIAL_FOR_S3' feature is used to access S3 files from EC2 Groundplex, without Access-key ID and Secret key in the AWS S3 account in the Snap. The IAM credential stored in the EC2 metadata is used to gain access rights to the S3 buckets. To enable this feature, set the Global properties (Key-Value parameters) and restart the JCC: This feature is supported in the EC2-type Groundplex only. Learn more. | ||||||
| Limitations and Known Issues |
If you use the PostgreSQL driver ( | ||||||
| Account: | This Snap uses account references created on the Accounts page of SnapLogic Manager to handle access to this endpoint. The S3 Bucket, S3 Access-key ID and S3 Secret key properties are required for the Redshift-Bulk Load Snap. The S3 Folder property may be used for the staging file. If the S3 Folder property is left blank, the staging file will be stored in the bucket. See Configuring Redshift Accounts for information on setting up this type of account. | ||||||
| Configurations: | Account & AccessThis Snap uses account references created on the Accounts page of SnapLogic Manager to handle access to this endpoint. The S3 Bucket, S3 Access-key ID and S3 Secret key properties are required for the Redshift-Bulk Load Snap. The S3 Folder property may be used for the staging file. If the S3 Folder property is left blank, the staging file will be stored in the bucket. See Configuring Redshift Accounts for information on setting up this type of account. Redshift IAM Account Setup
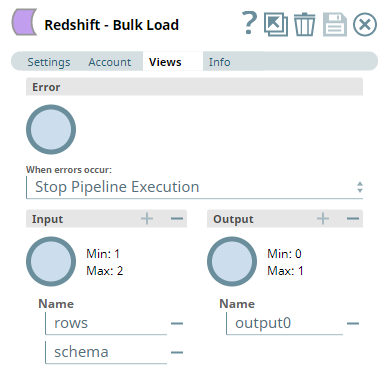
This applies only to the Redshift - Bulk Load, Redshift - Unload, and Redshift - S3 Upsert Snaps. Views:
| ||||||
Settings | |||||||
| Label* | Specify the name for the Snap. You can modify this to be more specific, especially if you have more than one of the same Snap in your pipeline. | ||||||
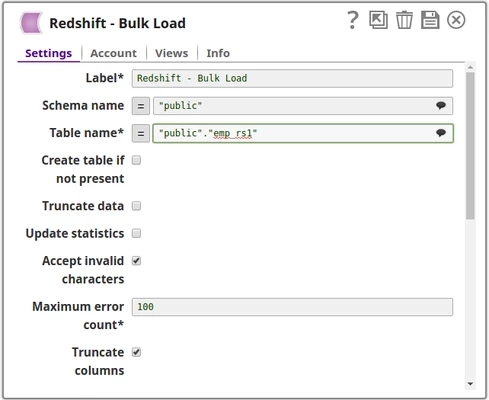
| Schema name | Specify the database schema name. In case it is not defined, then the suggestion for the Table Name will retrieve all tables names of all schemas. The property is suggestible and will retrieve available database schemas during suggest values. The values can be passed using the pipeline parameters but not the upstream parameter. Example: SYS | ||||||
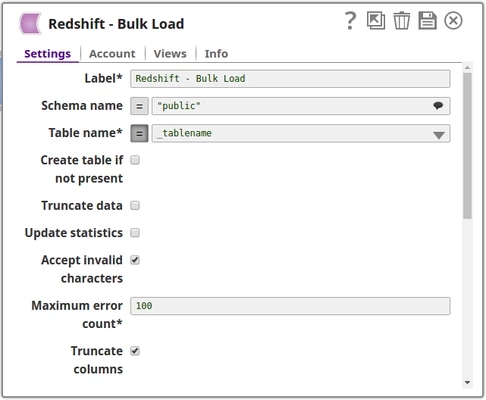
| Table name* | Specify the table on which to execute the bulk load operation. You can pass the values using the Pipeline parameters but not the upstream parameter. Example: people Default value: None | ||||||
| Create table if not present | Select this checkbox to automatically create the target table if it does not exist.
Due to implementation details, a newly created table is not visible to subsequent database Snaps during runtime validation. If you want to immediately use the newly updated data you must use a child Pipeline that is invoked through a Pipeline Execute Snap. | ||||||
| Data Source | Specify the source from where the data should load. The available options are Input view and Staged files.
| ||||||
| Validate input data | Select this checkbox to enable the Snap perform input data validation to verify all input documents are flat map data. If any value is a Map or a List object, the Snap writes an error to the error view, and if this condition occurs, no document is written to the output view. See the Troubleshooting section above for information on handling errors caused due to invalid input data. Default value: Not selected Recommendation If this property is not selected, the Snap does not validate the structure of input documents, converts all values to strings, writes the S3 CSV file, and executes the Redshift COPY command. If the COPY command finds error in the input CSV data, it writes errors to the error table, and the Snap routes these errors to the error view (if error view is enabled). However, some errors reported by the COPY command may not be easy to understand. Therefore, it is advisable to enable input data validation during pipeline development and testing, as this may also help troubleshoot the pipeline. Flat Map Data Flat map data is a collection of key-value pairs, where the values are all single-class objects unlike a Map or List. | ||||||
| Truncate data* | Select this checkbox to truncate existing data before performing data load. With the Bulk Update Snap, instead of doing truncate and then update, a Bulk Insert would be faster. Default value: Not selected | ||||||
Update statistics | Select this checkbox to update table statistics after data load by performing an Analyze operation on the table. Default value: Not selected | ||||||
| Accept invalid characters | Select this checkbox to accept invalid characters in the input. Invalid UTF-8 characters are replaced with a question mark when loading. Default value: Selected | ||||||
| Maximum error count* | Specify the maximum number of rows which can fail before the bulk load operation is stopped. Default: 100 | ||||||
| Truncate columns | Select this checkbox to truncate column values which are larger than the maximum column length in the table Default value: Selected | ||||||
| Disable data compression | Select this checkbox to disable compression of data being written to S3. Disabling compression will reduce CPU usage on the Snaplex machine, at the cost of increasing the size of data uploaded to S3. Default value: Not selected | ||||||
| Load empty strings | Select this checkbox to load empty strings in the input documents as empty strings to the string-type fields. Else, empty string values in the input documents are loaded as null. Null values are loaded as null regardless. Default value: Not selected | ||||||
| Additional options | Specify additional options to be passed to the COPY command. For example, EMPTYASNULL, this command indicates that the Redshift should load empty fields as NULL. Empty fields occur when data contains two delimiters in succession with no characters between the delimiters. Learn more about the available options in Amazon Redshift – Copy documentation. Default value: N/A | ||||||
| Parallelism | Define the number of files to be created in S3 per execution. If set to 1 then only one file will be created in S3 which will be used for the copy command. If set to n with n > 1, then n files will be created as part of a manifest copy command, allowing a concurrent copy as part of the Redshift load. The Snap itself will not stream concurrent to S3. It will use a round robin mechanism on the incoming documents to populate the n files. The order of the records is not preserved during the load. Default value: None | ||||||
| Instance type | Appears when the parallelism value is greater than 1. Select the type of instance from the following options:
Default Value: Default Example: High-performance S3 upload optimized | ||||||
| IAM Role | Select this check box if bulk load or unload has to be done using the IAM role. If you select IAM Role, ensure that you provide values for (AWS account ID, Role name, and Region name) fields in the Redshift Account. | ||||||
Server-side encryption | Select this checkbox to enable encryption for the data that is loaded. This defines the S3 encryption type to use when temporarily uploading the documents to S3 before you insert data into Redshift. Default value: Not selected | ||||||
| KMS Encryption type | Specify the type of Key Management Service (KMS) S3 encryption to be used on the data. The available encryption options are:
Default value: None If both the KMS and Client-side encryption types are selected, the Snap gives precedence to the SSE, and displays an error prompting the user to select either of the options only. | ||||||
| KMS key | Activates when KMS Encryption type is set to Server-Side Encryption with KMS. Specify the KMS key to use for the S3 encryption. For more information about the KMS key, refer to AWS KMS Overview and Using Server Side Encryption. Default value: None | ||||||
| Vacuum type | Select the option for Vacuum type. Vacuum type reclaims space and sorts rows in a specified table after the upsert operation. The available options to activate are FULL, SORT ONLY, DELETE ONLY and REINDEX. Refer to the AWS document on Vacuuming Tables for more information. Auto-commit needs to be enabled for Vacuum. Default value: None | ||||||
| Vacuum threshold (%) | Specifies the threshold above which VACUUM skips the sort phase. If this property is left empty, Redshift sets it to 95% by default. Default value: None | ||||||
Snap execution | Select one of the three modes in which the Snap executes. Available options are:
| ||||||
In a scenario where the Auto commit on the account is set to true, and the downstream Snap does depends on the data processed on an Upstream Database Bulk Load Snap, use the Script Snap to add delay for the data to be available.
For example, when performing a create, insert and a delete function sequentially on a pipeline, using a Script Snap helps in creating a delay between the insert and delete function or otherwise it may turn out that the delete function is triggered even before inserting the records on the table.
Redshift's Vacuum Command
In Redshift, when rows are DELETED or UPDATED against a table they are simply logically deleted (flagged for deletion), not physically removed from disk. This causes the rows to continue consuming disk space and those blocks are scanned when a query scans the table. This results in an increase in table storage space and degraded performance due to otherwise avoidable disk IO during scans. A vacuum recovers the space from deleted rows and restores the sort order.
Troubleshooting
Error | Reason | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| This issue occurs due to incompatibilities with the recent upgrade in the Postgres JDBC drivers. | Download the latest 4.1 Amazon Redshift driver here and use this driver in your Redshift Account configuration and retry running the Pipeline. |
Basic Use Case
The following Pipeline describes how the Snap functions as a standalone Snap in a Pipeline:
Use Case: Replicate a Database Schema in Redshift
MySQL Select to Redshift Bulk Load
In this example, a MySQL Select Snap is used to select data from 'AV_Persons' table belonging to the 'enron' schema. The Mapper Snap maps this data to the target table's schema and is then loaded onto the "bulkload_demo" table in the "prasanna" schema:
Select the data from the MySQL database.
Mapper will be used to map the data to the input schema that is associated with Redshift Bulkload database table.
Loads the input Documents that is coming from the Mapper to a S3 file.
Finally invoke the COPY command to invoke the created S3 file to insert the data into the destination table.
Typical Snap Configurations
Key configuration lies in how the SQL statements are passed to perform bulk load of the records. The statements can be passed:
Without Expression
The values are passed directly to the Snap.
With Expression
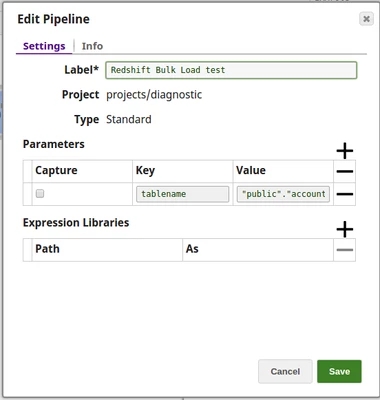
Using Pipeline parameters
The Table name is passed as a Pipeline parameter.
Basic Use Case #2: Use of twin inputs to define schema while creating tables in Redshift
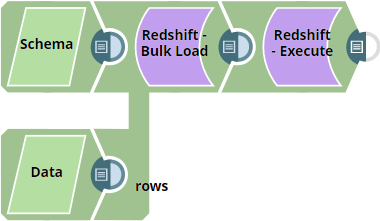
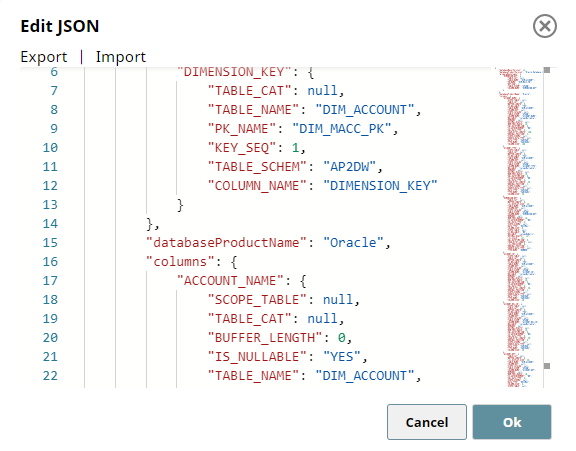
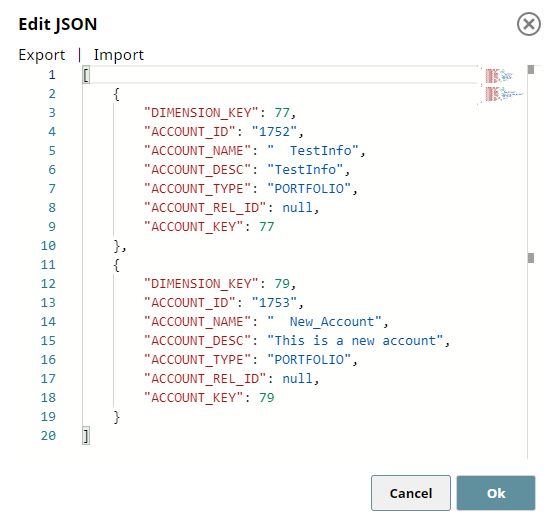
The following Pipeline demonstrates how to use the second input view of Redshift - Bulk Load Snap to define the schema for creating a non-existent table in Redshift data store.
We use two JSON Generator Snaps: one for passing the table schema and another for passing the data rows.
| Input 1: Schema | Input 2: Data |
|---|---|
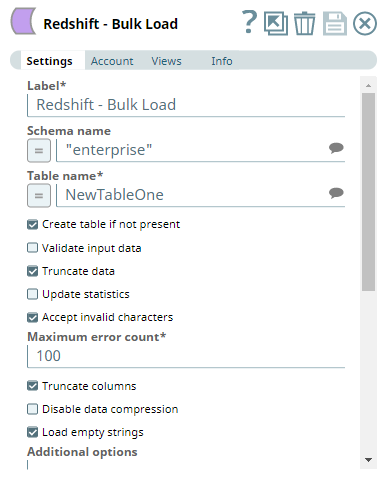
We use the Redshift Bulk Upload Snap to combine these two inputs — schema and data rows, and create a table, if it does not exist in the Redshift Data store.
| Redshift - Bulk Load Snap Settings | Views |
|---|---|
| Output | |
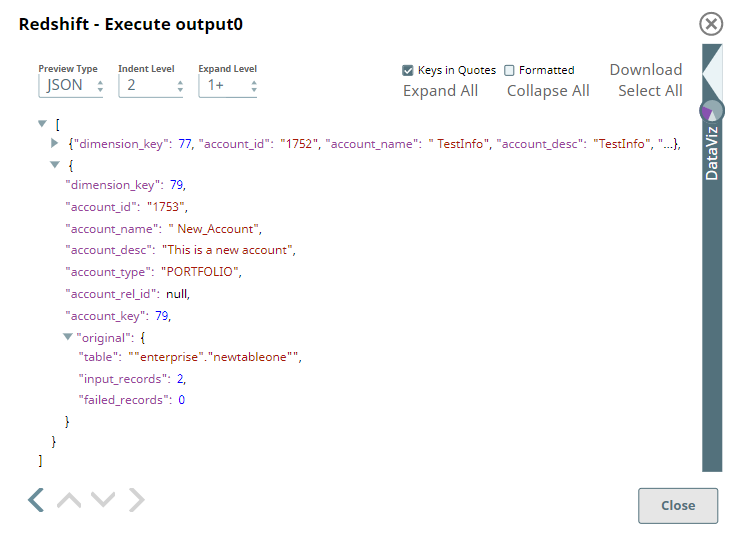
After creating the table and loading the data based on these inputs, the Snap displays the result in the output in terms of the number of records loaded into the specified table and the number of failed records.
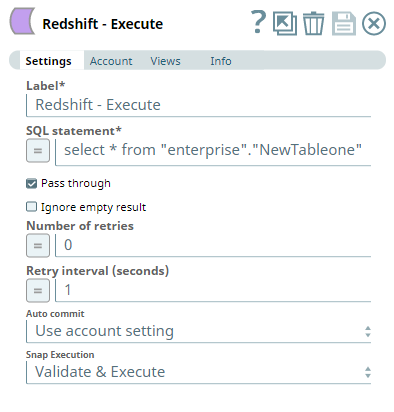
To see the records inserted into the new table, we can connect a Redshift - Execute Snap and run a select query on the newly-created table. It retrieves the data inserted into each record. It is possible that you see more records in the output, in case the table existed and the new rows are inserted into it.
| Redshift - Execute Snap | Output |
|---|---|
Advanced Use Case
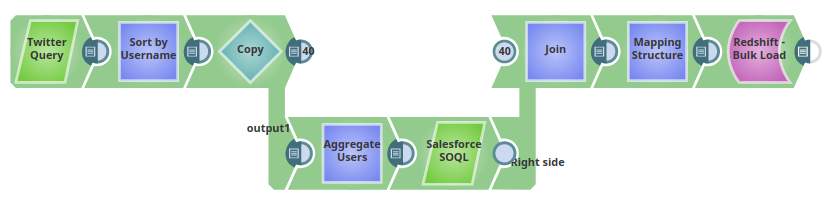
The following Pipeline describes how a lookup functionality is used in an enterprise environment. In this Pipeline, tweets pertaining to a keyword "#ThursdayThoughts" are extracted using a Twitter Query Snap and loaded into the table "twittersnaplogic" in the public schema using the Redshift Bulk Load Snap. When executed, all the records are loaded into the table.
The Pipeline performs the following ETL operations:
Extract: Twitter Query Snap selects 25 tweets (a value specified in the Maximum tweets property) pertaining to the Twitter query.
Transform: The Sort Snap, labeled Sort by Username in this pipeline, sorts the records based on the value of the field user.name.
Extract: The Salesforce SOQL Snap extract's records matching the user.name field value. Extracted records are LastName, FirstName, Salutation, Name, and Email.
Load: The Redshift Bulk Load Snap loads the results into the table, twittersnaplogic, on the Redshift instance.
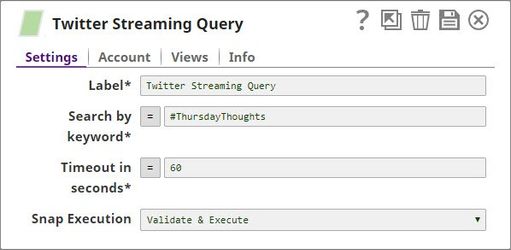
The configuration of the Twitter Query Snap is as shown below:
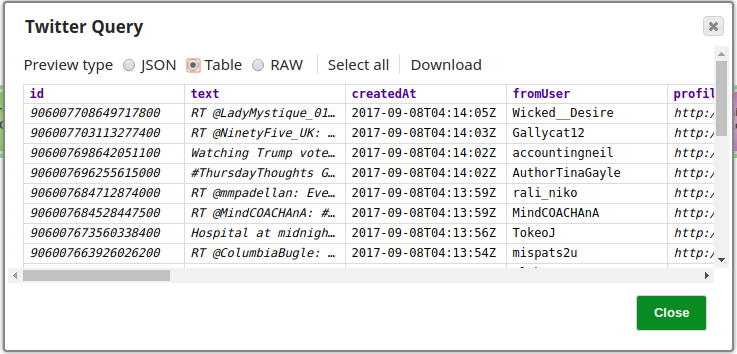
The Twitter Query Snap is configured to retrieve 25 records from the Account, a preview of the Snap's operation is shown below:
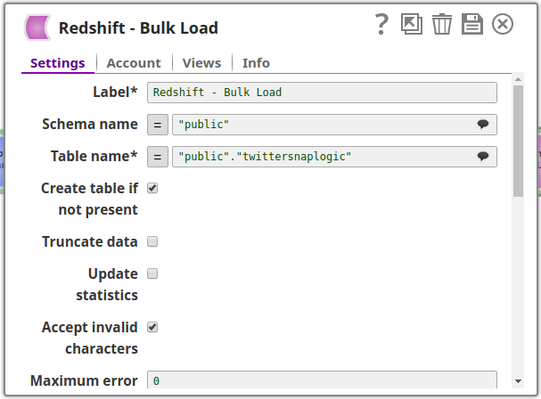
The Redshift Bulk Load Snap is configured as shown in the figure below:
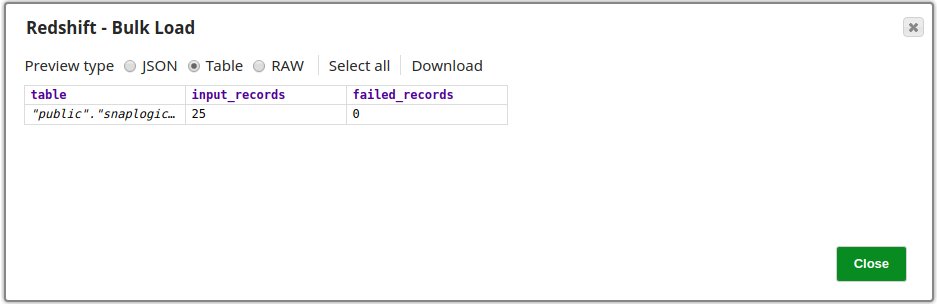
Successful execution of the Snap is denoted by a count of the records loaded into the specified table, note that the number of failed records is also shown provided it does not exceed the limit specified in the Maximum error count property, in which case it would stop the pipeline. The image below shows that all 25 records retrieved in the Twitter Query Snap have been loaded into the table successfully.
Advanced Use Case #2
The following Pipeline demonstrates how a bulk load functionality is used typically in an enterprise environment. In this Pipeline, the File Reader Snap reads the data, from which the data will be loaded in to the table using the Redshift Bulk Load Snap. When executed, all the records are loaded into the table.
The Pipeline performs the following ETL operations:
Extract: File Reader snap will read the data from the file and submit it to the CSV parser.
Transform: CSV Parser will perform the parsing of the provided data which will be written to the MySQL insert snap.
Extract: The entire data will be loaded into the Redshift table, by creating new table with the provided schema.
Downloads
Important steps to successfully reuse Pipelines
- Download and import the pipeline into the SnapLogic application.
- Configure Snap accounts as applicable.
- Provide pipeline parameters as applicable.
Snap Pack History
Have feedback? Email documentation@snaplogic.com | Ask a question in the SnapLogic Community
© 2017-2025 SnapLogic, Inc.
.png?version=1&modificationDate=1510743705391&cacheVersion=1&api=v2&width=490&height=344)